WASHINGTON, Oct. 17, 2023 – Wave energy technology is a proven source of power generation, but there is power inherent in every molecule of liquid on earth, even when the liquid is at rest. At the molecular scale, atoms and ions are always moving. If this nanoscale movement can be harvested, it could be a big source of energy.
Credit: Yucheng Luan and Wei Li
WASHINGTON, Oct. 17, 2023 – Wave energy technology is a proven source of power generation, but there is power inherent in every molecule of liquid on earth, even when the liquid is at rest. At the molecular scale, atoms and ions are always moving. If this nanoscale movement can be harvested, it could be a big source of energy.
“There are vast amounts of air and liquid on the earth, and their successful harvesting could produce a gigantic amount of energy for society,” author Yucheng Luan said.
In an article published this week in APL Materials, by AIP Publishing, Luan and his collaborators tested a molecular energy harvesting device that captures the energy from the natural motion of molecules in a liquid. Their work showed molecular motion can be used to generate a stable electric current.
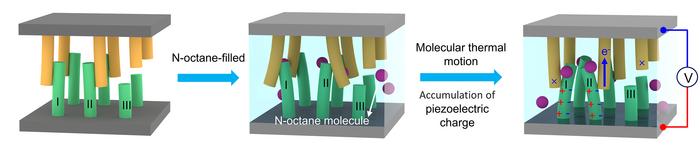
To create the device, the researchers submerged nanoarrays of piezoelectric material in liquid, allowing the movement of the liquid to move the strands like seaweed waving in the ocean, except in this case the movement is on the invisible, molecular scale, and the strands are made of zinc oxide. The zinc oxide material was chosen for its piezoelectric properties, which means that when it waves, bends, or deforms under motion, it generates electric potential.
“As a well-studied piezoelectric material, zinc oxide can be easily synthesized into various nanostructures, including nanowhiskers,” Luan said. “A nanowhisker is a neat and orderly structure of many nanowires, similar to the bristles on a toothbrush.”
Their energy harvesters could be used to power nanotechnologies like implantable medical devices, or they could be scaled to full-size generators and kilowatt-scale energy production. One key design feature of the device is that it doesn’t rely on any external forces, which increases its potential as a game-changing clean energy source.
“Molecular thermal motion harvester devices do not need any external stimulation, which is a big advantage compared with other energy harvesters,” Luan said. “At present, electrical energy is mainly obtained by external energy, such as wind energy, hydroelectric energy, solar energy, and others. This work opens up the possibility of generating electrical energy through the molecular thermal motion of liquids, from the internal energy of the physical system that is essentially different from ordinary mechanical motion.”
The authors are already working on the next phase of their design to improve the energy density of the device by testing different liquids, high-performing piezoelectric materials, and new device architectures and by enlarging the device.
“We believe this novel kind of system will become an indispensable way for human beings to obtain electrical energy in the near future.”
###
The article “Molecular thermal motion harvester for electricity conversion” is authored by Yucheng Luan, Fengwei Huo, Mengshi Lu, Wei Li, and Tonghao Wu. It will appear in APL Materials on Oct. 17, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0169055). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0169055.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Materials is an open access journal that features original research on significant topical issues within all areas of materials science. See https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apm.
###
Journal
APL Materials
DOI
10.1063/5.0169055
Article Title
Molecular thermal motion harvester for electricity conversion
Article Publication Date
17-Oct-2023




