Tokyo, May 8, 2023 — An increased risk of depression and anxiety among US older adults with dementia and poor activity participation has been demonstrated through an analysis of data from the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS), a nationally representative population-based study.
Credit: Dr. Miharu Nakanishi
Tokyo, May 8, 2023 — An increased risk of depression and anxiety among US older adults with dementia and poor activity participation has been demonstrated through an analysis of data from the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS), a nationally representative population-based study.
These findings were reached by a team of researchers from the Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Exploratory Oncology Research and Clinical Trial Center in National Cancer Center, and Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science, Japan. This study is published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports 7(1).
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has posed challenges to the health and lives of older adults with dementia. Social measures such as strict physical distancing to protect vulnerable groups, including older adults with dementia, increase the risk of social isolation among them.
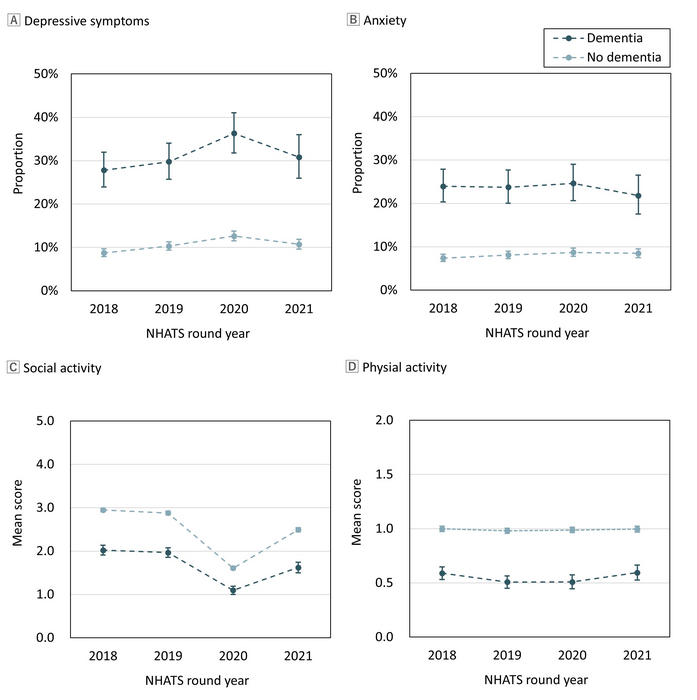
Participation in meaningful activities provides a sense of continuity, quality of life, and self-identity to people with dementia. Physical distancing measures during the pandemic could impede activity participation and lead to deterioration of mental well-being. Quantitative data show that people with dementia experienced worsening mental health following the first lockdown and the second wave of the pandemic. However, few studies included older adults without dementia as a control group and information on the level of activity participation.
The team analyzed data from 4,548 community-dwelling older adult participants of two or more NHATS survey rounds between 2018 and 2021. The main objective of the study was to investigate the longitudinal association between activity participation and mental health in individuals with dementia during the pandemic.
The findings
Multivariable binomial logistic regression analyses revealed an increased risk of depressive symptoms and anxiety among older adults with dementia before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. The overall level of depressive symptoms increased between 2019 and 2020 because of the onset of the pandemic and lifestyle changes caused by several restrictions. Poor activity participation was also associated with a high risk of depressive symptoms and anxiety. Furthermore, the association between dementia and worse mental health outcomes remained significant even after controlling for activity participation. However, there was no interaction effect between dementia and year of follow-up for depressive symptoms and anxiety.
Balancing infection management and dementia care
The results highlight that mental health deterioration was more prominent during the pandemic onset than in other one-year periods investigated and that widespread mental health challenges exist in the community-dwelling population. Older adults with dementia may experience chronic psychological distress because of their dependence to care in daily life stimulated by rapid lifestyle changes and reduced social contact in 2020. In addition, they may be more vulnerable to reduced contact than individuals without dementia since loneliness and social isolation are linked to an increased risk of dementia. Dementia care and support should address emotional and social needs using accessible means under long-term restrictions.
Journal
Journal of Alzheimer s Disease Reports
DOI
10.3233/ADR-230019
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Depression and Anxiety in Older Adults with Dementia During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Article Publication Date
20-Apr-2023




