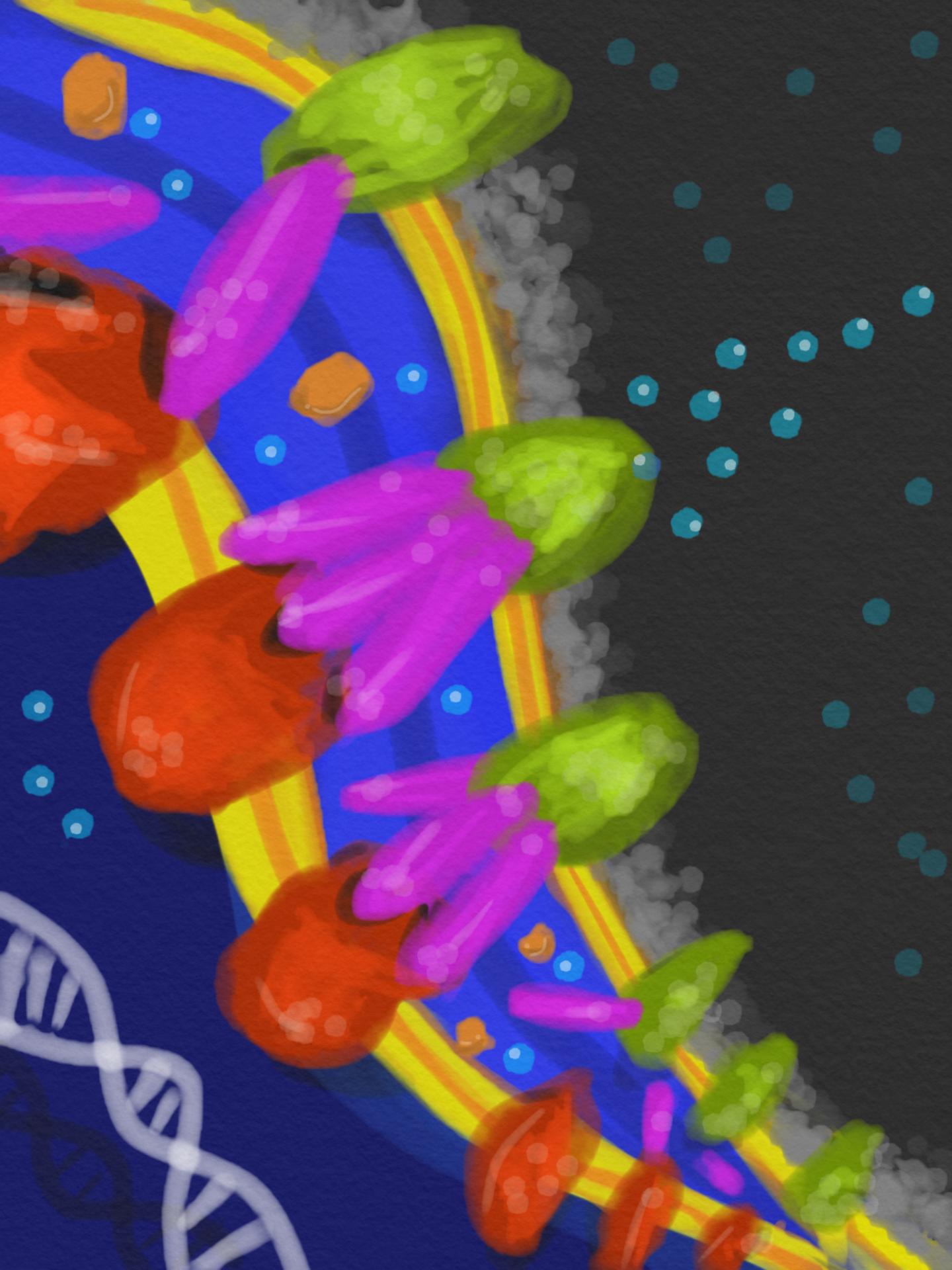
Credit: Ace George Santiago, Cornell University
By tagging a cell's proteins with fluorescent beacons, Cornell researchers have found out how E. coli bacteria defend themselves against antibiotics and other poisons. Probably not good news for the bacteria.
When undesirable molecules show up, the bacterial cell opens a tunnel though its cell wall and "effluxes," or pumps out, the intruders.
"Dynamic assembly of these tunnels has long been hypothesized," said Peng Chen, professor of chemistry and chemical biology. "Now we see them."
The findings could lead to ways to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria with a "cocktail" of drugs, he suggests: "One is to inhibit the assembly of the tunnel, the next is to kill the bacteria."
To study bacteria's defensive process, Chen and colleagues at Cornell selected a strain of E. coli known to pump out copper atoms that would otherwise poison the bacteria. The researchers genetically engineered it, adding to the DNA that codes for a defensive protein an additional DNA sequence that codes for a fluorescent molecule.
Under a powerful microscope, they exposed a bacterial cell to an environment containing copper atoms and periodically zapped the cell with an infrared laser to induce fluorescence. Following the blinking lights, they had a "movie" showing where the tagged protein traveled in the cell. They further genetically engineered the various proteins to turn their metal-binding capability on and off, and observed the effects.
Their research was reported in the Early Online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences the week of June 12. The Cornell researchers also collaborated with scientists at the University of Houston, the University of Arizona and the University of California, Los Angeles.
The key protein, known as CusB, resides in the periplasm, the space between the inner and outer membranes that make up the bacteria's cell wall. When CusB binds to an intruder – in this experiment, a copper atom – that has passed through the porous outer membrane, it changes its shape so that it will attach itself between two related proteins in the inner and outer membranes to form a complex known as CusCBA that acts as a tunnel through the cell wall. The inner protein has a mechanism to grab the intruder and push it through.
The tunnel locks the inner and outer membranes together, making the periplasm less flexible and interfering with its normal functions. The ability to assemble the tunnel only when needed, rather than having it permanently in place, gives the cell an advantage, the researchers point out.
This mechanism for defending against toxic metals may also explain how bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics, by mutating their defensive proteins to recognize them. Similar mechanisms may be found in other species of bacteria, the researchers suggested.
###
The work was supported by the Army Research Office and the National Institutes of Health.
Media Contact
Daryl Lovell
[email protected]
607-592-3925
@cornell
http://pressoffice.cornell.edu
Original Source
http://news.cornell.edu/stories/2017/06/e-coli-bacterias-defense-secret-revealed
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag