Credit: Journal of Hepatology
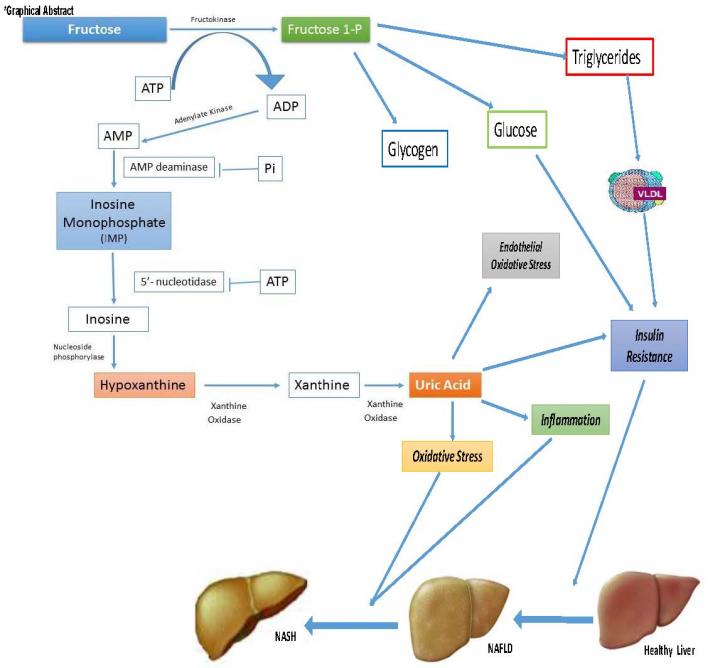
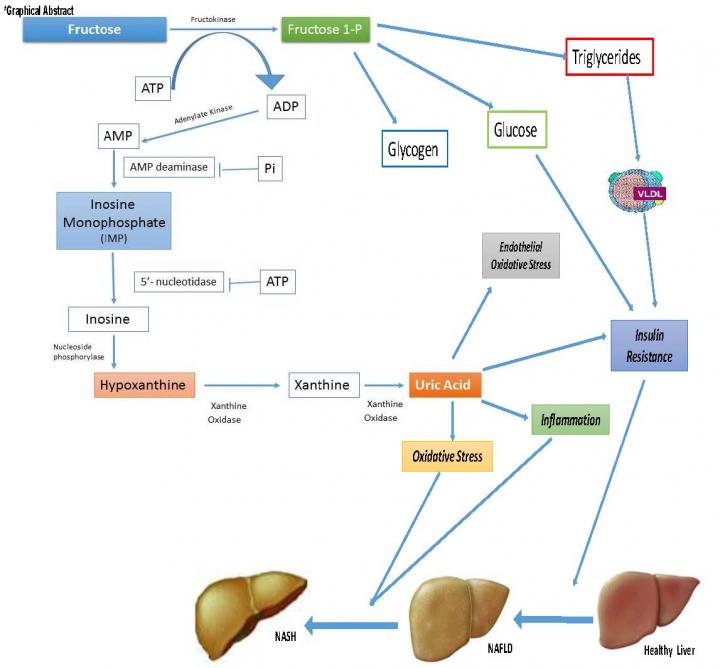
Amsterdam, The Netherlands, February 14, 2017 – Recent research suggests that dietary fructose intake may increase serum uric acid concentrations and that both uric acid concentration and fructose consumption may be increased in individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Investigators have now established that both dietary fructose consumption and serum uric acid concentrations are independently associated with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Their conclusions are published in the Journal of Hepatology.
NAFLD, the accumulation of extra fat in liver cells in people who drink little or no alcohol, is recognized as the fastest growing cause of liver disease in both Western and developing countries. It is estimated to affect up to 30% of the general population in Western countries and up to 9.6% of all children and 38% of obese children across a spectrum of liver disease, including NASH (defined as steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning and inflammation). Although NASH is a less aggressive form of NAFLD, it can progress to severe fibrosis and cirrhosis, with development of hepatocellular carcinoma in adults.
"It is plausible that dietary fructose intake and uric acid concentrations are potential risk factors for liver disease progression in NAFLD. Numerous studies have shown that high uric acid levels are associated with metabolic syndrome and NAFLD, but to date, to the best of our knowledge, no studies have tested the independence of associations among uric acid concentrations, fructose consumption, and NASH confirmed by biopsy," explained senior investigator Valerio Nobili, MD, Chief of the Hepatometabolic Unit Liver Diseases Laboratory, Bambino Gesù Hospital, IRCCS, Rome, Italy.
A team of researchers in Italy and the UK studied 271 obese children and adolescents with NAFLD (155 males, mean age 12.5 years) who underwent liver biopsy. All patients completed a food frequency questionnaire, indicating when specific foods were consumed (breakfast, morning snack, lunch, afternoon snack, dinner, etc.), how often (every day of the week, sometimes, or never), and portion size. Major sources of dietary fructose among children and adolescents are soda and other sweetened beverages. Nearly 90% reported drinking sodas and soft drinks one or more times a week. Almost 95% of patients regularly consumed morning and afternoon snacks consisting of crackers, pizza and salty food, biscuits, yogurt, or other snacks.
In the group of patients studied, 37.6% of patients had NASH and 47% of patients with NASH had high uric acid compared with 29.7% of patients who did not have NASH. Fructose consumption was independently associated with high uric acid, which occurred more frequently in patients with NASH than in not-NASH patients.
"In this study, we show for the first time that uric acid concentrations and dietary fructose consumption are independently and positively associated with NASH. The development of NASH may markedly affect life expectancy and quality of life in affected individuals and therefore it is crucial to understand the risk factors for NASH in children and adolescents in order to design effective interventions which can be used safely to treat this young group of patients," Dr. Nobili concluded.
Efforts geared towards behavior modification, nutrition education, and limiting access to soda and other sweetened beverages could potentially reduce fructose consumption in this particular population. Several countries have already launched campaigns to ban soda vending machines in schools.
###
Media Contact
Sybrand Boer Iwema
[email protected]
31-204-852-781
@elseviernews
https://www.elsevier.com/