Credit: Tokyo Tech
Due to their small size, nanoparticles find varied applications in fields ranging from medicine to electronics. Their small size allows them a high reactivity and semiconducting property not found in the bulk states. Sub-nanoparticles (SNPs) have an extremely small diameter of around 1 nm, making them even smaller than nanoparticles. Almost all atoms of SNPs are available and exposed for reactions, and therefore, SNPs are expected to have extraordinary functions beyond the properties of nanoparticles, particularly as catalysts for industrial reactions. However, preparation of SNPs requires fine control of the size and composition of each particle on a sub-nanometer scale, making the application of conventional production methods near impossible.
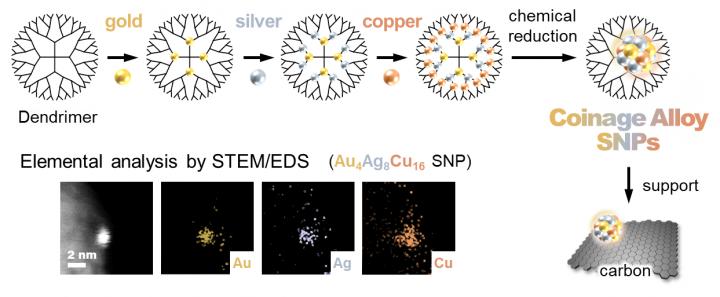
To overcome this, researchers at the Tokyo Institute of Technology led by Dr. Takamasa Tsukamoto and Prof. Kimihisa Yamamoto previously developed the atom hybridization method (AHM) which surpasses the previous trials of SNP synthesis. Using this technique, it is possible to precisely control and diversely design the size and composition of the SNPs using a “macromolecular template” called phenylazomethine dendrimer. This improves their catalytic activity than the NP catalysts.
Now, in their latest study published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition, the team has taken their research one step further and has investigated the chemical reactivity of alloy SNPs obtained through the AHM. “We created monometallic, bimetallic, and trimetallic SNPs (containing one, combination of two, and combination of three metals respectively), all composed of coinage metal elements (copper, silver, and gold), and tested each to see how good of a catalyst each of them is,” reports Dr Tsukamoto. Figure 1 describes the production process using AHM. Their catalytic activity was tested in the oxidation reaction of olefins, compounds made up of hydrogen and carbon with wide industrial uses.
Unlike corresponding nanoparticles, the SNPs created were found to be stable and more effective. Moreover, SNPs showed a high catalytic performance even under the milder conditions, in direct contrast to conventional catalysts. Monometallic, bimetallic, and trimetallic SNPs demonstrated the formation of different products, and this hybridization or combination of metals seemed to show a higher turnover frequency (TOF). The trimetallic combination “Au4Ag8Cu16” showed the highest TOF because each metal element plays a unique role, and these effects work in concert to contribute to high reaction activity (see Figure 2).
Furthermore, SNP selectively created hydroperoxide, which is a high-energy compound that cannot be normally obtained due to instability (see Figure 2). Mild reactions without high temperature and pressure realized in SNP catalysts resulted in the stable formation of hydroperoxide by suppressing its decomposition.
When asked about the relevance of these findings, Prof Yamamoto states: “We demonstrate for the first time ever, that olefin hydroperoxygenation can been catalyzed under extremely mild conditions using metal particles in the quantum size range. The reactivity was significantly improved in the alloyed systems especially for the trimetallic combinations, which has not been studied previously.”
The team emphasized that because of the extreme miniaturization of the structures and the hybridization of different elements, the coinage metals acquired a high enough reactivity to catalyze the oxidation even under the mild condition. These findings will prove to be a pioneering key in the discovery of innovative sub-nanomaterials from a wide variety of elements and can solve energy crises and environmental problems in the years to come.
###
Media Contact
Kazuhide Hasegawa
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




