Skin loses collagen and elastin and becomes progressively thinner with age leading to wrinkles, so reversing this age-related loss of skin density is the holy grail of anti-aging treatments. One compound capable of doing that is the naturally occurring peptide GHK-Cu (GHK from glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine bound to a copper ion), which affects 31.2% of the human genes by either activating or deactivating them (based on a criterion of a reduction or increment in gene activity of more than 50%), meaning that it works by inducing epigenetic alterations in the cells.
Credit: © 2023 Yuvan Research Inc.
Skin loses collagen and elastin and becomes progressively thinner with age leading to wrinkles, so reversing this age-related loss of skin density is the holy grail of anti-aging treatments. One compound capable of doing that is the naturally occurring peptide GHK-Cu (GHK from glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine bound to a copper ion), which affects 31.2% of the human genes by either activating or deactivating them (based on a criterion of a reduction or increment in gene activity of more than 50%), meaning that it works by inducing epigenetic alterations in the cells.
Exploiting these properties has been limited, to date, secondary to the difficulty in achieving adequate skin penetration of the compound. Yuvan Research Inc. (a California-based longevity biotech start-up), has developed novel formulation with pharmaceutical grade excipients (aids to skin penetration) that appears to have overcome this hurdle.
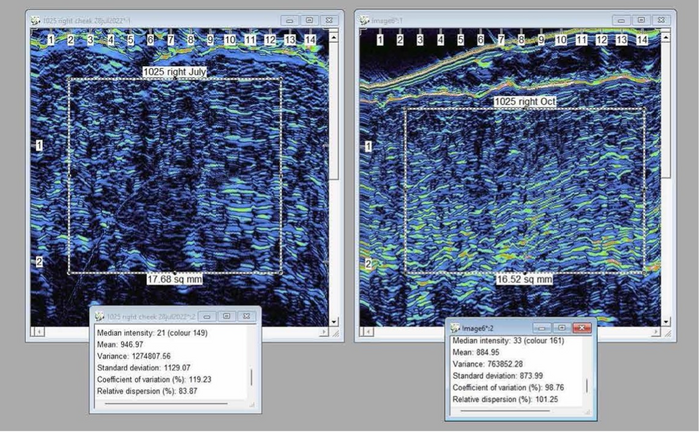
A clinical study conducted by Wayne Carey, MD, Professor of Dermatology McGill University (Canada), evaluated 21 subjects utilizing this formulation for 3 months, using pre and post ultra-high resolution ultrasound imaging of the facial skin. There was an average of 28% increase in subdermal echogenic density (which correlates with collagen/elastin elements). The top quartile of participants demonstrated an average of 51% improvement in collagen over 3 months.
High resolution dermal ultrasound equipment is a state of the art imaging modality that allows the visualization of near microscopic skin elements.
Although GHK-Cu was discovered in 1973, it was only recently that biomedical technology advanced to the point where the epigenetic modulation caused by it could be identified. After the sequencing of the human genome, in the early 2000s, the Broad Institute launched in 2010 the Connectivity Map, where numerous compounds were analyzed to find out what was their influence on the expression of genes. It was then that became evident the effect that GHK-Cu had on changing the human cellular phenotype by resetting the cells to a younger and healthier state.
YUVAN RESEARCH’s novel formulation of GHK-Cu (patent protected) provides greater stability to the compound and facilitates its transdermal delivery. According to Akshay Sanghavi, CEO and co-founder of Yuvan Research, “It is very rare to see a skin care product whose efficacy is proven by an Investigational Review Board – approved human clinical trial, conducted by a world class investigator at a renowned institution.”
YUVAN’s cofounder is Dr. Harold Katcher, a leading researcher in the rejuvenation science field. “Dr. Katcher believes that we must always have the conviction of scientific evidence before making any product available.”, says Sanghavi.
The discoverer of GHK-Cu, Dr. Loren Pickart, has previously highlighted system wide tissue repairs and physiologic improvements in skin, lung, liver, boney structures, and connective tissues in his research papers. Additionally, the peptide was also found to possess powerful cell-protective actions, such as anti-cancer activities and anti-inflammatory actions mediated through improved fibroblast activity and suppression of damaging inflammatory molecule production. Improved DNA repair and improved proteasome function are also other mechanisms of action.
The GHK-Cu-based gel used by Yuvan Research in the clinical trial is called “Neel” (www.Neelgel.com), which means “powerful blue” in Sanskrit, because of its natural blue color. Also, Neel gel is now available on Amazon.com and also it’s website neelgel.com.
In recent years, epigenetics has been gaining more and more relevance in the biomedical research environment by proving to be an essential determinant of human health, as well as a potential intervention mechanism. Thus, it became evident that human cells, and the organism as a whole, have intrinsic and natural repair mechanisms that, if activated, can be much more efficient than artificial therapies. GHK-Cu is one of the most powerful peptides in our body that goes down with age, and now this clinical study brings empirical evidence of improved collagen density by providing the skin with GHK-Cu in a stable and skin penetrating formulation.
Media contact:
Dharaa Suresha
Yuvan Research Inc.
Method of Research
Randomized controlled/clinical trial
Subject of Research
People




