Credit: Morteza Dehghani, et al.
New brain research by USC scientists shows that reading stories is a universal experience that may result in people feeling greater empathy for each other, regardless of cultural origins and differences.
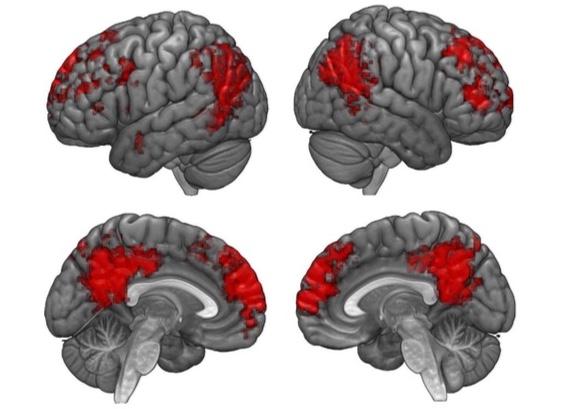
And in what appears to be a first for neuroscience, USC researchers have found patterns of brain activation when people find meaning in stories, regardless of their language. Using functional MRI, the scientists mapped brain responses to narratives in three different languages — English, Farsi and Mandarin Chinese.
The USC study opens up the possibility that exposure to narrative storytelling can have a widespread effect on triggering better self-awareness and empathy for others, regardless of the language or origin of the person being exposed to it.
"Even given these fundamental differences in language, which can be read in a different direction or contain a completely different alphabet altogether, there is something universal about what occurs in the brain at the point when we are processing narratives," said Morteza Dehghani, the study's lead author and a researcher at the Brain and Creativity Institute at USC.
Dehghani is also an assistant professor of psychology at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences, and an assistant professor of computer science at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering.
The study was published on Sept. 20 in the journal Human Brain Mapping.
Making sense of 20 million personal anecdotes
The researchers sorted through more than 20 million blog posts of personal stories using software developed at the USC Institute for Creative Technologies. The posts were narrowed down to 40 stories about personal topics such as divorce or telling a lie.
They were then translated into Mandarin Chinese and Farsi, and read by a total of 90 American, Chinese and Iranian participants in their native language while their brains were scanned by MRI. The participants also answered general questions about the stories while being scanned.
Using state-of-the-art machine learning and text-analysis techniques, and an analysis involving over 44 billion classifications, the researchers were able to "reverse engineer" the data from these brain scans to determine the story the reader was processing in each of the three languages. In effect, the neuroscientists were able to read the participants' minds as they were reading.
The brain is not resting
In the case of each language, reading each story resulted in unique patterns of activations in the "default mode network" of the brain. This network engages interconnected brain regions such as the medial prefrontal cortex, the posterior cingulate cortex, the inferior parietal lobe, the lateral temporal cortex and hippocampal formation.
The default mode network was originally thought to be a sort of autopilot for the brain when it was at rest and shown only to be active when someone is not engaged in externally directed thinking. Continued studies, including this one, suggest that the default mode network actually is working behind the scenes while the mind is ostensibly at rest to continually find meaning in narrative, serving an autobiographical memory retrieval function that influences our cognition related to the past, the future, ourselves and our relationship to others.
"One of the biggest mysteries of neuroscience is how we create meaning out of the world. Stories are deep-rooted in the core of our nature and help us create this meaning," said Jonas Kaplan, corresponding author at the Brain and Creativity Institute and an assistant professor of psychology at USC Dornsife.
###
Study co-authors include corresponding author Antonio Damasio, co-director of the Brain and Creativity Institute; Mary Helen Immordino-Yang, Reihane Borgati and Kingson Man, all from the Brain and Creativity Institute. Other co-authors were Andrew Gordon of the USC Institute for Creative Technologies and Ashish Vaswani of Google Brain.
The research is supported by the Institute for New Economic Thinking and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (grant number D12AP00069).
Media Contact
Ian Chaffee
[email protected]
213-740-8606
@USC
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23814