Credit: Bernstein Center Freiburg
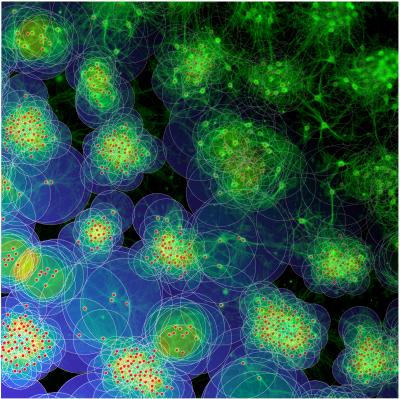
Neurons are not randomly arranged in the human brain. In the cortex, they are organized in interconnected clusters with high intrinsic connectivity. This modular connectivity structure, in which clusters eventually serve as functional units, is formed in early phases of development. The underlying self-organization process is regulated by neuronal activity but the detailed mechanisms are still poorly understood. Based on in vitro studies and computational modeling, neuroscientists Dr. Samora Okujeni and Prof. Dr. Ulrich Egert from the Bernstein Center Freiburg now made an important contribution to the understanding of brain networks and their development: in their current study, they show how neuronal outgrowth and migration interact in shaping network architecture and the degree of modularity in mature networks. Their findings have now been published in the open access online journal eLife.
Neurons are sociable cells that, on the long run, die in isolation. During development, they therefore grow out cellular processes, termed neurites, to establish synaptic connections with other neurons. Once they receive sufficient or too much synaptic input, however, they stop growing or shrink. By this, neurons avoid long-term over-excitation. It is widely assumed among researchers that neuronal growth is hereby controlled to stabilize neuronal activity at a specific target level.
Yet, to increase the probability of connections, neurons cannot only grow out their neurites but are also able to migrate towards other neurons. “In computer simulations we show that migration and neurite outgrowth may interact to shape specific mesoscale network architectures” says Samora Okujeni. The interaction regulates the relation between local connectivity within clusters and long-range inter-cluster connectivity and thereby the degree of network modularity. “This, in turn, influences the generation and spatiotemporal patterns of spontaneous activity.” Such interdependencies may be crucial for the proper development of the cortex.
The scientists tested the model predictions experimentally by investigating how cell migration, neurite outgrowth and activity interact in developing networks of cultured rat cortical neurons. To modulate cell migration in these networks they manipulated an enzyme that is centrally involved in the regulation of the neuronal cytoskeleton. As in their simulations, cell migration and clustering likewise promoted modular connectivity in vitro.
Yet, in addition, clustering promoted activity generation and led to higher activity levels. This was inconsistent with the assumed regulation of growth to establish a common target activity level. The scientists could resolve this discrepancy: “Cytoskeletal dynamics are not directly controlled by action potential activity but indirectly through an associated calcium influx that influences the balance between growth and degradation.” Okujeni explains. “Modularity increased the overall rate of action potentials but decreased their synchronization across the network that effectively determines the calcium influx per action potential. Given this dependence, we estimated that all network structures attain a similar target level of calcium influx during development.”
###
Original publication
Okujeni, S., Egert, U. (2019). Self-organization of modular network architecture by activity-dependent neuronal migration and outgrowth.
Elife 8. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.47996
Learn more about Samora Okujeni’s work
http://www.
Contact:
Bernstein Center Freiburg
Phone: +49 (0)761/203 – 7523
Media Contact
Dr. Samora Okujeni
[email protected]
49-761-203-7523
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




