Gentamicin is a common antibiotic used to treat critically ill neonates. It is water soluble and is primarily eliminated from the body through urine. For this reason, total body weight, which factors in the weight of the body’s water content, is used to determine gentamicin dosage. However, the total water content of a healthy neonate differs significantly from that of a premature baby. As such, using total body weight to calculate gentamicin dose may lead to non-optimal dose prescription. Premature babies also have weaker kidneys, which means that discrepancy in the drug dosage can negatively impact their kidney function. Thus, a more accurate way to calculate gentamicin dose for newborns is needed.
Credit: Dr. Kannan Sridharan from Arabian Gulf University
Gentamicin is a common antibiotic used to treat critically ill neonates. It is water soluble and is primarily eliminated from the body through urine. For this reason, total body weight, which factors in the weight of the body’s water content, is used to determine gentamicin dosage. However, the total water content of a healthy neonate differs significantly from that of a premature baby. As such, using total body weight to calculate gentamicin dose may lead to non-optimal dose prescription. Premature babies also have weaker kidneys, which means that discrepancy in the drug dosage can negatively impact their kidney function. Thus, a more accurate way to calculate gentamicin dose for newborns is needed.
Fat and fat-free mass are important measurements that can be used to calculate a variety of body parameters. Fat mass is simply the total amount of body fat while fat-free mass is the body’s weight after subtracting the fat mass. In a new study, a medical research team from the Arabian Gulf University, Bahrain, and the Bahrain Ministry of Health, led by Dr. Kannan Sridharan, demonstrated that fat-free mass is a better alternative to total body weight for calculating gentamicin dosage. “Our hypothesis was that the dosage of gentamicin shall need adjustment,” remarked Dr. Sridharan. The research was published in Pediatric Investigation on June 8, 2023.
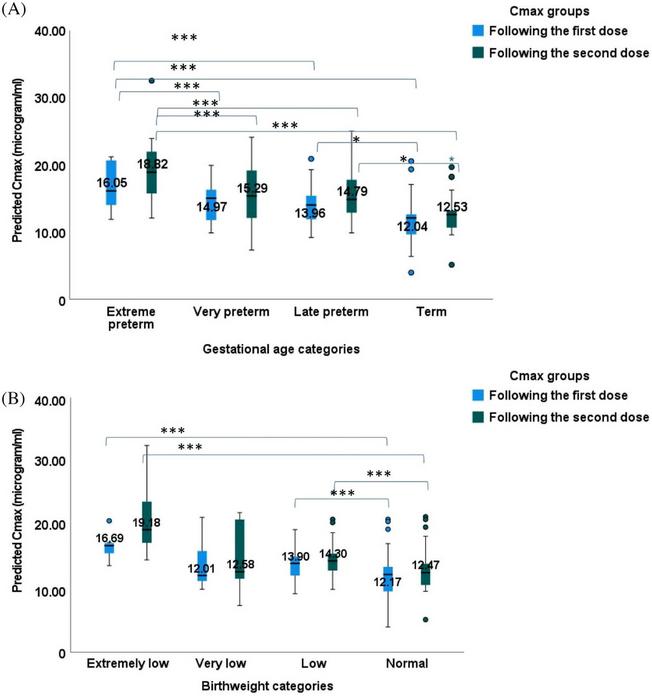
The test their hypothesis, the team measured the ‘peak’ or highest (Cmax) and ‘trough’ or lowest (Cmin) concentrations of gentamicin in the blood of critically ill newborns, after administering two doses of the antibiotic. The team used a latex-enhanced immunoturbidimetric method to measure gentamicin concentrations, based on fat-free mass. They determined the body fat and fat-free mass of the newborns by measuring skinfold thickness around their triceps. The researchers observed that premature babies had a much higher gentamicin concentration in the blood compared to term babies. In fact, the team observed a general trend where gentamicin concentration in the blood increased the more premature the babies were. Babies with low birth weight (often seen in premature babies) also showed higher blood concentrations of the antibiotic. Additionally, premature babies had more fat mass (21% more) than term neonates. “The most plausible reason for this is the administration of total parenteral nutrition in preterm neonates,” Dr. Sridharan explained.
Currently, the accepted gentamicin dosage is around 4 to 5 mg/kg every 24, 36, or 48 hours. The team found that this dosage regimen was insufficient for treatment in one-third of the newborns studied. Based on fat-free mass, the team determined the recommended gentamicin doses for extremely premature babies to be 7.95 mg/kg every 48 hours, and 7.30 mg/kg every 36–48 hours for very premature babies. For late premature babies, the optimal concentration was 5.90 mg/kg every 36–48 hours. Finally, for term babies, 5.10 mg/kg every 24 hours was found to be optimal.
The study demonstrated that fat-free mass is a more accurate parameter when calculating gentamicin doses for newborns, especially those of premature birth. “In the future, fat-free mass dosing may be considered for obtaining optimal therapeutic effects in neonatal populations,” concluded Dr. Sridharan. While further research is needed to establish the safety of fat-free mass-based gentamicin dosage, the study opens a promising alternative to the calculation of antibiotic dosage based on whole body weight.
***
Reference
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ped4.12386
Authors: Kannan Sridharan1*, Muna Al Jufairi2,3, Eman Al Ansari2, Lulwa Alsadah4, Howra Wasel4
Affiliations
1 Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Arabian Gulf University Manama Kingdom of Bahrain.
2 Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Salmaniya Medical Complex Ministry of Health Manama Kingdom of Bahrain.
3 Department of Pediatrics College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Arabian Gulf University Manama Kingdom of Bahrain.
4 College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Arabian Gulf University Manama Kingdom of Bahrain.
About Dr. Kannan Sridharan
Dr. Kannan Sridharan is an associate professor at the Arabian Gulf University, Bahrain. Before joining Arabian Gulf University, Dr. Sridharan was a faculty member at Fiji National University (2015-17) and Subharti University (2013-15). He has authored nearly 200 research papers and has received several awards for his contributions to the field.
Journal
Pediatric Investigation
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Is fat-free mass-based gentamicin dosing regimen preferable than whole-body weight in neonates?
Article Publication Date
8-Jun-2023




