Credit: Yokohama National University
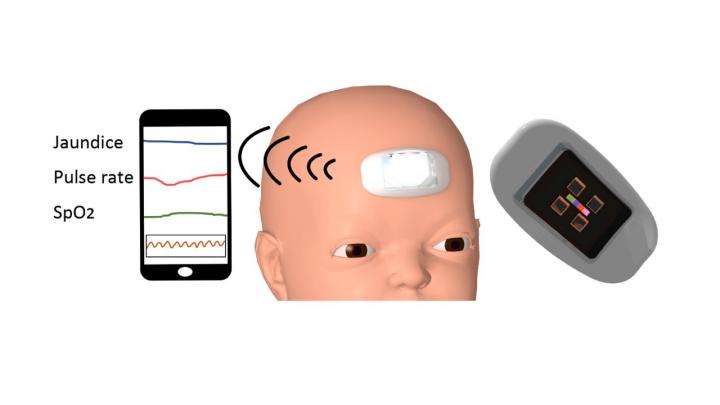
Researchers in Japan have developed the first wearable devices to precisely monitor jaundice, a yellowing of the skin caused by elevated bilirubin levels in the blood that can cause severe medical conditions in newborns. Jaundice can be treated easily by irradiating the infant with blue light that breaks bilirubin down to be excreted through urine. The treatment itself, however, can disrupt bonding time, cause dehydration and increase the risks of allergic diseases. Neonatal jaundice is one of the leading causes of death and brain damage in infants in low- and middle-income countries.
To address the tricky balance of administering the precise amount of blue light needed to counteract the exact levels of bilirubin, researchers have developed the first wearable sensor for newborns that is capable of continuously measuring bilirubin. In addition to bilirubin detection, the device can simultaneously detect pulse rate and blood oxygen saturation in real time.
Led by Hiroki Ota, associate professor of mechanical engineering in Yokohama National University’s Graduate School of System Integration, and Shuichi Ito, professor of department of Pediatrics in Yokohama City University’s Graduate School of Medicine, the team published their results on March 3 in Science Advances.
“We have developed the world’s first wearable multi-vital device for newborns that can simultaneously measure neonatal jaundice, blood oxygen saturation and pulse rate,” Ota said, noting that jaundice occurs in 60 to 80% of all newborns. “The real-time monitoring of jaundice is critical for neonatal care. Continuous measurements of bilirubin levels may contribute to the improvement of quality of phototherapy and patient outcome.”
Currently, medical professionals use handheld bilirubinometers to measure bilirubin levels, but there is not a device that can simultaneously measure jaundice and vitals in real time.
“In this study, we succeeded in miniaturizing the device to a size that can be worn on the forehead of a newborn baby,” Ota said. “By adding the function of a pulse oximeter to the device, multiple vitals can easily be detected.”
Held to the baby’s forehead by a silicone interface, the device has a lens capable of efficiently transmitting lights to neonatal skin via battery-powered light-emitting diodes, commonly known as LEDs.
“At the present stage, coin cell batteries are used, and the overall shape is very thick,” Ota said. “In the future, it will be necessary to further reduce the thickness and weight by using thin-film batteries and organic materials.”
The researchers tested the device on 50 babies, and they found that the device is not currently accurate enough to suffice for clinical decision-making. According to Ota, they will reduce the thickness and increase the flexibility of the device, as well as improve the silicone interface to facilitate better skin contact.
In the future, the researchers plan to develop a combined treatment approach that pairs a wearable bilirubinometer with a phototherapy device to optimize the amount and duration of light therapy based on continuous measurements of bilirubin levels.
###
Co-authors include first author Go Inamori, Umihiro Kamoto, Fumika Nakamura, Ryosuke Matsuda and Masaki Shimamura, Department of Mechanical Engineering at Yokohama National University; Yutaka Isoda, Graduate School of System Integration at Yokohama National University; Azusa Uozumi and Shuichi Ito, Department of Pediatrics, Graduate School of Medicine, Yokohama City University; and Yusuke Okubo, Division of Cellular and Molecular Toxicology, Biological Safety and Research Center, National Institute of Health Sciences.
The Japanese Science and Technology Agency, Takeda Science Foundation Life Science Research Grants, MIC/SCOPE, the Ogasawara research grant and Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development funded this work.
Yokohama National University (YNU or Yokokoku) is a Japanese national university founded in 1949. YNU provides students with a practical education utilizing the wide expertise of its faculty and facilitates engagement with the global community. YNU’s strength in the academic research of practical application sciences leads to high-impact publications and contributes to international scientific research and the global society. For more information, please see: https:/
Media Contact
Akiko Tsumura
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




