Seawater could be the perfect stockfeed for sustainable fuel: it is renewable, abundant, economic and contains exactly the right ingredients to produce high-quality hydrogen. The drawback is that it contains less-desirable ingredients, such as chlorine, that hinder the conversion technology. An international research team may have developed an alternative processing platform that reaps all the benefits without the chlorine-caused problems of previous attempts.
Credit: Nano Research Energy
Seawater could be the perfect stockfeed for sustainable fuel: it is renewable, abundant, economic and contains exactly the right ingredients to produce high-quality hydrogen. The drawback is that it contains less-desirable ingredients, such as chlorine, that hinder the conversion technology. An international research team may have developed an alternative processing platform that reaps all the benefits without the chlorine-caused problems of previous attempts.
They published their results on Sept. 06, 2022 in Nano Research Energy.
“Seawater electrolysis is an extremely attractive approach for harvesting clean hydrogen energy, but detrimental chlorines species, such as chloride or hypochlorite, cause severe corrosion at the anode,” said corresponding author Xuping Sun, professor at the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China and at the Shandong Normal University.
Electrolysis involves applying an electric charge to water and splitting its constituents, producing hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen can be used as clean fuel that emits only water as it burns, instead of the harmful carbon dioxide released by fossil fuels. The cathode, or negative electrode, attracts the OH– and helps them reduce into the target molecules of two hydrogen atoms. Simultaneously, the anode, or positive electrode, pulls the negatively charged molecules and gives them electrons, causing them to oxidize. In seawater electrolysis, however, the anode also attracts negatively charged chlorine elements, which compete with the OH– and can corrode the electrode beyond use.
The electrodes used in electrolysis can be made of a variety of noble-metal oxides, oxides without noble metals, and multimetallic oxides, according to Sun, but almost all result in the same competition and corrosion issues with chloride.
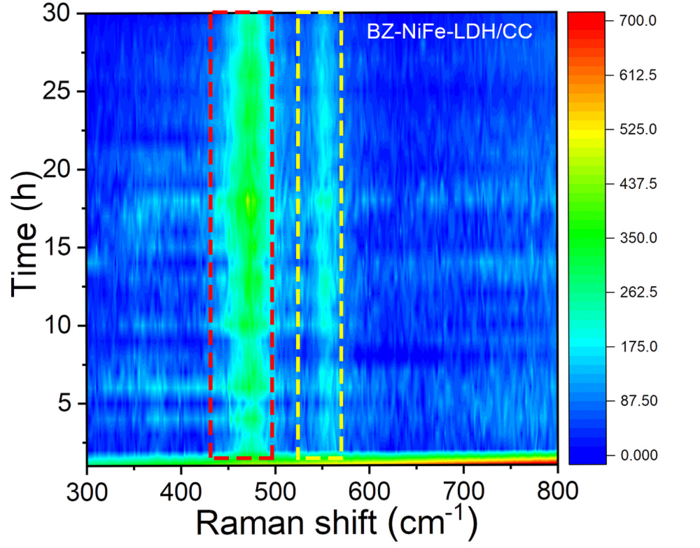
“Among the material options, layered double hydroxides are verified as a promising alternative for the desired reactions due to their tunable composition, lower costs and good catalytic activities,” Sun said.
Layered double hydroxides materials are brucite-like lamellar crystals composed of positive host layers and charge-balancing interlayers. These two layers sandwich water and the negatively attracted particles, such as chloride.
“Previous research in our group and others’ has demonstrated that nickel-iron layered double hydrides offer promising catalytic activity and selective oxidation reactions, but the service life of the material requires improvement,” Sun said. “This could be done by inhibiting side reactions, such as chloride corrosion, and improving the exchange of OH–, but long-term stability of at least 100 hours for a large current density has rarely been achieved on this material.”
To achieve a more stable electrode, the researchers developed a nickel-iron layered double hydride array on carbon cloth, with benzoate — best known as a food preservative when used with sodium — particles inserted into the layers.
“In this work, we report that the approach achieves efficient and stable seawater oxidation electrolysis,” Sun said. “Interestingly, the negatively charged benzoate ions not only act as a corrosion inhibitor with resistance against detrimental chlorine (electro)chemistry but as a proton acceptor to alleviate the local solution pH drop around the layered double hydrides electrode.”
In addition, the benzoate ions also expand the interlayer spacing of the material, enabling electrolytes to penetrate and diffuse through it. The platform can perform satisfactory electrolysis uninterrupted for 100 hours without suffering obvious structural change, according to Sun.
“This design successfully achieves the multiple needs of an anode toward efficient and stable seawater oxidation,” Sun said. “This work not only provides us with a robust catalyst for high-active seawater oxidation electrolysis, but also may open an exciting avenue to the surface engineering of anodic catalyst materials with enhanced durability.”
Other contributors include co-corresponding author Xiaodong Guo, Sichuan University; Longcheng Zhang, Jie Liang, Luchao Yue, Kai Dong, Jun Li, Donglin Zhao, Zerong Li, Shengjun Sun and Yongsong Luo, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China; Qian Liu, Chengdu University; Guanwei Cui, Shandong Normal University; and Abdulmohsen Ali Alshehri, King Abdulaziz University. Zhang is also affiliated with Sichuan University.
The National Natural Science Foundation of China supported this work.
##
About Nano Research Energy
Nano Research Energy is launched by Tsinghua University Press, aiming at being an international, open-access and interdisciplinary journal. We will publish research on cutting-edge advanced nanomaterials and nanotechnology for energy. It is dedicated to exploring various aspects of energy-related research that utilizes nanomaterials and nanotechnology, including but not limited to energy generation, conversion, storage, conservation, clean energy, etc. Nano Research Energy will publish four types of manuscripts, that is, Communications, Research Articles, Reviews, and Perspectives in an open-access form.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is a professional open access resource for discovery of scientific and technical content published by the Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners, providing the scholarly publishing community with innovative technology and market-leading capabilities. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, and identity management and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development by offering a range of options across all functions as Journal Layout, Production Services, Editorial Services, Marketing and Promotions, Online Functionality, etc. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
Journal
Nano Research Energy
DOI
10.26599/NRE.2022.9120028
Article Title
Benzoate anions-intercalated NiFe-layered double hydroxide nanosheet array with enhanced stability for electrochemical seawater oxidation
Article Publication Date
6-Sep-2022




