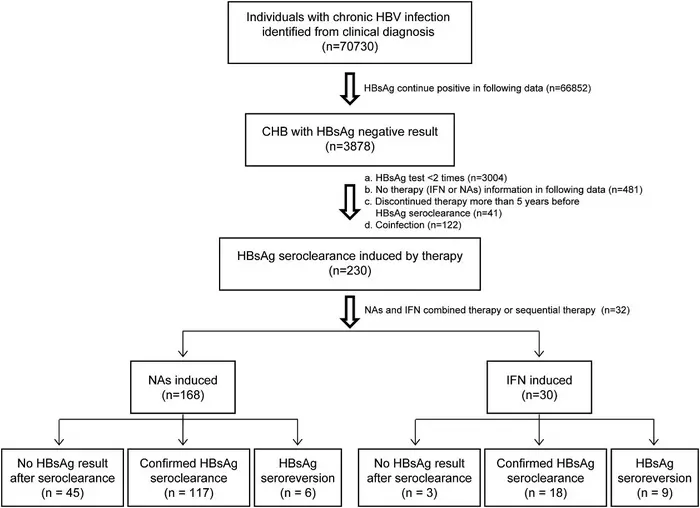
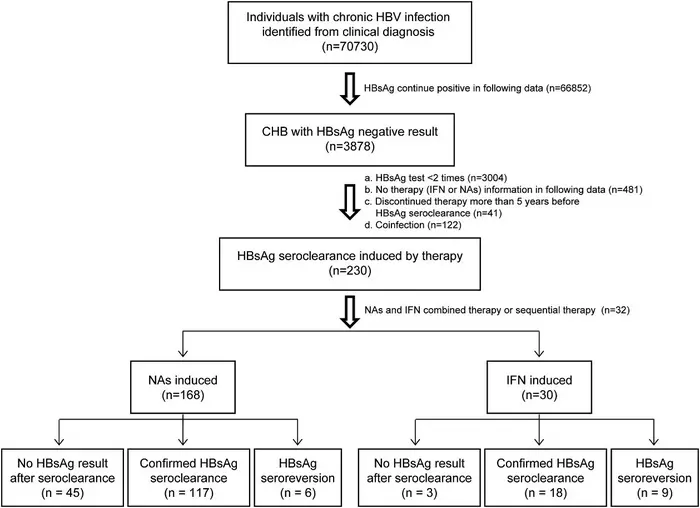
In a study published in the journal Genes & Diseases, researchers from The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University analyzed data from an extensive dataset comprising over 70,000 HBsAg-positive individuals at The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University. They compared two groups: those achieving HBsAg seroclearance through NAs monotherapy (168 patients) and those through IFN monotherapy (30 patients). NAs monotherapy patients were older, with a higher proportion achieving HBsAg seroclearance during treatment (48.8% vs. 30.0%). They also had a more favorable immune response, with a higher percentage developing concomitant anti-HBs. The NAs-monotherapy group had more individuals with normal ALT levels (78.6% vs. 40.0%). The time to achieve HBsAg seroclearance and therapy duration were similar between the groups, but NAs monotherapy showed a trend towards longer times. During follow-up, patients on NAs monotherapy had a significantly lower rate of HBsAg seroreversion compared to IFN monotherapy patients (4.9% vs. 33.3%). The one-year and three-year probabilities of confirmed HBsAg seroclearance were significantly higher with NAs therapy (one-year: 0.960 vs. 0.691; three-year: 0.931 vs. 0.641), indicating a more sustained functional cure. NAs monotherapy was independently associated with a lower risk of HBsAg seroreversion. Most patients experienced HBsAg seroreversion within the first year after seroclearance. IFN monotherapy patients with positive anti-HBs had a higher probability of confirmed HBsAg seroclearance during follow-up, while this difference was not seen in NAs monotherapy patients. This study provides valuable insights into the durability of HBsAg seroclearance induced by NAs or IFN monotherapy, with NAs monotherapy showing better outcomes and lower risk of recurrence. Age and ALT levels were also identified as factors associated with HBsAg seroreversion. Understanding these findings can guide clinicians in making informed treatment decisions for patients with chronic Hepatitis B, ensuring better clinical outcomes.
Credit: Genes & Diseases
In a study published in the journal Genes & Diseases, researchers from The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University analyzed data from an extensive dataset comprising over 70,000 HBsAg-positive individuals at The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University. They compared two groups: those achieving HBsAg seroclearance through NAs monotherapy (168 patients) and those through IFN monotherapy (30 patients). NAs monotherapy patients were older, with a higher proportion achieving HBsAg seroclearance during treatment (48.8% vs. 30.0%). They also had a more favorable immune response, with a higher percentage developing concomitant anti-HBs. The NAs-monotherapy group had more individuals with normal ALT levels (78.6% vs. 40.0%). The time to achieve HBsAg seroclearance and therapy duration were similar between the groups, but NAs monotherapy showed a trend towards longer times. During follow-up, patients on NAs monotherapy had a significantly lower rate of HBsAg seroreversion compared to IFN monotherapy patients (4.9% vs. 33.3%). The one-year and three-year probabilities of confirmed HBsAg seroclearance were significantly higher with NAs therapy (one-year: 0.960 vs. 0.691; three-year: 0.931 vs. 0.641), indicating a more sustained functional cure. NAs monotherapy was independently associated with a lower risk of HBsAg seroreversion. Most patients experienced HBsAg seroreversion within the first year after seroclearance. IFN monotherapy patients with positive anti-HBs had a higher probability of confirmed HBsAg seroclearance during follow-up, while this difference was not seen in NAs monotherapy patients. This study provides valuable insights into the durability of HBsAg seroclearance induced by NAs or IFN monotherapy, with NAs monotherapy showing better outcomes and lower risk of recurrence. Age and ALT levels were also identified as factors associated with HBsAg seroreversion. Understanding these findings can guide clinicians in making informed treatment decisions for patients with chronic Hepatitis B, ensuring better clinical outcomes.
The researchers anticipate that these findings will contribute to the development of more effective and personalized therapeutic strategies for CHB patients in the future. The study highlights the importance of continued research in this area and the potential for leveraging electronic health record data to gain deeper insights into disease management and treatment outcomes.
###
References
DOI
10.1016/j.gendis.2022.03.003
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2022.03.003
Funding information
Project from the Science & Technology Commission of Chongqing, China (cstc2018jcyjAX0027, cstc2018jscx-msybX0376, cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0159, and cstc2020jscx-dxwtBX0022), Chongqing Municipal Education Commission, China (KJQN201800422), Intelligent Medicine Project from Chongqing Medical University, China (ZHYX202028), 111 Project, China (D20028), National Key Research and Development Project, China (2018YFE0107500), Chongqing Talents Program, China (CQYC202005013).
About Genes & Diseases
Genes & Diseases is a journal for molecular and translational medicine. The journal primarily focuses on publishing investigations on the molecular bases and experimental therapeutics of human diseases. Publication formats include full length research article, review article, short communication, correspondence, perspectives, commentary, views on news, and research watch.
Journal
Genes & Diseases
DOI
10.1016/j.gendis.2022.03.003
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Durability of Hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in patients experienced nucleoside analogs or interferon monotherapy: A real-world data from Electronic Health Record
Article Publication Date
29-May-2023
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests