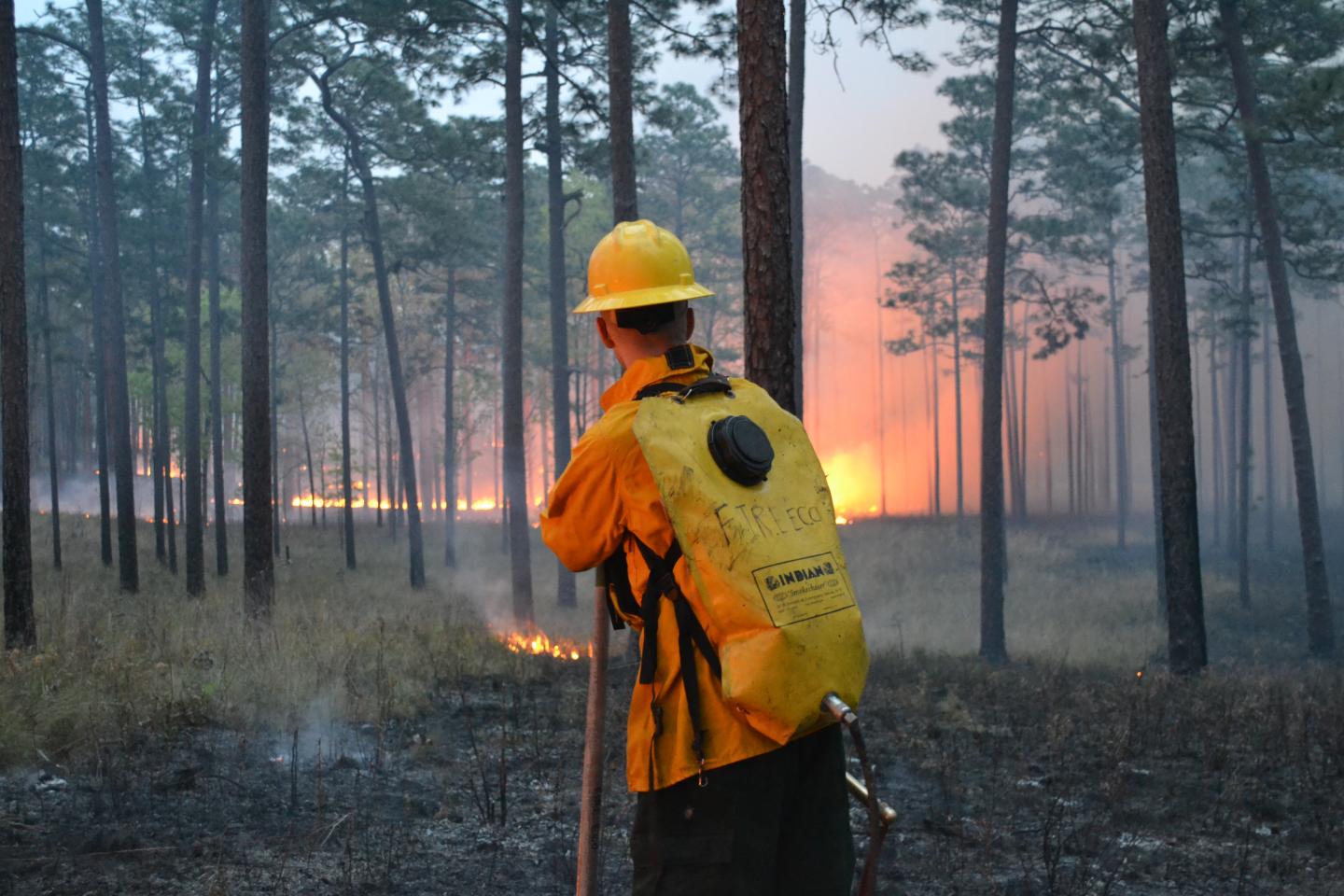
Credit: Kevin Robertson
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — A new study from Florida State University researchers indicates that common satellite imaging technologies have vastly underestimated the number of fires in Florida.
Their report, published in collaboration with researchers from the Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy, challenges well-established beliefs about the nature and frequency of fire in the Sunshine State. While there were more fires than expected, researchers said, strategically prescribed burns throughout the state are proving an effective force against the ravages of wildfire.
The paper appears in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
For scientists studying fire, sophisticated satellites whizzing far above the Earth's surface have long represented the best tool for monitoring wildfires and prescribed burns — carefully controlled and generally small fires intended to reduce the risk of unmanageable wildfires.
But FSU researchers suggest that fire experts themselves have been getting burned by faulty data, and that broadly-accepted estimates of fire area and fire-based air pollutants might be flawed.
"There are well-known challenges in detecting fires from satellites," said lead investigator Holly Nowell, a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Science. "Here we show that only 25 percent of burned area in Florida is detected."
Using comprehensive ground-based fire records from the Florida Forest Service — which regulates and authorizes every request for a prescribed burn in the state — researchers found dramatic discrepancies between fires detected by satellites and fires documented by state managers.
The majority of fires in Florida come in the form of prescribed burns, but because these fires are designed to be brief and contained, they often fall under the radar of satellites soaring overhead.
This is especially true in a state like Florida, where dense cloud cover is common and the warm, wet climate allows vegetation to regrow quickly after a blaze, disguising the scars that fires leave in their wake.
"Like a detective, satellites can catch a fire 'in the act' or from the 'fingerprints' they leave behind," said study co-author Christopher Holmes, an assistant professor in EOAS. "In our area, catching an active fire in a thermal image can be hard because the prescribed fires are short, and we have frequent clouds that obscure the view from space."
The state fire records also revealed a counterintuitive truth: Unlike in western states such as California, where dry conditions frequently produce massive increases in destructive and often uncontrollable fires, Florida actually experiences a decrease in land consumed by fire during drought.
When drought conditions emerge, researchers said, officials are less likely to authorize prescribed burns. And because prescribed burns account for the overwhelming majority of fires in the state, overall fire activity decreases.
This also suggests that prescribed burning programs — which aim to reduce the risk of wildfire in dry conditions — are having a materially positive effect.
"Although we still have occasional destructive wildfires, including the recent tragic Eastpoint fire, our results indicate that prescribed fire policy is helping to reduce wildfire risk," Holmes said, referencing the June 2018 wildfire that destroyed dozens of homes in Florida's Big Bend region.
While the team's study reconfirms the utility of prescribed burning, it calls into question prevailing estimates for airborne pollution from fire. If, as the study suggests, only 25 percent of fires in Florida are detected by satellites, then there could be "a rather large bias and a significant potential underestimation of emissions," Nowell said.
The study's findings are specific to Florida, but researchers suspect that similar satellite limitations may be skewing fire detection — and, consequently, emission estimates — in neighboring regions and geographically analogous areas like the savannas of Africa or the agricultural belts of Europe and Asia.
"We believe this result easily extends to the rest of the Southeast United States — which burns more area than the rest of the United States combined in a typical year — and other similar regions throughout the world that use small prescribed burns as a land management technique," Nowell said.
###
Kevin Robertson, Casey Teske and Kevin Hiers from Tall Timbers contributed to this study. The research was funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Media Contact
Zachary Boehm
[email protected]
850-645-1504
@floridastate
http://www.fsu.edu
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2018GL078679