Credit: Tokyo Tech
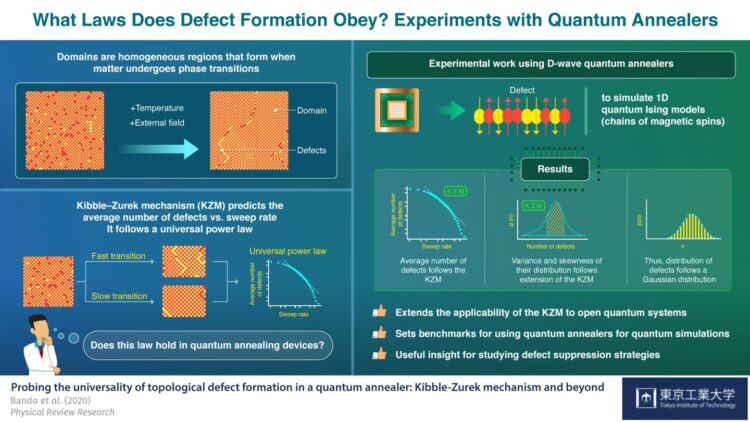
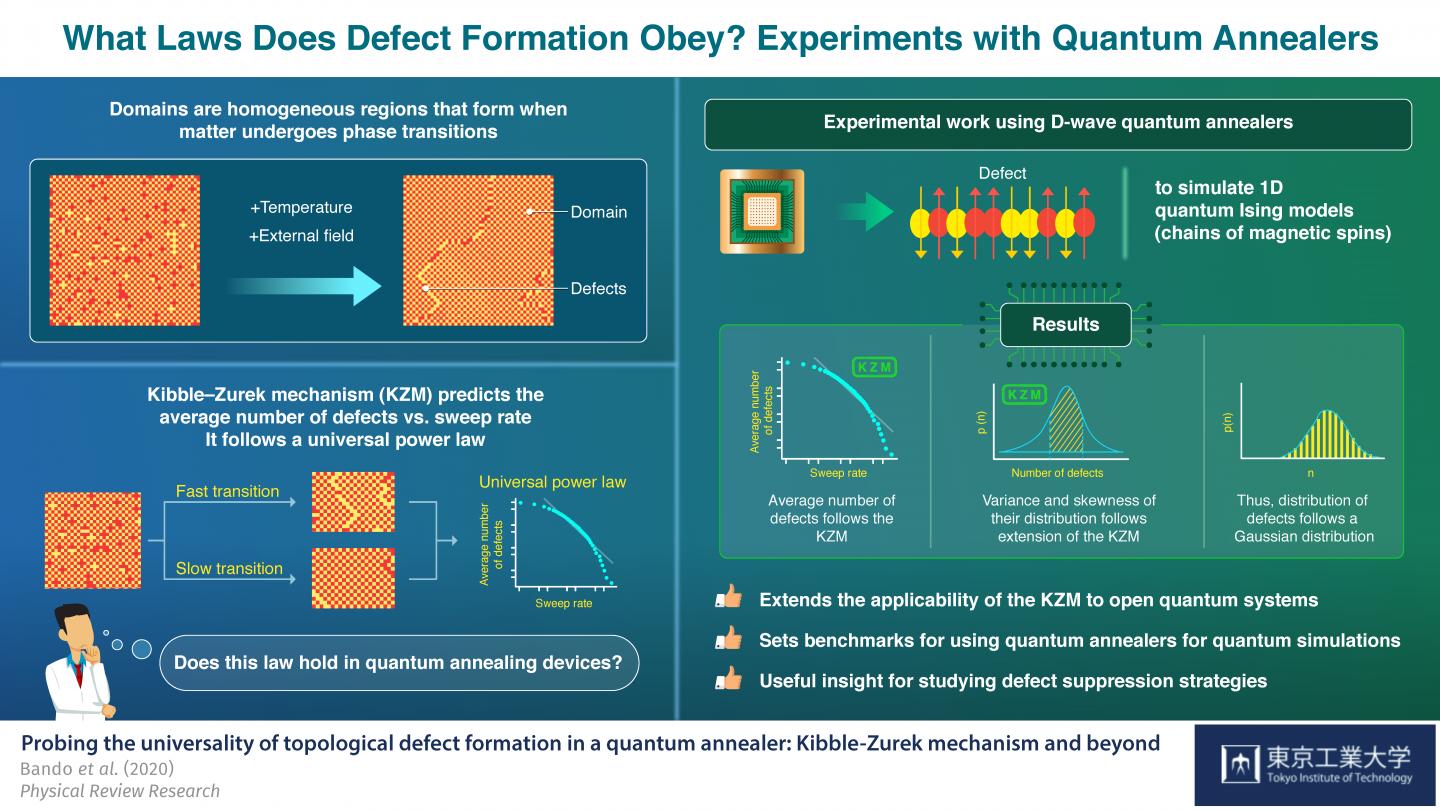
It is established that matter can transition between different phases when certain parameters, such as temperature, are changed. Although phase transitions are common (like water turning into ice in a freezer), the dynamics that govern these processes are highly complex and constitute a prominent problem in the field of nonequilibrium physics.
When a system undergoes a phase transition, matter in the new phase has many possible energetically equal “configurations” to adopt. In these cases, different parts of the system adopt different configurations over regions called “domains.” The interfaces between these domains are known as topological defects and reducing the number of these defects formed can be immensely valuable in many applications.
One common strategy to reduce defects is easing the system through the phase transition slowly. In fact, according to the “Kibble-Zurek” mechanism (KZM), it is predicted that the average number of defects and the driving time of the phase transition follow a universal power law. However, experimentally testing the KZM in a quantum system has remained a coveted goal.
In a recent study published in Physical Review Research, a team of scientists led by Professor Emeritus Hidetoshi Nishimori from Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan, probed the validity of the KZM in two commercially available quantum annealers, a type of quantum computer designed for solving complex optimization problems. These devices, known as D-Wave annealers, can recreate controllable quantum systems and control their evolution over time, providing a suitable experimental testbed for the KZM.
First, the scientists checked whether the “power law” between the average number of defects and the annealing time (driving time of the phase transition) predicted by the KZM held for a quantum magnetic system called the “one-dimensional transverse-field Ising model.” This model represents the orientations (spins) of a long chain of “magnetic dipoles,” where homogenous regions are separated by defects seen as neighboring spins pointing in incorrect directions.
While the original prediction of the KZM regarding the average number of defects was valid in this system, the scientists took it a step further: although this extension of the KZM was originally intended for a completely “isolated” quantum system unaffected by external parameters, they found good agreement between its predictions and their experimental results even in the D-Wave annealers, which are “open” quantum systems.
Excited by these results, Prof Nishimori remarks: “Our work provides the first experimental test of universal critical dynamics in a many-body open quantum system. It also constitutes the first test of certain physics beyond the original KZM, providing strong experimental evidence that the generalized theory holds beyond the regime of validity theoretically established.”
This study showcases the potential of quantum annealers to perform simulations of quantum systems and also helps gain insight on other areas of physics. In this regard, Prof Nishimori states: “Our results leverage quantum annealing devices as platforms to test and explore the frontiers of nonequilibrium physics. We hope our work will motivate further research combining quantum annealing and other universal principles in nonequilibrium physics.” Hopefully, this study will also promote the use of quantum annealers in experimental physics. After all, who doesn’t love finding a new use for a tool?
###
Media Contact
Kazuhide Hasegawa
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.