A new study has uncovered the potential of Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry (GNSS-R) for monitoring Earth’s surface changes with unprecedented precision. The research delves into the use of GNSS-R for detecting Earth’s surface characteristics, offering a game-changing approach for environmental monitoring and target detection.
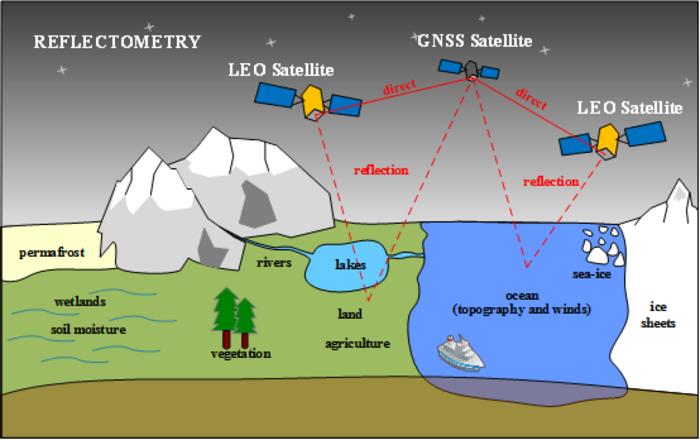
Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry (GNSS-R) is emerging as a pivotal technology in remote sensing due to its ability to provide high-precision, real-time data under all weather conditions. Traditionally, GNSS has been utilized for positioning, navigation, and timing. However, recent advancements have demonstrated its efficacy in environmental monitoring through scatterometry and reflectometry. GNSS-R capitalizes on the reflected signals from Earth’s surface and offers insights into surface properties like soil moisture, sea surface height, wind speed and ice thickness. Based on these challenges, it is essential to conduct in-depth research to further refine GNSS-R techniques and broaden their applications.
Scientists from international institutions have joined forces to explore the latest advances in GNSS-R, as published in the journal Satellite Navigation on 27 May 2024. The paper (DOI: 10.1186/s43020-024-00139-4) presents a comprehensive review of GNSS-R’s current status, theoretical developments, signal processing, parameters retrieval, and its applications in detecting changes in sea surface height, wind speed, vegetation, soil moisture, and ice thickness.
The study provides an extensive review of the principles, methods, and latest applications of GNSS-R, emphasizing its growing significance in remote sensing. GNSS-R utilizes reflected signals from multiple GNSS constellations (GPS, BDS, Galileo, GLONASS) to measure various environmental parameters. Key advancements include the development of new GNSS-R receivers and the implementation of ground, air, and space-borne experiments. These innovations have led to improved accuracy in retrieving data on soil moisture, sea surface height, wind speed, and ice thickness. Significant applications highlighted in the study include evaluating ocean altimetry, estimating soil moisture content, and measuring ice thickness. The research also delves into the challenges faced in GNSS-R development, such as signal processing complexities and the need for enhanced receiver technology. Future prospects are discussed including multi-GNSS reflectometry, new receiver designs, and emerging applications like microplastics detection and natural hazards monitoring.
Prof. Shuanggen Jin, the lead researcher, states, “Our research showcases the incredible potential of GNSS-Reflectometry in revolutionizing environmental monitoring. By harnessing reflected signals from GNSS constellations, we can achieve unprecedented accuracy in measuring critical parameters on the atmosphere, oceans, land, vegetation, and cryosphere. This opens new avenues for scientific exploration and practical applications in environmental management.”
The implications of this research are far-reaching, with potential applications spanning from tracking mesoscale ocean eddies to detecting microplastics in the ocean. The technology’s capacity to monitor natural hazards and landslides could revolutionize disaster management. Furthermore, GNSS-R’s potential in mapping soil moisture and vegetation offers valuable tools for agricultural planning and environmental conservation efforts. Moreover, GNSS-R technology provides promising opportunities for target detection in various domains. Whether in maritime, urban, or environmental applications, GNSS-R signals offer valuable information about target characteristics. As the technology matures, its integration into existing remote sensing platforms is expected to enhance our global monitoring capabilities significantly.
Credit: Satellite Navigation
A new study has uncovered the potential of Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry (GNSS-R) for monitoring Earth’s surface changes with unprecedented precision. The research delves into the use of GNSS-R for detecting Earth’s surface characteristics, offering a game-changing approach for environmental monitoring and target detection.
Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry (GNSS-R) is emerging as a pivotal technology in remote sensing due to its ability to provide high-precision, real-time data under all weather conditions. Traditionally, GNSS has been utilized for positioning, navigation, and timing. However, recent advancements have demonstrated its efficacy in environmental monitoring through scatterometry and reflectometry. GNSS-R capitalizes on the reflected signals from Earth’s surface and offers insights into surface properties like soil moisture, sea surface height, wind speed and ice thickness. Based on these challenges, it is essential to conduct in-depth research to further refine GNSS-R techniques and broaden their applications.
Scientists from international institutions have joined forces to explore the latest advances in GNSS-R, as published in the journal Satellite Navigation on 27 May 2024. The paper (DOI: 10.1186/s43020-024-00139-4) presents a comprehensive review of GNSS-R’s current status, theoretical developments, signal processing, parameters retrieval, and its applications in detecting changes in sea surface height, wind speed, vegetation, soil moisture, and ice thickness.
The study provides an extensive review of the principles, methods, and latest applications of GNSS-R, emphasizing its growing significance in remote sensing. GNSS-R utilizes reflected signals from multiple GNSS constellations (GPS, BDS, Galileo, GLONASS) to measure various environmental parameters. Key advancements include the development of new GNSS-R receivers and the implementation of ground, air, and space-borne experiments. These innovations have led to improved accuracy in retrieving data on soil moisture, sea surface height, wind speed, and ice thickness. Significant applications highlighted in the study include evaluating ocean altimetry, estimating soil moisture content, and measuring ice thickness. The research also delves into the challenges faced in GNSS-R development, such as signal processing complexities and the need for enhanced receiver technology. Future prospects are discussed including multi-GNSS reflectometry, new receiver designs, and emerging applications like microplastics detection and natural hazards monitoring.
Prof. Shuanggen Jin, the lead researcher, states, “Our research showcases the incredible potential of GNSS-Reflectometry in revolutionizing environmental monitoring. By harnessing reflected signals from GNSS constellations, we can achieve unprecedented accuracy in measuring critical parameters on the atmosphere, oceans, land, vegetation, and cryosphere. This opens new avenues for scientific exploration and practical applications in environmental management.”
The implications of this research are far-reaching, with potential applications spanning from tracking mesoscale ocean eddies to detecting microplastics in the ocean. The technology’s capacity to monitor natural hazards and landslides could revolutionize disaster management. Furthermore, GNSS-R’s potential in mapping soil moisture and vegetation offers valuable tools for agricultural planning and environmental conservation efforts. Moreover, GNSS-R technology provides promising opportunities for target detection in various domains. Whether in maritime, urban, or environmental applications, GNSS-R signals offer valuable information about target characteristics. As the technology matures, its integration into existing remote sensing platforms is expected to enhance our global monitoring capabilities significantly.
###
References
DOI
10.1186/s43020-024-00139-4
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1186/s43020-024-00139-4
Funding information
This work was supported by the Henan International Science and Technology Cooperation Key Project (Grant No. 241111520700) and Strategic Priority Research Program Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA23040100).
About Satellite Navigation
Satellite Navigation (E-ISSN: 2662-1363; ISSN: 2662-9291) is the official journal of Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The journal aims to report innovative ideas, new results or progress on the theoretical techniques and applications of satellite navigation. The journal welcomes original articles, reviews and commentaries.
Journal
Satellite Navigation
DOI
10.1186/s43020-024-00139-4
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Remote sensing and its applications using GNSS reflected signals: advances and prospects
Article Publication Date
27-May-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.




