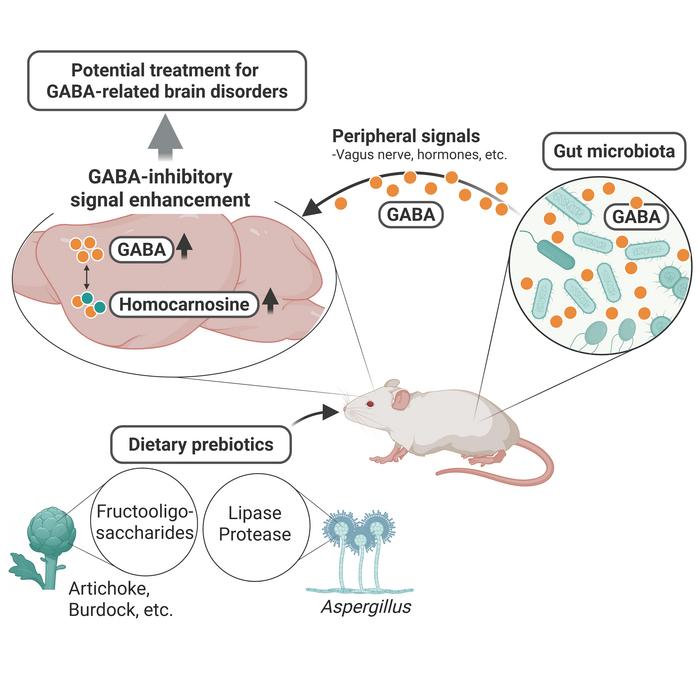
Recent research unveils a compelling link between the gut microbiome and brain health, specifically focusing on the amino acid gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), known for its crucial role as the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. This connection is particularly relevant considering that low levels of GABA have been associated with various neurological disorders, including depression, epilepsy, and Alzheimer’s disease. As scientists probe deeper into the gut-brain axis, the ongoing exploration seeks to illuminate how dietary modifications can enhance our mental well-being through gut modulation.
GABA is fundamental to the brain’s functioning, as it directly influences inhibitory processes. The neurotransmitter acts as a natural relaxant, potentially reducing anxiety and creating a sense of calm. Despite the recognized importance of GABA, traditional therapies often overlook the gut’s potential influence on its levels. This is increasingly concerning given that many individuals suffer from neurological conditions that may stem from imbalances not only in their brain chemistry but also in their gut microbiota.
Innovative studies have turned toward prebiotics, which are dietary fibers resistant to digestion that beneficially stimulate the growth of certain gut bacteria. Recent findings suggest that prebiotics can effectively boost GABA production by fostering an environment where beneficial gut microbiota thrive. The exciting revelation that specific prebiotics can enhance gut health and, in turn, potentially elevate GABA levels in the brain is a breakthrough in understanding how dietary choices impact mental health.
.adsslot_UWwvQrsA1j{width:728px !important;height:90px !important;}
@media(max-width:1199px){ .adsslot_UWwvQrsA1j{width:468px !important;height:60px !important;}
}
@media(max-width:767px){ .adsslot_UWwvQrsA1j{width:320px !important;height:50px !important;}
}
ADVERTISEMENT
Groundbreaking research conducted at Hiroshima University utilized a model involving adolescent mice to investigate how specific oligosaccharides, namely fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS), influence GABA levels. Researchers treated the mice with FOS and observed marked increases in brain GABA concentrations in regions of the brain such as the cortex and hippocampus. The significance of these findings emphasizes how dietary components can alter biochemical pathways, thereby highlighting the tangible benefits of gut microbiota modulation through specific prebiotic strategies.
Notably, the results suggested a direct correlation between gut-derived GABA, brain GABA, and gut microbiota. Although there remain many unanswered questions—particularly concerning whether gut microbiota-derived GABA can pass the blood-brain barrier—these initial findings indicate that there may be other pathways at play, such as those involving the Vagus nerve or hormonal pathways. This comprehensive understanding lays down a framework for future research to dissect the complex interactions within the gut-brain axis.
While the studies on mice serve as a promising starting point, researchers harbor hopes that this knowledge can translate into effective therapeutic methodologies for human applications. The ability of prebiotics to raise brain GABA levels could herald a new era of dietary interventions for brain disorders, potentially offering a non-invasive approach to treat conditions like epilepsy and depression. This shift towards natural dietary solutions resonates well with a growing populace that increasingly favors holistic approaches over pharmaceutical interventions.
The research team, led by Thunatchaporn Kumrungsee, has called for further investigations to elucidate the mechanisms through which dietary prebiotics affect GABA levels in humans. They suggest that understanding these biochemical connections is critical for advancing treatments for neuropsychiatric conditions that plague so many individuals today. As they put it, “Our study suggests that prebiotics possess the ability to prevent or treat those brain diseases by enhancing GABA levels via alterations in gut microbiota.”
Supplementary ingredients, such as enzymes derived from microbes like Aspergillus, have also been shown to enhance GABA levels in conjunction with prebiotic intake. Remarkably, these findings not only bolster our understanding of GABA but also showcase the potential that specific fungal enzymes offer in nutritional science. The application of such enzymes may significantly augment the benefits of dietary prebiotics, creating a holistic approach to improving brain health.
Researchers are keenly aware that despite this promising outlook, more rigorous investigations are necessary to confirm the translatability of these findings to human subjects. The extensive interplay of gut-derived signals influencing brain function should not be taken lightly, as the implications for nutrition science and neurologically-targeted therapies could be monumental. The clinical significance of establishing a successful link between diet, gut health, and brain function cannot be overstated—especially as mental health issues continue to rise dramatically.
The ramifications of these discoveries extend beyond basic science, questioning conventional dietary practices and challenging how we understand the interplay between nutrition and mental well-being. The prospect of utilizing common dietary changes in an effort to engineer tangible improvements in brain function stands to revolutionize preventive approaches in mental health care. As the research community stands on the precipice of understanding the gut-brain nexus, it opens doors to a host of possibilities regarding food as medicine.
In summary, the synergy between GABA production and gut health, bolstered by prebiotics and specific enzymes, represents an exciting frontier in neuroscience and nutrition. The link between our diet and brain chemistry is increasingly evident, urging us to consider how holistic and integrative strategies could pave the way for improved mental health outcomes. As the science evolves, it will undoubtedly bring renewed hope and innovative pathways to tackle the numerous challenges faced by those living with GABA-related disorders.
This burgeoning field of study holds the promise of redefining how we approach health interventions, illustrated through remarkable research breakthroughs and the potential for impactful lifestyle changes. As more extensive and focused research is undertaken, the integration of dietary science into clinical practices may reshape our understanding of mental health, fundamentally transforming how we support cognitive and emotional well-being.
In the context of ongoing discoveries, the narrative surrounding the gut-brain relationship continues to expand, encouraging adherence to dietary practices that not only nourish the body but elevate mental health. The quest for knowledge in this domain is vital as we strive to improve the quality of life for individuals grappling with neurological challenges, catalyzing a future where food choices could significantly influence brain health for good.
Subject of Research: The impact of prebiotics on brain GABA levels through gut microbiota modulation
Article Title: Fructooligosaccharides and Aspergillus enzymes increase brain GABA and homocarnosine by modulating microbiota in adolescent mice
News Publication Date: 3-Apr-2025
Web References: doi.org
References: Publication in npj Science of Food
Image Credits: Credit: Created in BioRender. Kumrungsee, T. (2025)
Keywords
GABA, prebiotics, gut microbiota, neuroscience, dietary science, brain health, neurological disorders, homocarnosine
Tags: connection between gut health and depressiondietary modifications for mental well-beingenhancing GABA production with prebioticsGABA as a natural relaxantgut microbiome and GABAgut-brain axis researchinhibitory neurotransmitters and anxietyinnovative studies on prebiotics and GABAlow GABA levels and neurological disordersneurological conditions and gut microbiotaprebiotics and brain healthprebiotics role in mental health