Researchers at Hebrew University combine quantum dot ‘atoms’ and create new ‘molecules’
Credit: Meirav Oded and Somnath Koley.
Are you ready for the future? Back in 1869, Russia’s Dmitri Mendeleev began to classify the elements according to their chemical properties, giving rise to the Periodical Table of Elements. “I saw in a dream a table where all elements fell into place as required. Awakening, I immediately wrote it down on a piece of paper,” Mendeleev recalled.
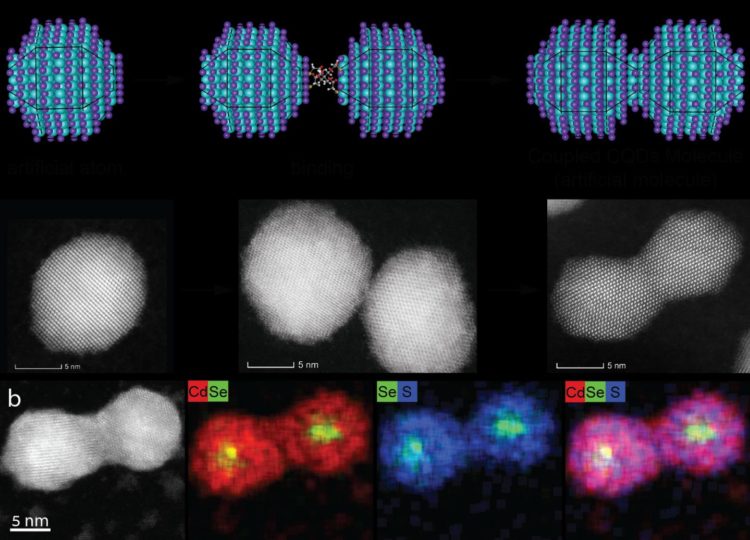
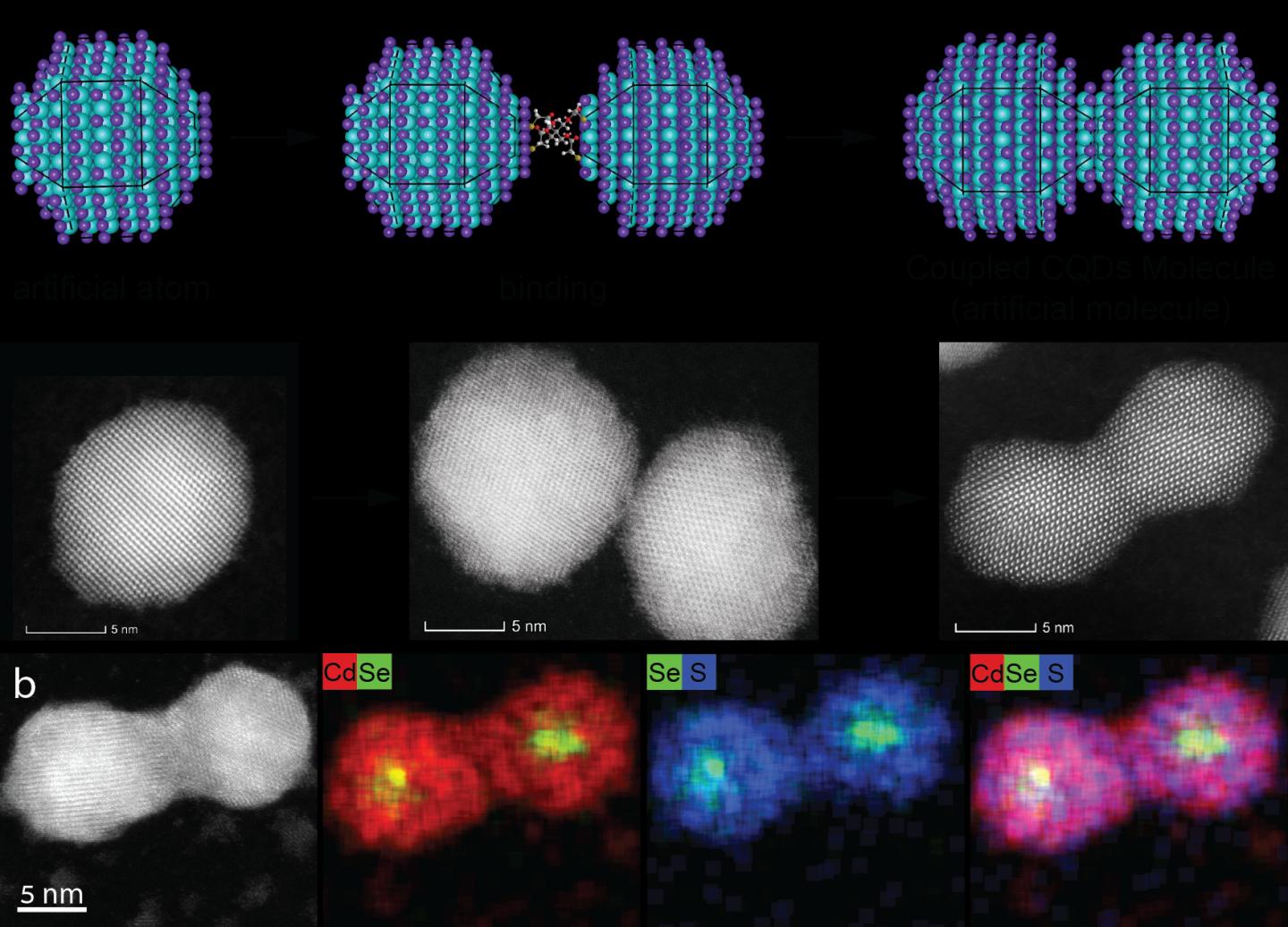
Fast forward 150 years to Israel where a team of scientists, led by Professor Uri Banin at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem’s Institute of Chemistry and Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, is reinventing the concept of the periodic table but for artificial atoms, otherwise known as colloidal quantum dots. The nanoscience research team developed a method that enables quantum dots to join together and form new molecular structures. Their findings were published in the latest edition of Nature Communications.
Quantum dots are nano-sized chunks of crystal, each containing hundreds to thousands of semiconductor atoms. When viewed through an electron microscope they look like dots. As with real atoms, when you combine artificial atoms together, they create a new (artificial) molecule with unique properties and characteristics. These molecules are referred to as “artificial” because they’re not one of the 150 million original molecules that have been formed by combining atoms from the 118 known elements in our Periodic Table.
Unlike their Periodic Table counterparts, quantum dot atoms are mercurial in nature, changing their physical, electronic and optical properties when their size changes. For example, a larger quantum dot will emit a red light, while a smaller one, of the same material, will emit a green light. Banin and his team devised a method wherein scientists may create new quantum dot molecules while still retaining control over their composition. “I began considering the infinite possibilities that could arise from creating artificial molecules from artificial atom building blocks,” Banin shared.
In the past twenty years, both scientists’ understanding of the physical properties of quantum dots and their levels of control over these tiny particles have increased tremendously. This has led to a widespread application of quantum dots in our daily lives–from bio-imaging and bio-tracking (relying on the fact that quantum dots emit different colors based on their size) to solar energy and next-generation TV monitors with exceptional color quality.
This new development lays the foundations for the formation of a wide variety of fused quantum dot molecules. “Considering the rich selection of size and composition among colloidal quantum dots, we can only imagine the exciting possibilities for creating a selection of artificial molecules with great promise for their utilization in numerous opto-electronic, sensing and quantum technologies applications,” explained Banin.
###
Media Contact
Tali Aronsky
[email protected]
972-556-664-371
Related Journal Article
http://dx.