Credit: Hitoshi Matsui
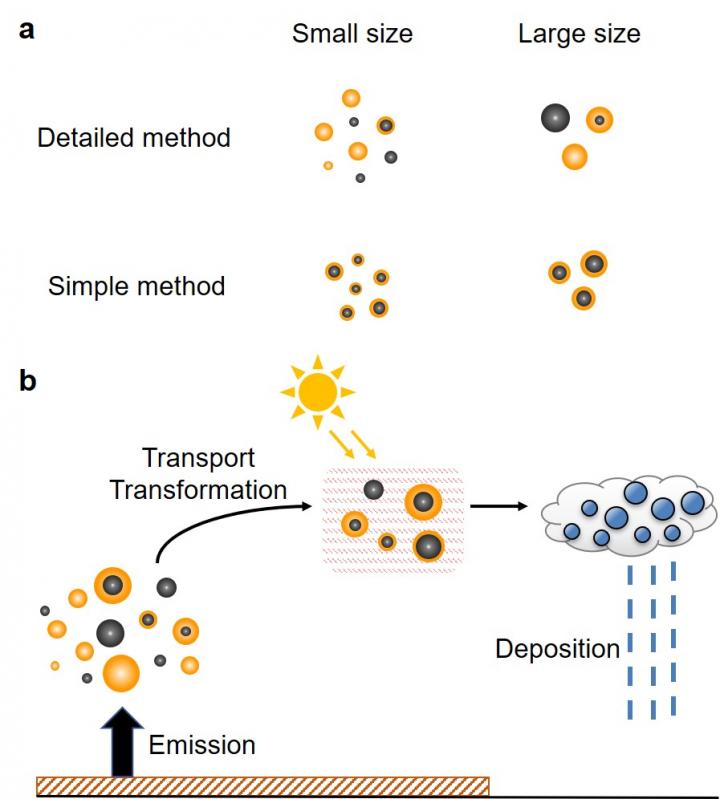
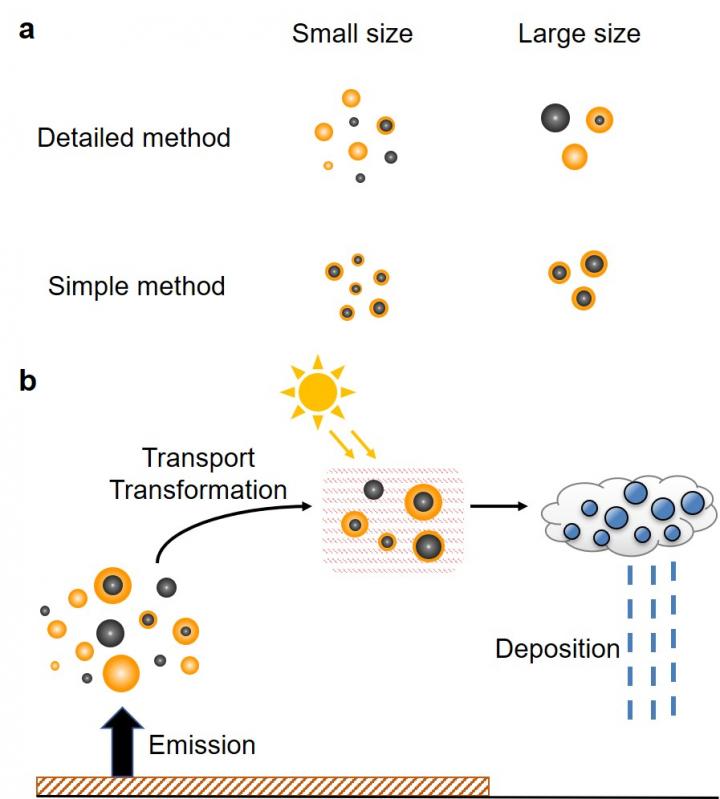
Nagoya, Japan – Black carbon refers to tiny carbon particles that form during incomplete combustion of carbon-based fuels. Black carbon particles absorb sunlight, so they are considered to contribute to global warming. However, the contribution of black carbon to the heating of the Earth's atmosphere is currently uncertain. Models that can accurately assess the warming effect of black carbon on our atmosphere are needed so that we can understand the contribution of these tiny carbon particles to climate change. The mixing state of black carbon particles and their particle size strongly influence their ability to absorb sunlight, but current models have large uncertainties associated with both particle size and mixing state.
Researchers from Nagoya and Cornell Universities have combined their expertise to develop a model that can predict the direct radiative effect of black carbon with high accuracy. The team achieved such a model by considering various particle sizes and mixing states of black carbon particles in air.
"Most aerosol models are using one or two black carbon mixing states, which are not sufficient to accurately describe the mixing state diversity of black carbon in air," says Hitoshi Matsui. "Our model considers that black carbon particles have multiple mixing states in air. As a result, we can model the ability of black carbon particles to heat air more accurately than in previous estimates."
The researchers found that the direct radiative effect of black carbon predicted by their model was highly sensitive to the particle size distribution only when the complex mixing states of black carbon were suitably described.
High sensitivity was obtained by the developed model because it calculated factors like the lifetime of black carbon in the atmosphere, the ability of black carbon to absorb sunlight, and the effect of materials coating the black carbon particles on their ability to absorb sunlight realistically. All of these factors are influenced by the particle size and mixing state of black carbon.
The results show that properly describing the particle size and mixing state of black carbon is very important to understand the contribution of black carbon to climate change.
The team's results suggest that the interactions of black carbon with atmospheric and rain patterns are likely to be more complex than previously considered. The developed model improves our ability to estimate the effectiveness of removing black carbon from the atmosphere to suppress future changes in temperature, which should help to direct research on strategies to mitigate climate change.
###
The article "Black carbon radiative effects highly sensitive to emitted particle size when resolving mixing-state diversity" is freely available from Nature Communications at DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05635-1
Media Contact
Sebastian Eifrid
[email protected]
@NU__Research
http://www.nagoya-u.ac.jp/en/
Original Source
http://en.nagoya-u.ac.jp/research/activities/news/2018/09/09112018-env.html http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05635-1