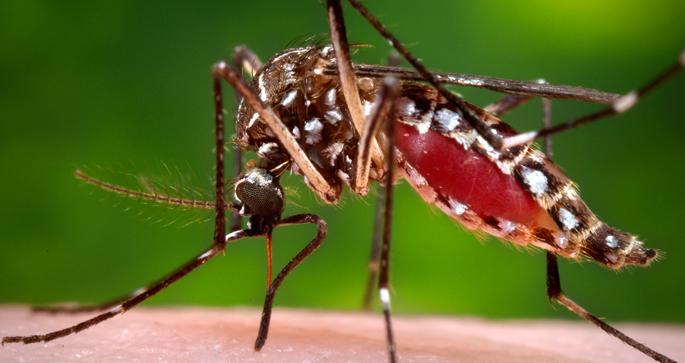
Credit: Photo by James Gathany/CDC
In a new study, Vanderbilt pharmacologist Jerod Denton, Ph.D., Ohio State entomologist Peter Piermarini, Ph.D., and colleagues report an experimental molecule that inhibits kidney function in mosquitoes and thus might provide a new way to control the deadliest animal on Earth.
The investigators aim their inhibitor, named VU041, at the mosquito Anopheles gambiae, the leading vector for malaria, and Aedes aegypti, a mosquito that transmits Zika virus and other pathogens. The study appears in the journal Scientific Reports.
Over several decades of exposure, mosquitoes have evolved genetic resistance to various insecticides that attack their nervous system. The new study shows for the first time that inducing kidney failure — or, more correctly, Malpighian tubule failure — in mosquitoes can circumvent resistance to conventional insecticides.
"We're essentially preventing mosquitoes from producing urine after they take a blood meal," said Denton, associate professor of Anesthesiology and Pharmacology.
According to Denton, in taking a blood meal mosquitoes can double or even triple their body weight.
Besides providing nutrients, blood meals carry toxic salts; the potassium chloride lurking in red blood cells, if not quickly voided, can depolarize cell membrane potentials and kill straightaway.
"So they've evolved a rapid diuretic process to very quickly separate the salt water from all the nutrients that they need for egg development. A lot of people don't realize that mosquitoes have kidneys, and when they take a blood meal from you they also urinate on you almost simultaneously.
"What our compounds do is stop urine production, so they swell up and can't volume regulate, and in some cases they just pop," he said.
Conventional mosquitocides cause death of males and females at all stages of mosquito development, and in doing so exert considerable selective pressure for the development of genetic resistance.
"By targeting blood feeding female mosquitoes, we predict that there will be less selective pressure for the emergence of resistant mutations," Denton said.
The investigators show VU041 to be effective when applied topically, which indicates that it potentially could be adapted as a sprayed insecticide. They also show that it doesn't harm honeybees.
Arrangements are underway to test VU041 in a spray formulation. If that's successful, additional safety testing would be needed before deciding about commercial development, Denton said.
###
Denton and Piermarini are joined in the study by former Vanderbilt research fellow Daniel Swale, Ph.D., now a faculty member at Louisiana State University, and colleagues from Ohio State, Vanderbilt, the University of Florida and the University of Nebraska Medical Center.
Other Vanderbilt participants in the study include Darren Engers, Ph.D., Sean Bollinger and Emily Days.
The study was funded in part by a grant (DK082884) from the National Institutes of Health.
Media Contact
Craig Boerner
[email protected]
615-322-4747
http://www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/npa
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag