Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have compared how well different Alzheimer’s biomarkers predict the progression of the disease and its effect on the memory. They found that early accumulation of tau proteins in the brain as measured by PET scanner was more effective at predicting memory impairment than biomarkers in the cerebrospinal fluid or amyloid plaque in the brain. The results are published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
Credit: Marco Bucci
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have compared how well different Alzheimer’s biomarkers predict the progression of the disease and its effect on the memory. They found that early accumulation of tau proteins in the brain as measured by PET scanner was more effective at predicting memory impairment than biomarkers in the cerebrospinal fluid or amyloid plaque in the brain. The results are published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
Over 50 million people around the world suffer from dementia. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia and is characterised by an accumulation of the proteins beta-amyloid (Ab) and tau in the brain, followed by a continuous progression in memory decline. The pathological progression can take different forms and it is difficult to predict how quickly the symptoms will develop in any particular individual. Moreover, the presence of Ab in a person’s brain – known as amyloid plaque – does not necessarily mean that the he or she will develop Alzheimer’s dementia.
“There’s been a rapid development of different Alzheimer’s biomarkers in recent years, enabling us to measure and detect early signs of the disease in patients,” says the study’s first author Marco Bucci, researcher at the Center for Alzheimer Research, part of the Department of Neurobiology, Care Sciences and Society, Karolinska Institutet. “But we still need to find tests that can predict the development of the disease with greater specificity, so that we can improve not only its diagnosis but also its prognosis and treatment.”
Some biomarkers identify accumulations of Aβ or tau, while others are used to measure the loss of nerve function (neurodegeneration). Protein accumulation and neurodegeneration can be measured in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma, or through brain imaging using positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Current guidelines for the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease with biomarkers endorse the interchangeability of brain imaging methods and analyses of CSF biomarkers (pTau and Ab), but this has been mooted. There is also a lack of longitudinal studies showing how the biomarkers are linked to gradual cognitive impairment.
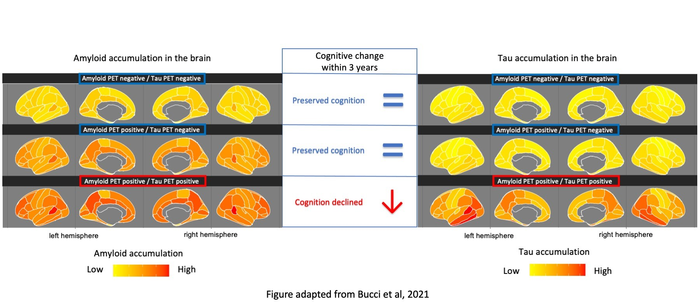
“Our study shows that the presence of amyloid plaque in the brain and changes in concentrations of Ab and pTau in the CSF can be detected early during the course of the disease, but they do not seem to have any correlation with later memory loss,” says Dr Bucci. “However, our results show that the presence of tau in the brain measured by a PET scanner is linked to a rapid decline, especially of the episodic memory, which is often affected at an early stage of the disease. Our observation suggests that tau PET should be recommended for the clinical prognostic assessment of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s patients.”
The results are based on brain imaging (PET and MRI) and CSF analyses in a group of 282 participants comprising people with mild cognitive impairment, people with Alzheimer’s dementia and healthy controls. 213 of the participants were also monitored for three years with tests of episodic memory (i.e. short term memory related to daily events).
“Our findings show that the concentration of tau in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease plays an important part in its pathological progression and may become a key target for future drug treatments,” says principal investigator Agneta Nordberg, professor at the Center for Alzheimer Research, Karolinska Institutet.
The study was financed by the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research, the Swedish Research Council, Region Stockholm, the Swedish Brain Fund, the Swedish Alzheimer’s Foundation, the Centre for Innovative Medicine and the Swedish Society for Medical Research. There are no reported conflicts of interest.
Publication: “Alzheimer’s disease profiled by fluid and imaging markers: Tau PET best predicts cognitive decline”, Marco Bucci, Konstantinos Chiotis & Agneta Nordberg for the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Molecular Psychiatry, online 1 October 2021, doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01263-2.
Journal
Molecular Psychiatry
DOI
10.1038/s41380-021-01263-2
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Alzheimer’s disease profiled by fluid and imaging markers: Tau PET best predicts cognitive decline
Article Publication Date
1-Oct-2021




