Credit: Department of Molecular Craniofacial Embryology,TMDU
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) use genetic engineering in mice to further understand how cell fate is determined in the head
Tokyo, Japan – Mammalian embryonic development is an extremely complex and precise process. Specific molecular events act as cues that tell cells in the embryo where to move and what type to mature into. The expression levels of different genes in these cells can change at certain points of development, helping produce the signals that further the progression. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have used experiments with mice to show how a particular gene helps direct generation of tissues in the head.
In an article published in Scientific Reports, a group of researchers from TMDU determined that expression of a gene called Distal-less homeobox 5 (Dlx5) assists certain cells in the mouse head mature into cartilage cells, while others become bone cells. This is critical for proper cranial formation.
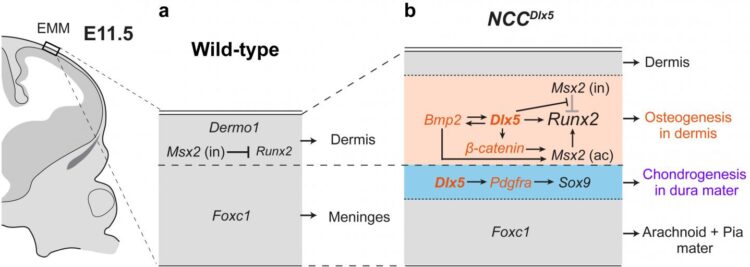
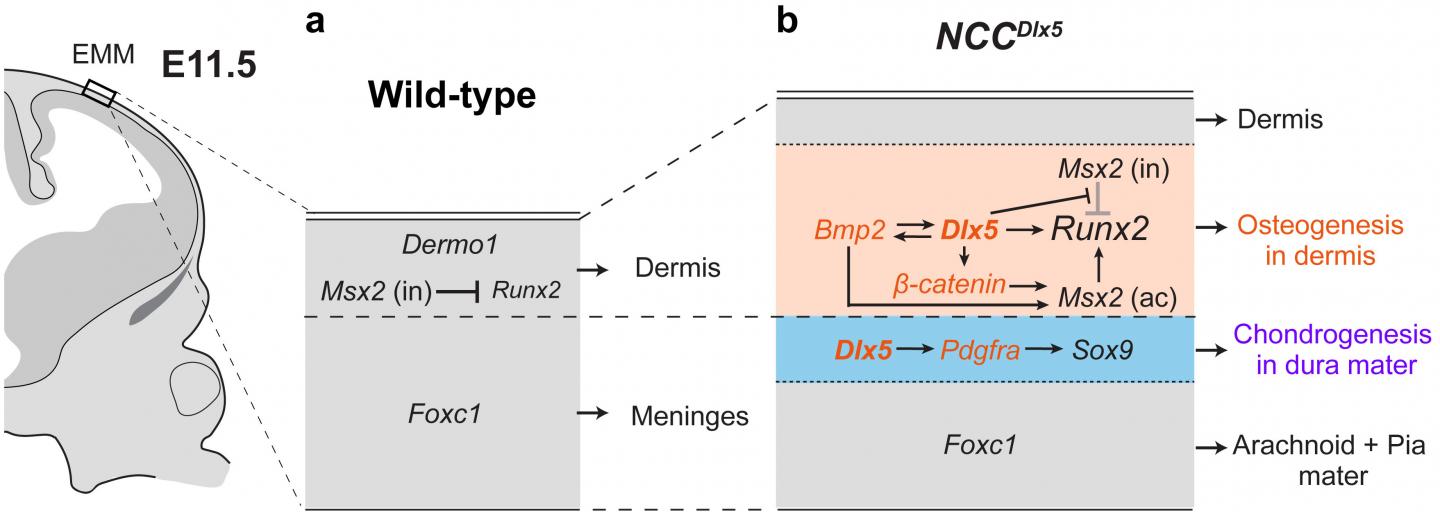
Neural crest cells (NCCs) have been a recent focus of developmental biology research because they can transition into many cell types including neurons, and those in the head region additionally differentiate into bone and cartilage. NCCs form an initial layer that constructs dermis and the meninges in early stages of development, then another group of NCCs present at the supraorbital region becomes bone forming cells and the cell domain expands apically as the overlying layer to form the calvarium to protect the brain. From these previous observations, the TMDU group became interested in how experimentally increasing Dlx5 expression would affect NCC differentiation.
“We worked with a mouse model to further understand how over-expressed Dlx5 affects cranial development,” says lead author of the study Tri Vu Hoang. “We used a method where we could force higher expression levels of Dlx5 in NCCs in a group of mice, then compared their head development with mice not genetically engineered in this way.”
The researchers first confirmed that Dlx5 was being expressed in NCCs in the engineered moue as they expected before examining cranial bone and cartilage formation in the two groups of mice. They observed enhanced layers of both bone and cartilage in the mice with higher NCC Dlx5 expression compared with the controls.
“We saw an interesting response with Dlx5 overexpression in the NCCs,” describes Sachiko Iseki, senior author. “NCCs intrinsically forming soft tissues of the initial layer transform into bone and cartilage in the vertex of the Dlx5-engineered mice.”
The group also examined expression of several bone and cartilage growth-promoting genes in the regions where new cartilage and bone were formed. They observed upregulation of multiple major genes for bone and cartilage formation including β-catenin and Pdgfrα, bone genes were expressed in the region close to the skin and cartilage genes near the brain in the Dlx5-engineered mice that was not seen in the control animals. The observation shows that the initial soft tissue layer transform into the two different layers around the time of bone and cartilage formation.
“Our results shed light on early development of the head layer of NCCs in the mouse vertex; there two cell layers exhibiting differentiating potential for bone and cartilage.” says Vu Hoang. “Overexpression of Dlx5 in NCCs is an artificial situation in embryonic development, but it showed us an interesting phenomenon to discuss uncovered developmental mechanisms in the vertex of the head.”
This study provides fascinating data that will help move the developmental biology field forward. The researchers have successfully helped reveal the complicated mechanisms involved with cranial development.
###
The article, “Dlx5-augmentation in neural crest cells reveals early development and differentiation potential of mouse apical head mesenchyme,” was published in Scientific Reports at DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-81434-x
Media Contact
Sachiko ISEKI
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.