Credit: CEBSIT
A recent study published in Neuron described in greater detail than ever before the anatomical embodiment of color sensations in the cerebral cortex, linking brain structure to perceptual function.
This discovery was the fruit of cooperative work between researchers in Dr. WANG Wei’s lab at the Institute of Neuroscience, Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Neuroscience, and Dr. TANG Shiming’s lab at Peking University.
Color is often found at the center of philosophical debates about the nature of conscious experience, mainly because color, more than any other sensation, illustrates that all perception is a mental creation. As realised early in the 18th century by Isaac Newton, visible wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation are not intrinsically colored; all the thousands of different hues we can recognize are simply arbitrary tags devised by the brain to represent various spectral compositions of light across the retinal image.
More technically, the outputs of retinal photoreceptors that discriminate wavelengths are combined and processed to eventually generate a perceptual color space. Color signals are processed through multiple neural stages in the deep brain; however, how our brains transform quantum-level events in photoreceptors to yield the many thousands of different hues we see every day is poorly understood.
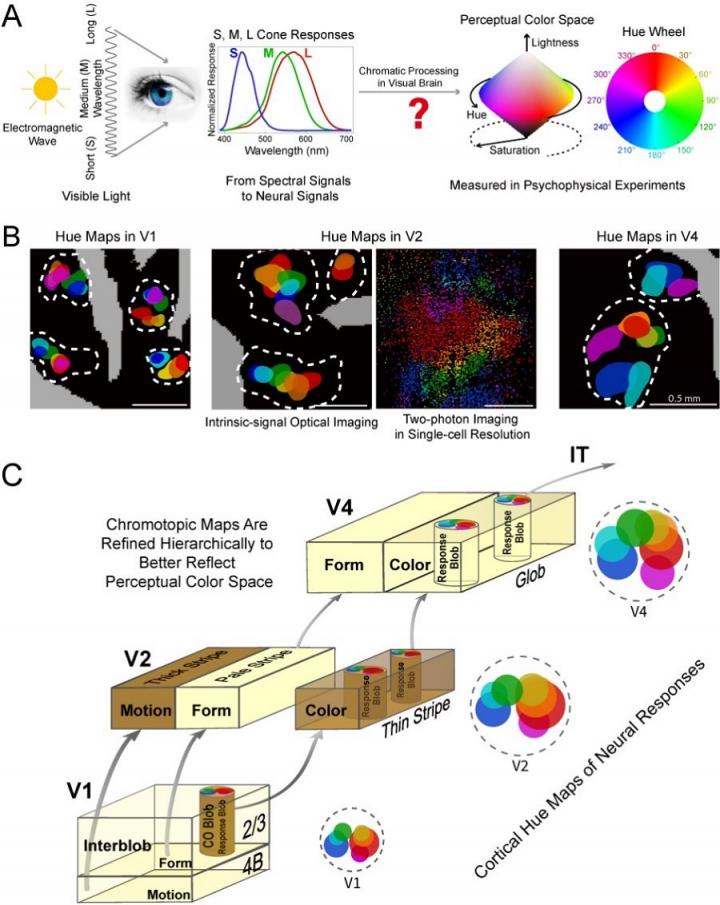
To address this question, researchers in Drs. WANG and TANG’s labs applied multiple techniques capable of imaging macaque brain activity at different scales and levels of resolution across successive processing stations in the cortex known as areas V1, V2 and V4. The aim of their study was to examine hierarchical changes in the patterns of activity when these areas process exactly the same color pattern.
The imaging methods reveal “hue maps,” i.e., color palettes in the brain, spectrally organized arrangements of multiple hue responses. Figuratively, they can be thought of as rainbows of various conformations that are scattered across the brain surface.
The novel findings of this study arise from the fine structure of these hue maps. In V1, red and blue hues predominate, but this pattern of so-called “endspectral” dominance recedes in V2 and is nearly absent in V4. Essentially, the brain’s hue maps develop hierarchically toward the uniformity of the perceptual hue map.
Computationally, the brain appears to be progressively integrating two distinct classes of cone-opponent signals originating in the retina. The information defining the precise hue of any given light is thus present in V1, coded by the ratio of activity between cone-opponent inputs – but it is not perceptible until it undergoes combinatorial processing by single neurons in area V4 and higher processing stations.
In summary, this comparative study reveals a progressive integration from cone-activation signals to isotropic hue representation along the visual hierarchy upon which our perceptual color space is built.
###
The study, entitled “Hierarchical Representation for Chromatic Processing Across Macaque V1, V2 and V4” was published as a research article online in Neuron on Aug. 26.
Drs. LIU Ye and LI Ming were co-first authors of this paper. Drs. Stewart Shipp from University College London, Niall McLoughlin from University of Manchester and YANG Yupeng from University of Science & Technology of China, have contributed to this work at various stages.
This research was supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Shanghai Municipality, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Chinese Ministry of Education.
Media Contact
WANG Wei
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




