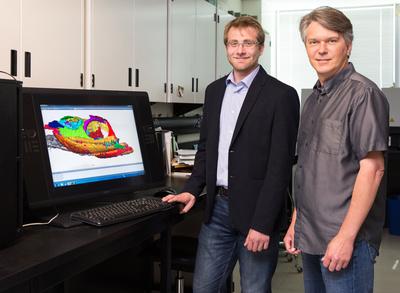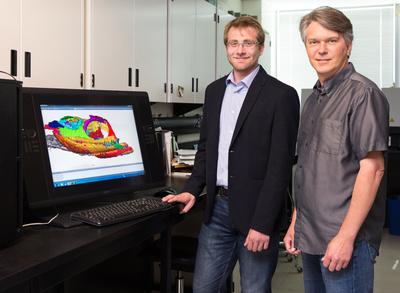
Credit: Photo by Riley Brandt, University of Calgary
"It's like a snake on the outside, but a fish on the inside."
The fossil of an early snake-like animal – called Lethiscus stocki – has kept its evolutionary secrets for the last 340-million years.
Now, an international team of researchers, led by the University of Calgary, has revealed new insights into the ancient Scottish fossil that dramatically challenge our understanding of the early evolution of tetrapods, or four-limbed animals with backbones.
Their findings have just been published in the prestigious international research journal Nature. "It forces a radical rethink of what evolution was capable of among the first tetrapods," said project lead Jason Anderson, a paleontologist and Professor at the University of Calgary Faculty of Veterinary Medicine (UCVM).
Before this study, ancient tetrapods–the ancestors of humans and other modern-day vertebrates – were thought to have evolved very slowly from fish to animals with limbs.
"We used to think that the fin-to-limb transition was a slow evolution to becoming gradually less fish like," he said. "But Lethiscus shows immediate, and dramatic, evolutionary experimentation. The lineage shrunk in size, and lost limbs almost immediately after they first evolved. It's like a snake on the outside but a fish on the inside."
Lethicus' secrets revealed with 3D medical imaging
Using micro-computer tomography (CT) scanners and advanced computing software, Anderson and study lead author Jason Pardo, a doctoral student supervised by Anderson, got a close look at the internal anatomy of the fossilized Lethiscus. After reconstructing CT scans its entire skull was revealed, with extraordinary results.
"The anatomy didn't fit with our expectations," explains Pardo. "Many body structures didn't make sense in the context of amphibian or reptile anatomy." But the anatomy did make sense when it was compared to early fish.
"We could see the entirety of the skull. We could see where the brain was, the inner ear cavities. It was all extremely fish-like," explains Pardo, outlining anatomy that's common in fish but unknown in tetrapods except in the very first. The anatomy of the paddlefish, a modern fish with many primitive features, became a model for certain aspects of Lethiscus' anatomy.
Changing position on the tetrapod 'family tree'
When they included this new anatomical information into an analysis of its relationship to other animals, Lethiscus moved its position on the 'family tree', dropping into the earliest stages of the fin-to-limb transition. "It's a very satisfying result, having them among other animals that lived at the same time," says Anderson.
The results match better with the sequence of evolution implied by the geologic record. "Lethiscus also has broad impacts on evolutionary biology and people doing molecular clock reproductions of modern animals," says Anderson. "They use fossils to calibrate the molecular clock. By removing Lethiscus from the immediate ancestry of modern tetrapods, it changes the calibration date used in those analyses."
###
Media Contact
Collene Ferguson
[email protected]
403-210-6615
@UCalgary
http://www.ucalgary.ca
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag