Credit: Ulf Andersson Vang Ørom
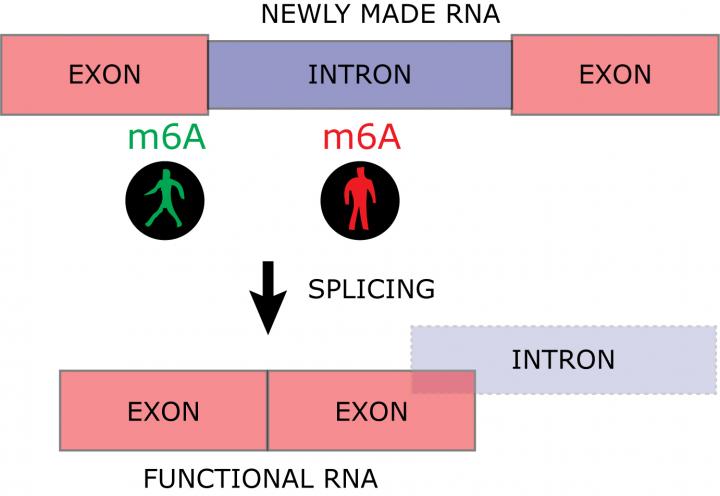
RNA modifications can encrypt the RNA code and are responsible for a very sophisticated control of RNA function. A Danish-German research team has shown that modified RNA bases have a great impact on the dynamics of gene expression from DNA to functional RNA. The study yields important new insight into how the basis of RNA modifications can affect the function of mature RNA molecules. The genetic material, DNA, is located in the cell nucleus where gene expression is controlled. DNA is copied into the less stable RNA for translation into protein in the cytoplasm (mRNA or protein-coding RNA) or for mediating independent functions as non-coding RNA. RNA is processed through several maturation steps to ensure its proper expression and localization. One of these maturation steps is called splicing. The non-functional introns are excised from the newly made RNA in the splicing process to build a mature and functional RNA consisting of exons only (Figure 2).
RNA is composed of four bases (abbreviated A, U, G and C), thereby disseminating its message with a fairly simple code. In recent years, research has shown an unprecedented impact of RNA modifications at all steps of the maturation process. More than a hundred RNA modifications have been identified with roles in both inhibiting and facilitating binding to proteins, DNA and other RNA molecules. This encryption by RNA modification is a way to prevent the message of the RNA in being read by the wrong recipients.
The research-team has focused on the RNA-modification m6A and shown that RNA can be labeled with this modification while being copied from DNA. The work has been possible thanks to a newly developed technique, TNT-sequencing, that labels newly made RNA for purification from the entire cellular RNA pool. The part of the newly made RNA labeled with m6A can subsequently be isolated using antibodies. The results demonstrate that an m6A positioned at an exon next to an intron increases the RNA maturation process, while m6A within the introns slows down the maturation of RNA (Figure 2).
The novelty of the study is that m6A has primarily been considered a label put on mature and functional RNA, and the results therefore expand our understanding of the role of RNA-modifications in RNA production and function.
The research has been carried out by researchers from Aarhus University's Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics in Berlin and the Max Delbrück Center in Berlin. Ulf Andersson Vang Ørom, Associate Professor at Aarhus University, has been in charge of the research team behind the study just published in the prestigious journal Cell Reports.
###
"Transient N-6-methyladenosine Transcriptome sequencing reveals a regulatory role of m6A in splicing efficiency". Annita Louloupi, Evgenia Ntini, Thomas Conrad and Ulf Andersson Vang Ørom. Cell Reports, 23 (2018) pp. 3429-3437.
For further information, please contact
Associate Professor Ulf Andersson Vang Ørom
Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics,
Aarhus University, Denmark
[email protected] – +45 22288766
Media Contact
Ulf Andersson Vang Ørom
[email protected]
45-22-28-87-66
@aarhusuni
http://www.au.dk
Original Source
http://mbg.au.dk/en/news-and-events/news-item/artikel/encrypted-messages-in-biological-processes/ http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.05.077