Credit: ViEWS, Dept of Peace and Conflict Research, Uppsala University, Sweden
The challenges of preventing, mitigating, and adapting to largescale political violence are daunting, particularly when violence escalates where it is not expected. With funding from the European Research Council, ViEWS: a political Violence Early-Warning System at Uppsala University, is developing a system that is rigorous, data-based, and publicly available to researchers and the international community. On 7 June, ViEWS released its first public forecasts for Africa.
The ViEWS project (2017-2021) is an ERC Advanced Grant project, led by Håvard Hegre, Dag Hammarskjöld Professor in Peace and Conflict Research at Uppsala University, Sweden. ViEWS assesses the risk of three forms of political violence: state-based armed conflict involving states and rebel groups, armed conflict between non-state actors, and violence against civilians. It makes available predictions for countries, sub-national geographical units, and actors.
The predictions are systematically compared to what actually happened and models are revised to optimize predictions. The models' performances are also evaluated and the results made public. ViEWS is committed to providing full transparency on data, documentation and source code. The current forecasts are based on data recorded by the Uppsala Conflict Data Program (UCDP).
"The principle of full transparency is very important to us," says Professor Håvard Hegre. "There are already analytic tools based on intelligence information that are used by for example the UN. We have chosen to maximize transparency and only use open-source data in order to see how far it takes us. This means that we might not get the absolutely best warning system, but it will be the most open. That is our contribution."
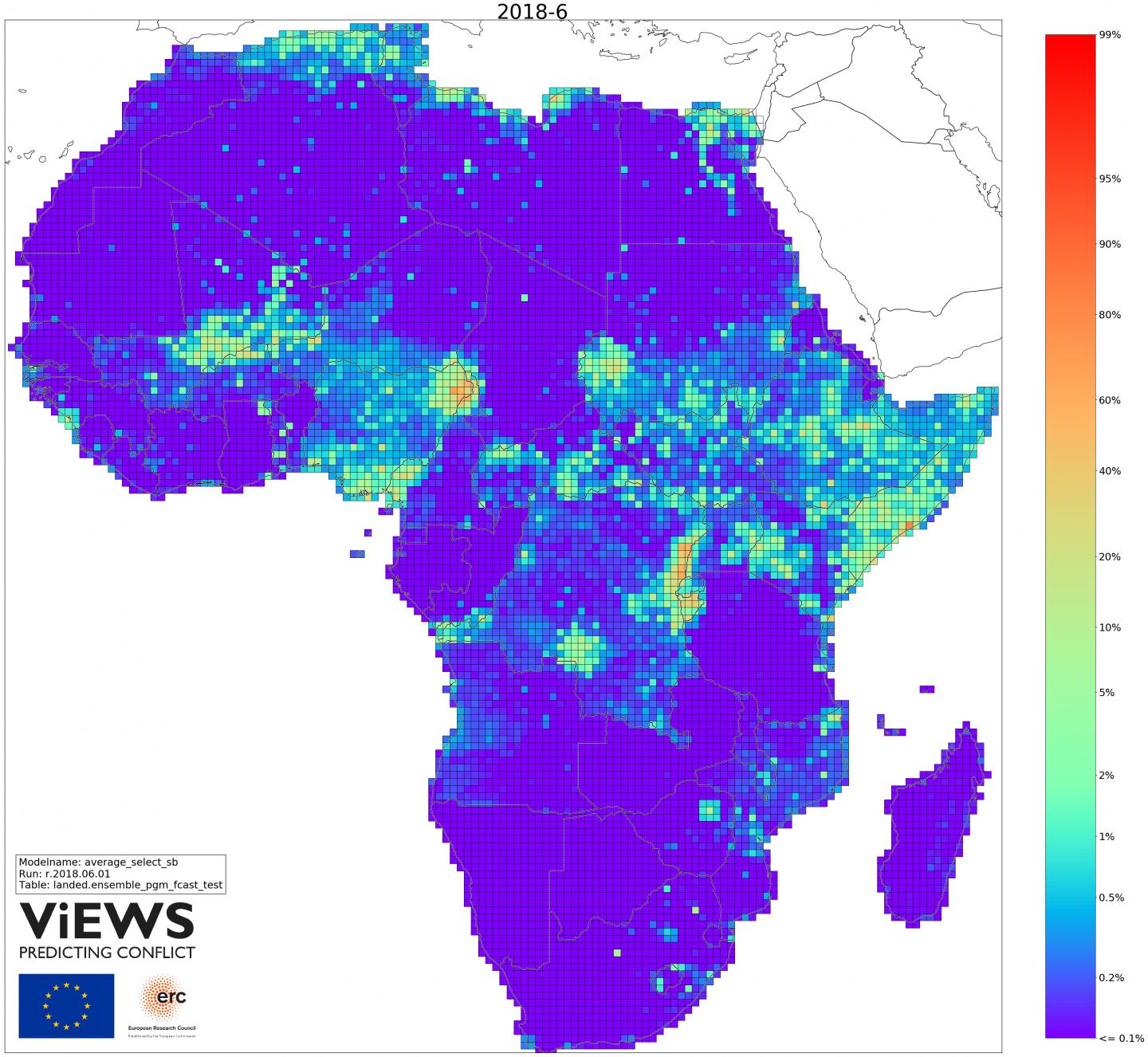
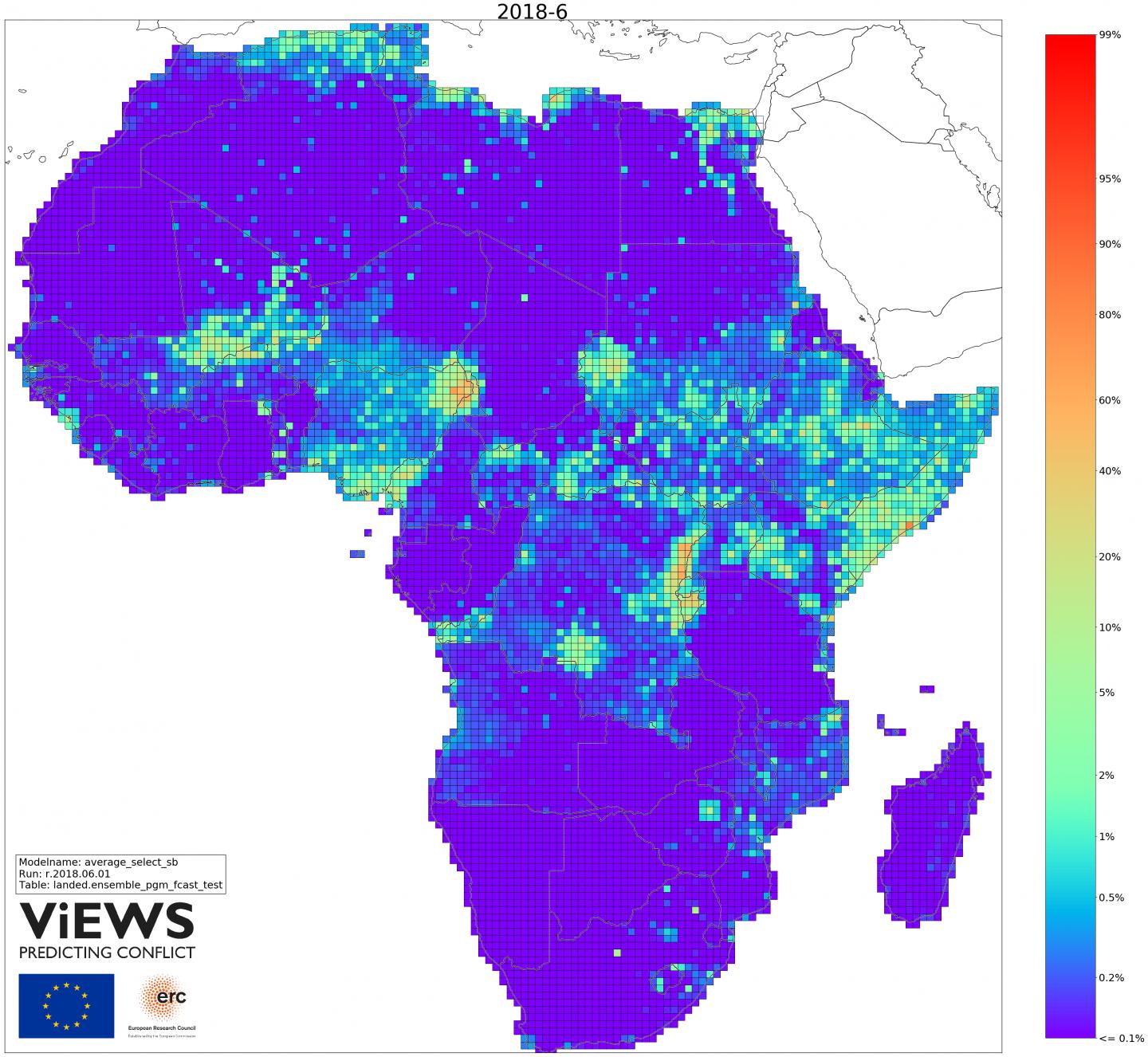
Figure 1 shows the first ViEWS forecasts. The system suggests a continued high risk of conflict in Somalia, Nigeria, and other countries in Central Africa. Recent violence in other places, e.g. in Kenya, is forecasted to recede.
Along with optimizing evaluation procedures, the project is researching how to set up criteria that make the forecasts maximally useful. For instance, ViEWS will analyze the difficult trade-offs in forecasting efforts. An ability to correctly identify in advance a large proportion of conflict cases typically is associated with a large number of false alarms. ViEWS will contribute to the assessment of the costs and benefits of predictions and false alarms.
Two new UCDP datasets "ViEWS Outcomes" and "UCDP-Candidate" will also be introduced.. UCDP is widely recognized as the world-leading provider of conflict data.
###
ViEWS receives funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement no 694640). ViEWS computations are performed on resources provided by the Swedish National Infrastructure for Computing (SNIC) at Uppsala Multidisciplinary Center for Advanced Computational Science (UPPMAX).
Please visit http://pcr.uu.se/research/views/ for a detailed project description.
For more information:
Professor Håvard Hegre, Dag Hammarskjöld Professor in Peace and Conflict Research at Uppsala University, Sweden +46-70-96 46 200, email: [email protected] or [email protected]
Figure 1: Predicted risk of state-based armed conflict across Africa, June 2018. It shows the first ViEWS forecasts. The system suggests a continued high risk of conflict in Somalia, Nigeria, and other countries in Central Africa. Recent violence in other places, e.g. in Kenya, is forecasted to recede.
Media Contact
Prof Håvard Hegre
[email protected]
0046-709-646-200
@UU_University
http://www.uu.se
Original Source
http://www.uu.se/en/news-media/press-releases/press-release/?id=4356&area=3,8&typ=pm&lang=en