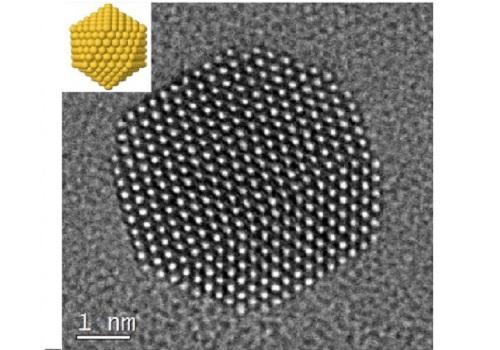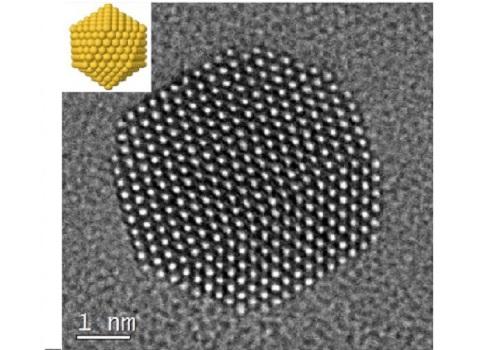
Credit: Reproduced with permission from ref 1. © 2017 Nature Publishing Group
Expanding the potential of gold nanoparticles for a range of uses requires methods to stabilize the clusters and control their size. Researchers at KAUST reveal how simple organic citrate ions, derived from readily available citric acid, can interact with the gold atoms to yield the stable nanoparticles needed for further research.
Such clusters of gold atoms are proving increasingly useful as catalysts, drug delivery systems, anti-cancer agents and components of solar cells among other applications.
"The potential applications of gold nanoparticles could have a huge impact on society, and understanding stabilizers like citrate might be crucial to progress," said Jean-Marie Basset, Director of the KAUST Catalysis Center and Distinguished Professor of Chemical Science, and a member of the research team, Professor Luigi Cavallo.
Along with colleagues at The University's Core Labs and coworkers in UK, Switzerland and France, the researchers have shown different ways that citrate ions can bind to gold atoms at the surface of nanoparticles1. They also discovered how to influence the binding mode by controlling the ratio of the nanoparticle/citrate ions. Different modes can influence the structures and properties of nanoparticles.
"The experimental and theoretical characterization of these systems is challenging due to the flexible nature of the interaction between citrate and gold," said Basset. He explained that collaboration between KAUST teams was essential for meeting the challenges, allowing creation of the stabilized nanoparticles and their analysis and imaging at high resolution (see image).
One reason for gold's usefulness in medical applications is its chemically stable nature. Other researchers have shown that this stability allows gold to carry drugs through the body without causing chemical side effects.
Controlling the structure of gold nanoparticles could also fine tune their interaction with light to exploit a phenomenon known as surface plasmon resonance. This may allow the energy of light to be harnessed to kill cancer cells. Attaching antibodies can guide the nanoparticles to the specific cells that need treatment. The type of interaction with light depends on nanoparticle structure and could also yield applications in solar cells and micro-electronics.
The researchers consider that the insights from this work at KAUST may also be applicable to some other metals and plan to explore this as the next phase of the research. "We want to take on that wider challenge," said Basset.
###
Media Contact
Michelle D'Antoni
[email protected]
http://kaust.edu.sa/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag