Credit: Bruce Palmer/FSU Photography Services
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — A Florida State University researcher has uncovered a new geophysical phenomenon where a hurricane or other strong storm can spark seismic events in the nearby ocean as strong as a 3.5 magnitude earthquake.
“We’re calling them ‘stormquakes,'” said lead author Wenyuan Fan, an assistant professor of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Science. “This involves coupling of the atmosphere-ocean and solid earth. During a storm season, hurricanes or nor’easters transfer energy into the ocean as strong ocean waves, and the waves interact with the solid earth producing intense seismic source activity.”
The research is published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
Fan and his colleagues analyzed nearly a decade of seismic and oceanographic records from September 2006 to February 2019 and found a connection between strong storms and intense seismic activity near the edge of continental shelves or ocean banks.
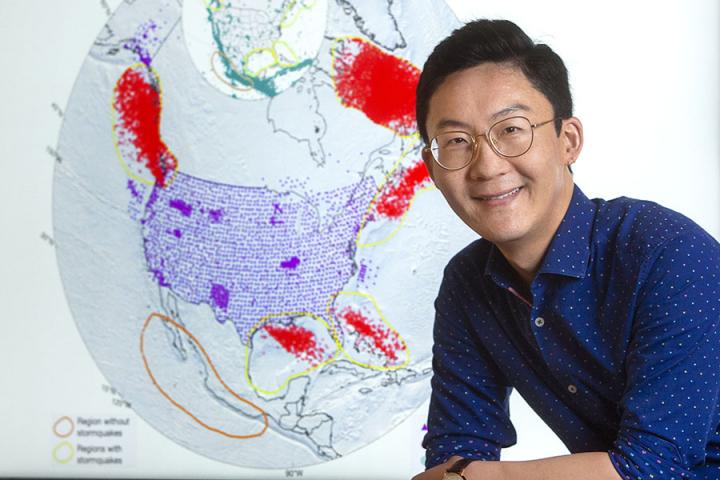
Specifically, researchers found evidence of more than 10,000 stormquakes from 2006 to 2019 offshore of New England, Florida and in the Gulf of Mexico in the United States, as well as offshore of Nova Scotia, Newfoundland and British Columbia in Canada.
“We can have seismic sources in the ocean just like earthquakes within the crust,” Fan said. “The exciting part is seismic sources caused by hurricanes can last from hours to days.”
Fan and his colleagues developed a novel approach to detect and locate seismic events and determine whether the seismic event is a stormquake. It must occur during a stormy day and meet other geophysical standards to determine the robustness of the correlation between the storm and the seismic event. Additionally, other seismic events such as earthquakes must be ruled out.
One example the researchers cited was Hurricane Bill, an Atlantic hurricane that originated on Aug. 15, 2009, strengthened into a Category 4 hurricane and ultimately struck Newfoundland as a tropical storm. It was a Category 1 hurricane when it approached offshore New England on Aug. 22, 2009.
When the hurricane arrived, numerous seismic events were located off the New England and Nova Scotia coasts, which produced transcontinental surface waves.
Similarly, Hurricane Ike in 2008 caused stormquake activity in the Gulf of Mexico and Hurricane Irene in 2011 did the same near Little Bahama Bank off Florida’s shore.
Fan and his colleagues noted that not all hurricanes cause stormquakes. There are hotspots. Scientists detected no evidence of stormquakes off of Mexico or from New Jersey to Georgia in the United States. Even Hurricane Sandy, one of the costliest storms on record in the United States, did not spur stormquakes.
This suggests that stormquakes are strongly influenced by the local oceanographic features and seafloor topography, Fan said.
“We have lots of unknowns,” Fan said. “We weren’t even aware of the existence of the natural phenomenon. It really highlights the richness of the seismic wave field and suggests we are reaching a new level of understanding of seismic waves.”
###
Researchers from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution as well as Scripps Institution of Oceanography and the U.S. Geological Survey contributed to this research.
Media Contact
Kathleen Haughney
[email protected]
850-644-1489
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




