Credit: Polina Nesterova
Scientists led by a team at Caltech have developed a new method for potentially removing nearly all sulfur compounds from gas and diesel fuel.
Sulfur compounds in fuels such as gasoline and diesel create air pollution when the fuel is burned. To address that challenge, large-scale oil refinery processes remove the majority of sulfur from fuel down to a government-mandated level. The new technique, however, has the potential to reduce sulfur down to a fraction of that amount, which would further reduce air pollution and extend the lifetime of vehicles' catalytic converters, which control tailpipe emissions.
The results–from a team led by Caltech and BP, and in collaboration with researchers at UCLA, ETH Zürich, and China's Nanjing University–are described in a new study published online February 17 in the journal Nature Energy.
"We simulated a high-sulfur oil and eliminated almost all of the sulfur through a simple chemical process. The next step is figuring out how to streamline the process and make it work on an industrial scale," says lead author Anton Toutov, a graduate student in the lab of Robert Grubbs, the Victor and Elizabeth Atkins Professor of Chemistry at Caltech.
The new method uses a potassium salt to induce the chemical reactions required to remove sulfur from fuel. Potassium is an abundant element on Earth and cheaper and more environmentally friendly to use than rare metal catalysts that are used for similar reactions.
"We were really surprised how well the potassium salt worked," says Toutov, who is also a Dow-Resnick Fellow at the Resnick Sustainability Institute at Caltech. "The sulfur is contained in small organic molecules, and this process just rips it right out."
The discovery that potassium salts can be used to promote key chemical reactions came unexpectedly a couple of years ago. Researchers in the Grubbs laboratory had been testing ways to break carbon-oxygen bonds, which is most efficient when done with a precious metal catalyst such as platinum. Alexey Fedorov of ETH Zürich, who was a postdoctoral fellow in the Grubbs laboratory at the time, ran a control experiment without the metal catalyst and found that the reaction still worked. After several tests, the researchers confirmed that a potassium salt, called potassium tert-butoxide, was, in fact, driving the reaction. Next, Toutov optimized the process and further showed that the reaction produced compounds with carbon-silicon bonds, which normally require metal catalysts to form. Carbon-silicon bonds are found in many products, such as polymers, agricultural chemicals, and semiconductors.
"They left the metal out of the reaction, and it still worked," says Grubbs. "This was a huge surprise."
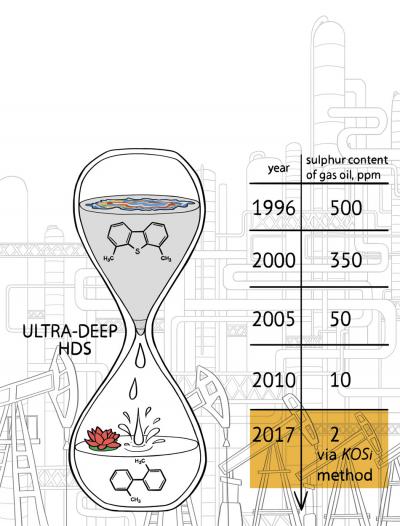
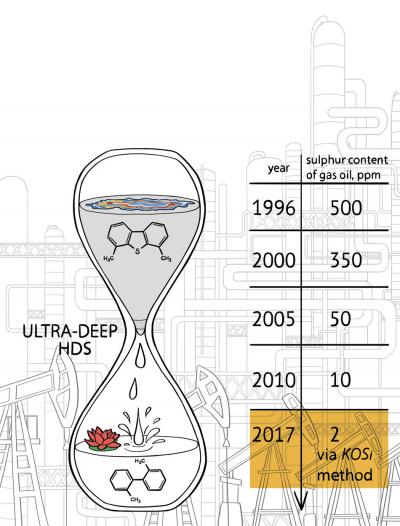
As described in the Nature Energy paper, Toutov and his colleagues in the Grubbs lab have used the potassium salt method to remove sulfur from carbon compounds found in diesel fuel. They partnered with BP to test their method on the company's refined diesel samples, reducing the sulfur levels down from 8 parts per million (comparable to the highest quality of diesel you can get from a typical gas pump today) to an extremely low 2 parts per million. They also repeated the experiment with diesel spiked with high levels of sulfur and achieved similar results.
The new method could be used as an additional step in the oil refinement process to get rid of the last traces of sulfur in fuels. The next step for Toutov, who is co-founding a new company, Fuzionaire, is to commercialize this technology. "We have a number of ideas in mind on how to do that," he says, including recycling waste products from other industries for use in the process.
###
The study is titled "A potassium tert-butoxide and hydrosilane system for ultra-deep desulfurization of fuels." The research was funded by BP. Support for Toutov was also provided by the Resnick Sustainability Institute at Caltech, Dow Chemical Company, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. Additional co-authors are Kerry Betz (BS '15); Mike Salata, Renan Cariou, John Shabaker from BP; Yun-Fang Yang and Kendall Houk from UCLA; Yong Liang from Nanjing University; and Erik Couzijn from ETH Zürich.
Media Contact
Robert Perkins
[email protected]
626-395-1862
@caltech
http://www.caltech.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag