Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify the T cells that, when activated, are pathogenic in a subset of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
Credit: Department of Rheumatology, TMDU
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify the T cells that, when activated, are pathogenic in a subset of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
Tokyo, Japan – Inflammation is an important part of the body’s defenses, eliminating threats and repairing damage. When the immune system is overactivated, though, it can turn from friend to foe. Now, researchers from Japan have identified the culprit responsible for one type of harmful inflammation that occurs in certain muscular disorders.
In a study published last month in the Journal of Autoimmunity, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have revealed that certain T cells, when activated, play a key role in stoking harmful inflammation. The T cells are referred to as ‘PD-1+ cells’; they express a protein called ‘programmed cell death 1’ (PD-1).
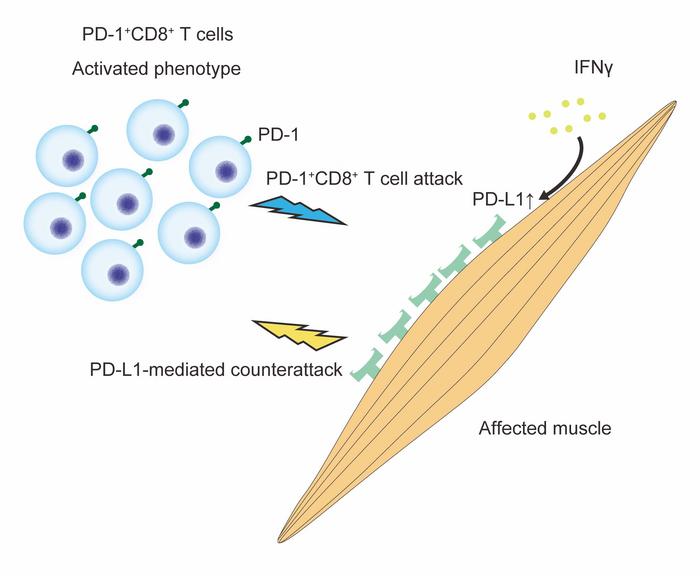
The group of disorders in question are termed idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs): chronic autoimmune diseases that affect the muscles, leaving patients with body-wide weakness and pain. A characteristic feature of these disorders is the presence of large numbers of the cells that express PD-1. What’s more, the binding partner of PD-1, PD-L1, is expressed by muscles at sites of inflammation in some patients.
“It is assumed that PD-1+ cells are pathogenic in IIMs. However, in other conditions these cells are unable to induce inflammation, which we call an exhausted phenotype,” explains lead author of the study Dr. Hirokazu Sasaki. “So, our question was, are PD-1+ cells in IIMs exhausted, or are they activated?”
The researchers sought to clarify the role of PD-1+ cells in IIMs and determine whether PD-L1 expression in the muscles of these patients protects against inflammation. To do this, they analyzed the production of cell-damaging molecules by PD-1+ cells and the protective effects of PD-L1 using samples from patients with an IIM and a mouse model of the condition.
“The results were very clear,” says Dr. Shinsuke Yasuda, senior author. “We found that PD-1+ cells infiltrated the muscles expressing PD-L1, and that they expressed high levels of cell-damaging molecules in patients with active disease, indicating that the cells were activated and not exhausted.”
Furthermore, mice that could not express PD-L1 developed severe disease and exhibited large numbers of PD-1+ cells expressing cell-damaging molecules. In addition, mice that could not produce the protein IFNγ, which promotes PD-L1 expression, had worse disease symptoms than normal mice.
“Our findings show that PD-1+ T cells are pathogenic in a subset of IIMs, and that muscular PD-L1 expression, regulated by IFNγ, exerts a protective effect in patients with these conditions,” says Dr. Sasaki.
Given that PD-1+ T cells appear to be the main culprits in causing IIM symptoms, treatment targeting this cell population seems promising. Indeed, a recent clinical trial showed that an antibody targeting PD-1 could be an effective treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis, suggesting that existing therapies for other inflammatory diseases could be applied to IIMs.
###
The article, “Pathogenicity of functionally activated PD-1+CD8+ cells and counterattacks by muscular PD-L1 through IFNγ in myositis,” was published in the Journal of Autoimmunity at DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103131
Journal
Journal of Autoimmunity
DOI
10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103131
Article Title
Pathogenicity of functionally activated PD-1+CD8+ cells and counterattacks by muscular PD-L1 through IFNγ in myositis




