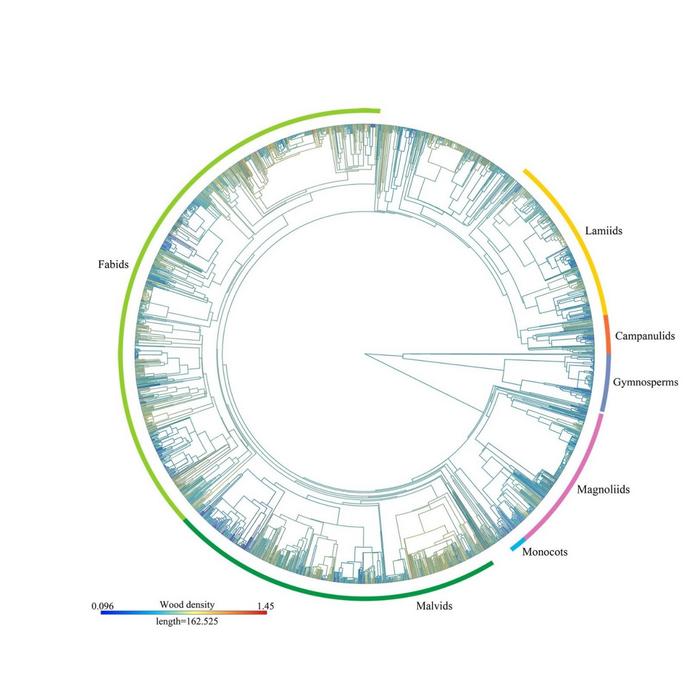
Ecology and evolutionary biology suggest that closely related species are more likely to exhibit morphological and functional similarities compared to distantly related species. Each tree species represents a unique genetic reservoir and is a product of long-term evolutionary processes, with specific morphological structures and functional traits. However, previous studies have overlooked the relationship between the allometric biomass and wood density and phylogeny.
Credit: Li, F. et al.
Ecology and evolutionary biology suggest that closely related species are more likely to exhibit morphological and functional similarities compared to distantly related species. Each tree species represents a unique genetic reservoir and is a product of long-term evolutionary processes, with specific morphological structures and functional traits. However, previous studies have overlooked the relationship between the allometric biomass and wood density and phylogeny.
To that end, our study utilized a comprehensive global dataset to show that phylogeny plays a significant role in shaping wood density patterns. We assessed phylogenetic signal in different taxonomic (e.g., angiosperms and gymnosperms) and ecological (e.g., tropical, temperate, and boreal) groups of tree species, explored the biogeographical and phylogenetic patterns of wood density, and quantified the relative importance of current environmental factors (e.g., climatic and soil variables) and evolutionary history (i.e., phylogenetic relatedness among species and lineages) in driving global wood density variation.
We found that wood density displayed a significant phylogenetic signal. Notably, wood density differed among different biomes and climatic zones, with higher mean values of wood density in relatively drier regions (highest in subtropical desert).
Our study, published in the KeAi journal Plant Diversity, revealed that at a global scale, for angiosperms and gymnosperms combined, phylogeny and species (representing the variance explained by taxonomy and not direct explained by long-term evolution process) accounted for 84.3% and 7.7% of total wood density variation, respectively. In contrast, current environmental factors accounted for only 2.7% of total wood density variation. When analyzing angiosperms and gymnosperms separately, the breakdown of explained variation differed: 84.2%, 7.5% and 6.7% for angiosperms, and 45.7%, 21.3% and 18.6% for gymnosperms.
###
Contact the author: Xing-Zhao Huang, Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Forest Resources and Silviculture, [email protected]
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Journal
Plant Diversity
DOI
10.1016/j.pld.2024.04.002
Method of Research
Meta-analysis
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Evolutionary history shapes variation of wood density of tree species across the world
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.




