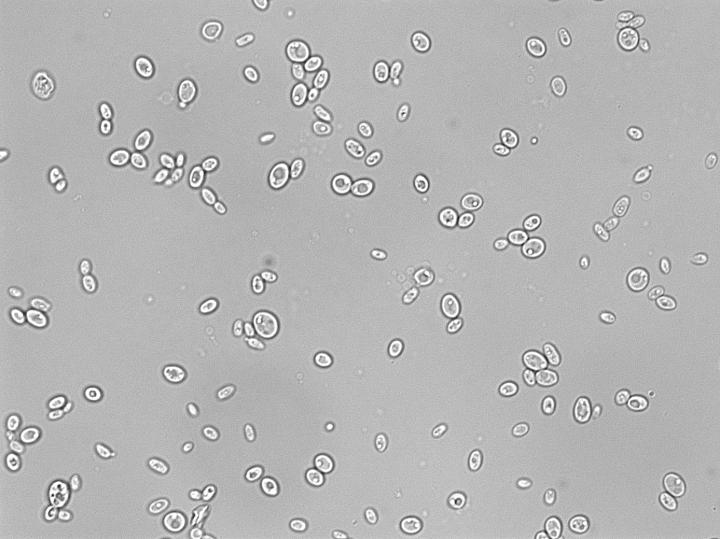
Credit: Ewa Ksiezopolska & Toni Gabaldon, CRG.
Working together with researchers in the Université Paris-Sud in France and University Medical Centre Göttingen in Germany, ICREA Research Professor Toni Gabaldón and his team at the Centre for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona read the genetic code of 33 separate strains of the yeast Candida glabrata, the second most common cause of candidiasis*.
They discovered that all the samples were very different from each other at a genetic level, particularly within genes encoding molecules that help the yeast to infect humans.
Until now, it was thought that C. glabrata only reproduced asexually by budding, even though the yeast contains genes required for sexual reproduction.
Gabaldón and his team found strong genetic evidence that C. glabrata could reproduce sexually, giving it the opportunity to swap genetic information. This ability may give the yeast new ways to evolve resistance to treatment and increase their infectious ability.
By using this genetic data to reconstruct a 'family tree' for all the strains, the researchers showed that there were originally seven distinct types of C. glabrata in separate parts of the world which have only recently come into contact and intermingled, presumably as a result of increased global human migration and travel.
The findings also raise some intriguing questions about the lifestyle of C. glabrata, which was previously thought only to survive on the human body.
Microbes that can only live on one organism (known as obligate commensals) tend to evolve in lock-step with their host, with specific strains tending to be restricted to particular geographical areas.
But the CRG team found evidence of rapid evolution across different strains of C. glabrata, even in the same region, suggesting that it must also live independently in a currently unknown niche, such as soil or plants.
"Many micro-organisms come into contact with humans, but most of them don't cause us any harm," says Gabaldón. "Our results show that C. glabrata is an opportunistic emerging pathogen, and has only managed to infect humans relatively recently. Discovering that these yeasts can reproduce sexually helps us to anticipate how they might evolve in the future, and whether they are likely to develop drug resistance through the exchange of genes."
Understanding more about the life cycle and transmission routes of C. glabrata could also help to pinpoint new ways to treat or prevent the condition. But Gabaldón's study raises a cautionary note for scientists working in the field.
"Most researchers working on C. glabrata use only one or two model strains," explains Laia Carreté, PhD student in Gabaldon's laboratory and first author of the study. "Our work shows that there is a lot of genetic diversity, comparatively larger than in other pathogens, creating yeast with many different characteristics. This needs to be taken into account when studying Candida infections."
###
Media Contact
Laia Cendros
[email protected]
34-607-611-798
@CRGenomica
http://www.crg.es
Original Source
http://www.crg.eu/en/news/genetic-study-uncovers-fungal-sex-secrets-which-shed-light-candidiasis http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.11.027