“This study reflects transdisciplinary efforts to link aging and circadian biology in human-derived tissues, which is an understudied area of biology.”
Credit: 2024 Kapar et al.
“This study reflects transdisciplinary efforts to link aging and circadian biology in human-derived tissues, which is an understudied area of biology.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 16, 2024 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 1, entitled, “Effects of resveratrol on in vitro circadian clock gene expression in young and older human adipose-derived progenitor cells.”
Observational studies in preclinical models demonstrate age-related declines in circadian functions. In this new study, researchers Sophie G.C. Kapar, Maria F. Pino, Fanchao Yi, Miguel A. Gutierrez-Monreal, Karyn A. Esser, Lauren M. Sparks, and Melissa L. Erickson from AdventHealth and the University of Florida hypothesized that age would be associated with declines in function of cell-autonomous circadian clocks in human tissue.
“Accordingly, we cultured adipose progenitor cells (APCs) from previously collected white-adipose tissue biopsies from abdominal subcutaneous depots of young (Age: 23.4 ± 2.1 yrs) vs. older female participants (Age: 70.6 ± 5.9 yrs).”
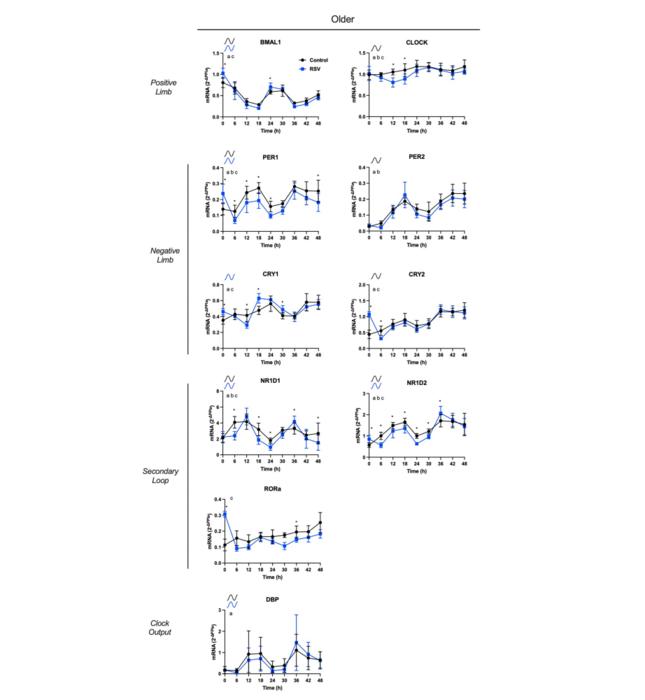
Using an in vitro model, the researchers compared rhythmic gene expression profiles of core clock components, as an indicator of circadian oscillatory function. They observed consistent circadian rhythmicity of core clock components in young and older-APCs. Expression analysis showed increased levels of some components in older-APCs (CLOCK, CRY1, NR1D1) vs. young.
The team also investigated resveratrol (RSV), a well-known longevity-enhancing effector, for its effects on rhythmic clock gene expression profiles. They found that RSV resulted in gained rhythmicity of some components (CLOCK and CRY), loss of rhythmicity in others (PER2, CRY2), and altered some rhythmic parameters (NR1D1 and NR1D2), consistent in young and older-APCs. The observation of detectable circadian rhythmicity retained in vitro suggests that the oscillatory function of the cell-autonomous core clock in APCs is preserved at this stage of the aging process.
“RSV impacts core clock gene expression in APCs, implicating its potential as a therapeutic agent for longevity by targeting the core clock.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205292
Corresponding Authors: Lauren M. Sparks, Melissa L. Erickson – [email protected], [email protected]
Keywords: circadian clock, circadian rhythm, aging, adipose-derived progenitor cells, resveratrol
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.205292
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging (Aging-US) publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- SoundCloud
- X, formerly known as Twitter
- YouTube
- LabTube
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.205292
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Effects of resveratrol on in vitro circadian clock gene expression in young and older human adipose-derived progenitor cells
Article Publication Date
6-Jan-2024




