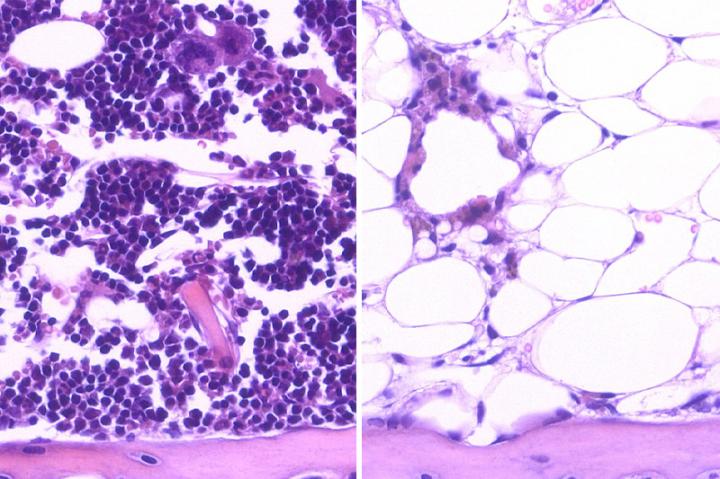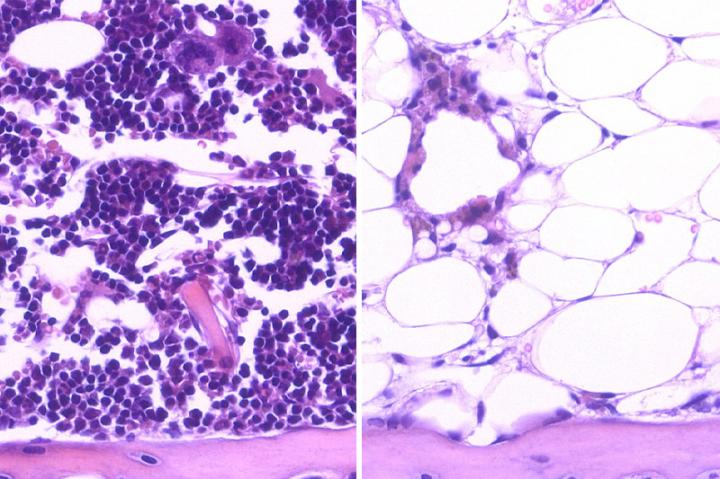
Credit: UCLA/Nature Medicine
FINDINGS
Researchers from the UCLA Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology Oncology and the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA have published two studies that define how key genetic factors affect blood-forming stem cells by either accelerating or hindering the cells' regenerative properties. The findings could one day lead to improved treatments for people undergoing common therapies for cancer such as chemotherapy and radiation.
BACKGROUND
Blood-forming stem cells, or hematopoietic stem cells, are found in the bone marrow. These cells have two unique properties: They can self-renew and, through a process called differentiation, they can form any type of blood cell. A healthy immune system depends on the regenerative abilities of hematopoietic stem cells.
Common cancer therapies such as chemotherapy and radiation can eliminate cancer by killing cancer cells. But these treatments also damage hematopoietic stem cells, which can impede the cells' ability to regenerate blood, slowing the immune system and resulting in a longer, more complicated recovery for people with cancer. Previous research indicated that certain genes may alter hematopoietic stem cells' regenerative capacity by either accelerating or hindering the cells' ability to restore the immune system, but more research was needed to pinpoint the specific genetic activity and effects.
METHOD
One of the new studies focused on a gene called Grb10 that is expressed by hematopoietic stem cells. Grb10's function was previously not known, so to better understand its role, the scientists deleted Grb10 from hematopoietic stem cells in lab dishes and in mice that had received radiation. They found that deleting Grb10 strongly promotes hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation.
In the other study, researchers analyzed a protein called DKK1. DKK1 is produced by a gene expressed by a specific "bone progenitor" cell that is present in the "niche," or cellular environment, that surrounds the hematopoietic stem cell. Typically, bone progenitor cells regenerate bone, but scientists had previously hypothesized that these cells also play an important role in regulating hematopoietic stem cells' ability to self-renew and differentiate into other blood cells.
"The cellular niche is like the soil that surrounds the stem cell 'seed' and helps it grow and proliferate," said Dr. John Chute, professor of medicine in the Division of Hematology Oncology in the UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine and the study's senior author. "Our hypothesis was that the bone progenitor cell in the niche may promote hematopoietic stem cell regeneration after injury."
The researchers showed that adding DKK1 to hematopoietic stem cells in lab dishes and mice that had received radiation produced a cascade effect within the cell niche that greatly enhanced hematopoietic stem cells' ability to self-renew and differentiate into other blood cells.
IMPACT
Taken together, the studies uncover two molecular mechanisms that could potentially be manipulated to increase the regenerative properties of hematopoietic stem cells and improve cancer therapy. Scientists can now test drugs that inhibit Grb10 or test the effectiveness of administering DKK1 intravenously to promote immune regeneration in people who have received chemotherapy and radiation or those undergoing bone marrow transplants.
###
AUTHORS
Chute, who also is a member of the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, is the senior author of both papers. The first author of the Nature Medicine study is Heather Himburg and other authors are Mamle Quarmyne, Xiao Yan, Joshua Sasine, Liman Zhao, Grace Hancock, Jenny Kan, Katie Pohl and Evelyn Tran of UCLA; and Phuong Doan, Nelson Chao and Jeffrey Harris of Duke University.
Other authors of the Cell Reports study are Yan, Himburg, Pohl, Quarmyne, Tran, Yurun Zhang, Tianchang Fang, Kan and Zhao of UCLA; and Doan and Chao of Duke University.
JOURNALS
The studies were published in the journals Nature Medicine (embargo lifts at 11:00 a.m. US Eastern time on Monday, December 5, 2016) and Cell Reports (published on November 1, 2016).
FUNDING
The studies were funded by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (HL-086998-05), the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (AI-067798), a California Institute for Regenerative Medicine Leadership Award (LA1-08014), a National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases' Centers for Medical Countermeasures Against Radiation Pilot Award (2U19AI067773-11), and by the UCLA Broad Stem Cell Research Center.
Media Contact
Mirabai Vogt-James
[email protected]
310-562-8664
@uclahealth
http://www.uclahealth.org/