Credit: The University of Manchester
Two gene mutations that trigger a retinal disease that causes blindness in one in 5,000 males have been mapped, leading to the potential for new therapeutic treatments.
Researchers from The University of Manchester undertook a structural analysis of X-linked Retinoschisis (XLRS), a genetic disease leading to a type of macular degeneration in which the inner layers of the retina split causing severe loss of vision and gradual blindness. Currently, there is no effective treatment for XLRS, with research focused on understanding how the disease occurs in the retina.
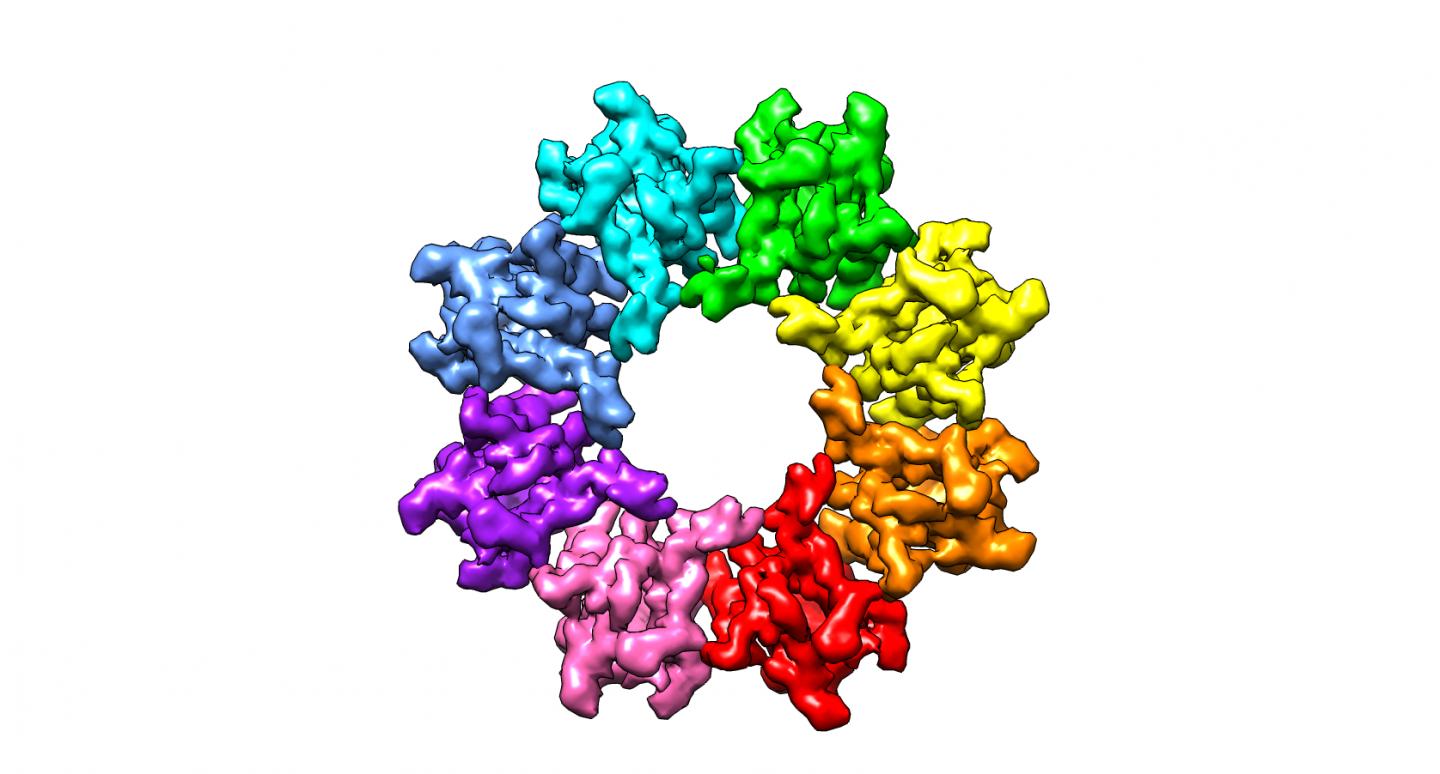
XLRS is caused by mutations in the retinal protein retinoschisin. The protein plays a crucial role in the cellular organisation of the retina, assembling itself to form paired octameric (consisting of eight retinoschisin) rings. The rings each resemble an 8-bladed propeller. This new structural insight yielded important clues into how retinoschisin performs its crucial role in the retina and spurred efforts to investigate what happens to this structure when it is mutated in XLRS.
Using a cryo-electron microscope, the team examined the paired rings as well as the effects on the rings of two XLRS-causing mutations. The effects of these mutations, despite being reported to cause the disease, were unknown and may offer explanations on how the normal protein functions in the retina.
Clair Baldock, Professor of Biochemistry at The University of Manchester and lead author of the research team's resulting paper, said the cryo-electron microscopy allowed them to identify the location of the mutations on the rings.
"We found that one disease-causing mutation sits in the interface between the octamer rings, causing retinoschisin to be less stable. The other mutation is on the propeller tip which we think is a novel interaction site for other binding proteins in the retina."
As well as identifying the mutations and precisely mapping their locations, the research team held out the possibility that future work could lead to genetic interventions and treatments, which could limit or prevent the damage caused by XLRS.
"XLRS is a promising candidate for gene therapy, so our findings on these two different classes of mutations will be informative for future therapeutic strategies," concluded Professor Baldock.
###
The paper, entitled 'Structural analysis of X-linked retinoschisis mutations reveal distant classes which differently affect retinoschisin function', was published in the journal Human Molecular Genetics.
Media Contact
Jamie Brown
[email protected]
44-161-275-8383
@UoMNews
http://www.manchester.ac.uk