Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) has emerged as a critical concern for healthcare professionals globally, especially in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus. The intersection between viral infection and cardiovascular disease is complex and multifaceted, leading to heightened risks of ACS in infected patients. Recent findings suggest that the mechanisms underlying this relationship extend beyond traditional risk factors, unveiling new pathways of viral-induced inflammation and ensuing vascular complications that could redefine management strategies in post-pandemic cardiology.
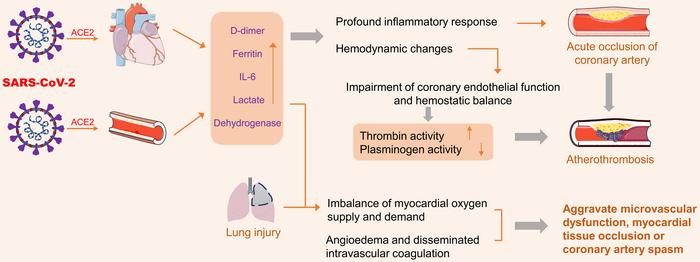
The entry of SARS-CoV-2 into human cells relies heavily on the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, which is abundant in the heart and blood vessels. While ACE2 is crucial for regulating various cardiovascular functions, its interaction with the virus leads to detrimental effects. Upon infection, the virus displaces ACE2 from endothelial cells, disrupting the renin-angiotensin system and resulting in vasoconstriction, increased blood pressure, and heightened inflammation. The ensuing damage is not merely localized but extends throughout the cardiovascular system, promoting acute inflammatory responses that significantly elevate the risk of myocardial injury.
One major pathway implicated in the exacerbation of ACS is the cytokine storm, a hyper-inflammatory reaction characterized by excessive production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). These cytokines are known to activate platelets, leading to thrombus formation and destabilization of atherosclerotic plaques. The severity of inflammation can also lead to microvascular dysfunction, further compromising myocardial perfusion and increasing the likelihood of adverse cardiac events. Understanding this cascade of inflammatory responses presents new avenues for therapeutic intervention that could mitigate the cardiovascular consequences associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Moreover, hypoxic conditions often present during severe COVID-19 infections can exacerbate these inflammatory phenomena, creating a vicious cycle of injury. Hemodynamic instability due to the systemic effects of the virus compounds the risk of ACS, emphasizing the urgent need for comprehensive strategies addressing both viral and cardiovascular health. This dual focus is especially critical in managing patients who already have underlying cardiovascular conditions, who are consequently more vulnerable to the complications posed by SARS-CoV-2.
In efforts to mitigate these complications, recent research into therapeutic options has gained traction. Among these strategies, modulation of the ACE2 receptor has emerged as a point of focus for innovative treatments. While traditional ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) remain under scrutiny due to their potential to upregulate ACE2 expression, emerging evidence points towards alternative therapeutic agents that may confer cardioprotective effects without exacerbating the viral entry process.
Melatonin has been highlighted in recent studies as a promising adjunct therapy in this context. By enhancing nitric oxide bioavailability, melatonin stabilizes arterial plaques and reduces oxidative stress, thereby providing a protective effect during viral-induced inflammation. The implementation of such novel agents in clinical practice could spell a shift in how physicians approach the treatment of patients presenting with ACS as a complication of COVID-19.
Ayurvedic and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) approaches have also gained attention for their potential to address both viral replication and cardiovascular impairment. The pharmacological properties of various herbal compounds, such as licorice and honeysuckle, showcase their ability to inhibit viral entry and mitigate cytokine storms effectively. Licorice’s glycyrrhizic acid exhibits antiviral properties while simultaneously protecting against oxidative damage through the modulation of key cellular signaling pathways. The integrative use of these natural products alongside conventional therapies might represent a holistic approach towards managing the multifactorial impacts of COVID-19 and its cardiovascular sequelae.
While herbal medicine presents significant benefits, innovative non-herbal pharmacological interventions are also under investigation. Recent findings suggest the efficacy of peptide fusion inhibitors like EK1C4 and IL-1 antagonists such as anakinra in reducing thromboembolic events and the incidence of ACS in patients battling the severe manifestations of COVID-19. Particularly, anakinra has shown promise in curbing hyperinflammation, correlating with improved survival outcomes during severe COVID-19 cases.
Nanotechnology also represents a groundbreaking frontier in the management of COVID-19 and its associated complications. Nanoparticle platforms have revolutionized vaccine delivery systems, enhancing the stability and efficacy of mRNA vaccines like those developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna. These lipid nanoparticles not only protect the mRNA from enzymatic degradation but also optimize immune response elicitation. Additionally, alternative nanoparticles such as nanoceria and silver nanoparticles are being explored for their antioxidative properties and ability to hinder viral replication.
As the field advances, future directions must include clinical trials to establish standardized dosages for herbal formulations, thereby validating their safety and efficacy in larger populations. Detailed mechanistic studies utilizing emerging imaging technologies like cryo-electron microscopy could elucidate the interactions between herbal compounds and viral receptors. Moreover, optimizing nanoparticle delivery and enhancing target-specific mechanisms will grant greater precision in therapy, ultimately improving patient outcomes in the context of viral-induced cardiovascular disease.
With these diverse strategies contributing to the fight against SARS-CoV-2, the collective promise of phytomedicine and advanced therapeutic modalities heralds a new paradigm in addressing the multifaceted complications of COVID-19. Bridging traditional medical knowledge with cutting-edge science offers an integrated approach that prioritizes safety, efficacy, and patient-centered care in the evolving landscape of post-pandemic cardiology. Adapting to these paradigms will be paramount in redefining therapeutic strategies while ensuring comprehensive care for patients grappling with both viral infections and cardiovascular challenges.
Understanding the interplay between SARS-CoV-2 and acute coronary syndrome is crucial as we navigate the complexities of treating affected patient populations. Education, research, and innovative approaches are essential in overcoming the cardiovascular ramifications of viral infections amidst the ongoing challenges presented by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Subject of Research: The relationship between SARS-CoV-2 infection and acute coronary syndrome (ACS)
Article Title: Potential of Phytomedicine in Benefiting Both Long COVID and Acute Coronary Syndromes: A State-of-the-art Review
News Publication Date: 13-May-2025
Web References: Exploratory Research and Hypothesis in Medicine
References: doi:10.14218/ERHM.2024.00043
Image Credits: Credit: Qing Liu, Rongyuan Yang, Xiao Jiang, Yiran Lu, Yu Ding
Keywords
COVID-19, acute coronary syndrome, ACE2, phytomedicine, nanotechnology, herbal medicine, cytokine storm, inflammation, cardiovascular disease, therapeutic strategies.
Tags: ACE2 and Inflammationacute coronary syndrome managementCardiovascular Complications Post COVID-19COVID-19 Impact on Cardiovascular SystemCytokine Storm in COVID-19Herbal Remedies for COVID-19 SymptomsInflammation and Myocardial InjuryIntegrative Approaches to Heart HealthPhytomedicine for Long COVIDPost-Pandemic Cardiology StrategiesSARS-CoV-2 and Cardiovascular HealthViral Infection and Heart Disease