Credit: COPYRIGHT (C) TOYOHASHI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
The research team at the Visual Perception and Cognition Laboratory of the Toyohashi University of Technology has revealed that face-likeness is judged by early visual processing at around 100ms after viewing an object. The present study focuses on the relation between face-likeness recognition and brain activity to suggest for the first time that face-likeness recognition is influenced by early visual processing. The results of the present study were published in the open access journal Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
Face-likeness recognition is the act of recognizing a non-face object as a human face. This phenomenon is called "pareidolia," and refers to "perceiving an inherently meaningless object such as a pattern, landscape or object as another object with meaning." Many spirit photographs rely on this phenomenon. While pareidolia has been argued to occur in relatively low-level visual processing, at what level of visual processing pareidolia actually occurs was never previously discerned.
Therefore, the research team of the Visual Perception and Cognition Laboratory at the Toyohashi University of Technology decided to study the relation between behavior when a face-like object is viewed and brain activity to reveal the level of visual processing at which face-likeness is recognized.
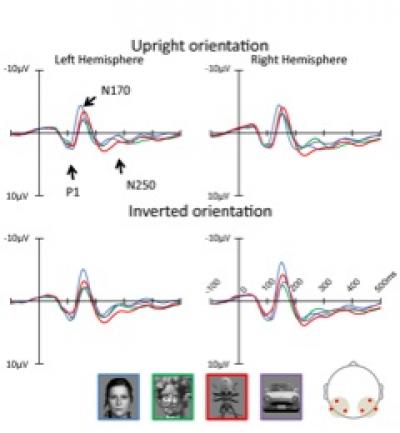
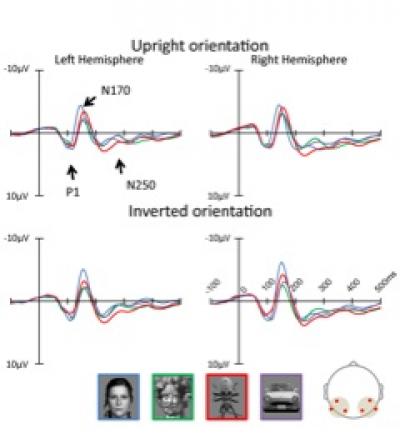
PhD student and lead author of the study Yuji Nihei explains that, "Visual processing of the human face is divided into three different stages. The first stage is early visual processing of roughly identifying the object. Then, if the object is a face, distinguishing the parts of the face (eyes, nose, mouth) from one another and processing the outline and parts of the face. Lastly, expression and individual differences are distinguished. We studied the relation between activity at these three stages of processing and the results of actual recognition and determined that face-likeness recognition occurs in the first stage of visual processing. This processing occurs at a speed of approximately 100ms after viewing an object, and so we believe that face-likeness processing occurs before we are aware of the object."
Associate Professor Minami Testuto, who leads the research team, says that, "While seeing face-likeness in various objects could be considered incorrect in terms of object recognition, we believe this is not just a mistake and actually makes us reconsider an important cognitive function. We would like to continue our study of face-likeness recognition from an objective approach."
The results of this study are believed to serve as a key to uncovering the mechanism of how humans recognize and distinguish between two types of information – "face-likeness" and objects. The results of the present study also suggest that "face-likeness" recognition occurs in early visual processing and that face-like objects are processed in the same manner as a human face in later stages. Due to this, we believe that face-likeness can be caused by an effect that gathers attention to the face, or some other like stimulus.
###
The present study was conducted with the assistance of Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research numbers A(26240043) and C(25330169) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The lead writer Yuji Nihei also received a grant as part of the Program for Leading Graduate Schools (R03) run by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Reference: Nihei, Y., Minami, T., Nakauchi, S., Brain Activity Related to the Judgment of Face-Likeness: Correlation between EEG and Face-Like Evaluation, Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2018.00056
Media Contact
Yuko Ito
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2018.00056