Hamilton, ON (April 14, 2022) – A study at McMaster University has found that brown adipose tissue (BAT) is less active in boys with obesity compared to boys with a normal body mass index (BMI).
Credit: McMaster University
Hamilton, ON (April 14, 2022) – A study at McMaster University has found that brown adipose tissue (BAT) is less active in boys with obesity compared to boys with a normal body mass index (BMI).
Senior author Katherine Morrison said that BAT, also known as brown fat, helps the body burn regular fat and is activated by cold, but her research team noticed reduced BAT activity in the boys with obesity in response to a cold stimulus.
The researchers of McMaster’s Centre for Metabolism, Obesity and Diabetes Research performed MRI scans to measure BAT activity in 26 boys between the ages of eight and 10. They studied the BAT tissue in the neck before and after one hour of exposure to a cold suit set at a temperature of 18 degrees Celsius. The patient sample included 13 boys with a normal BMI and the same number again with obesity, in the first study of its kind in children.
“The promise of this study is that if we can better understand BAT and how to mimic or stimulate its effects, it might offer us new therapies to treat obesity,” said Morrison, a professor in the university’s Department of Pediatrics and pediatrician at the McMaster Children’s Hospital.
“Beyond helping families improve their nutrition, physical activity, and sleep, we have few treatments to assist children and adolescents with obesity. There are new medications that reduce appetite used in some adolescents. Investigating BAT activity holds out the hope of developing a new class of drugs that increase the amount of energy you burn.”
However, Morrison said that it is still unknown whether a lack of BAT activity causes obesity, or if the condition simply impairs brown fat’s ability to burn energy.
She said that newborn babies have large amounts of BAT, but it steadily decreases through childhood, so that by adulthood it is mostly present only in the neck region. The reason for decreasing brown fat levels in children remains unknown.
Morrison said her team used MRI scans to measure BAT activity as it did not expose the boys to ionizing radiation, unlike CT or PET scans. This potential safety risk has impeded research in children until now.
This study was funded by an internal grant from the Boris Family and external funding for the study was provided by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
-30-
Editors:
The paper is available at https://bit.ly/3jF1fnG
An MRI scan is attached.
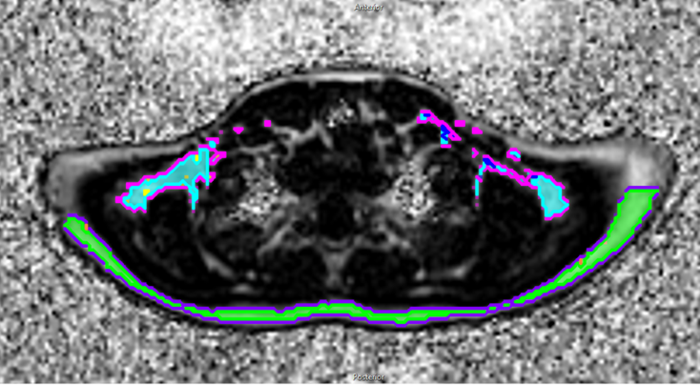
Cutline: MRI image of brown fat in the posterior neck (the area in teal blue outlined in pink) Credit: McMaster University
A photo of Katherine Morrison is also attached.
For information, please contact:
Veronica McGuire
Media Relations
Faculty of Health Sciences
McMaster University
289-776-6952
Journal
Diabetes
DOI
10.2337/db21-0799
Method of Research
Imaging analysis
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Impaired Cold Stimulated Supraclavicular Brown Adipose Tissue Activity in Young Boys with Obesity
Article Publication Date
16-Mar-2022
COI Statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest related to this article.




