Utrecht, November 8, 2023 – Researchers from the Center for Translational Immunology at University Medical Center Utrecht (the Netherlands) have identified that a transient inflammatory pain causes mitochondrial and redox changes in sensory neurons that persist beyond pain resolution. These changes appear to predispose to a failure in resolution of pain caused by a subsequent inflammation. Additionally, targeting the cellular redox balance prevents and treats chronic inflammatory pain in rodents.
Credit: Cell Reports Medicine
Utrecht, November 8, 2023 – Researchers from the Center for Translational Immunology at University Medical Center Utrecht (the Netherlands) have identified that a transient inflammatory pain causes mitochondrial and redox changes in sensory neurons that persist beyond pain resolution. These changes appear to predispose to a failure in resolution of pain caused by a subsequent inflammation. Additionally, targeting the cellular redox balance prevents and treats chronic inflammatory pain in rodents.
Pain often persists in patients with an inflammatory disease, even after the inflammation has subsided. The molecular mechanisms leading to this failure in pain resolution and the transition from acute to chronic pain are poorly understood. For some time, there have been clues that mitochondrial dysfunction may be involved. In a clinical study, approximately 70 percent of patients with heritable mitochondrial diseases develop chronic pain. However, the exact role of mitochondria in the resolution of inflammatory pain is unclear.
Mitochondrial disturbances
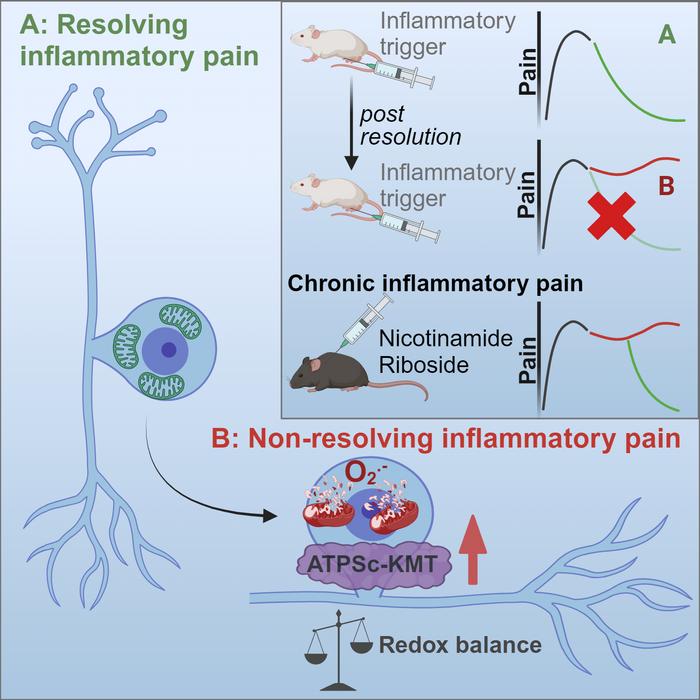
To unravel the role of mitochondria in pain resolution, Hanneke Willemen PhD in the research group lead by Niels Eijkelkamp PhD (Center for Translational Immunology, UMC Utrecht) used a model of hyperalgesic priming. In this model, a transient inflammation causes neuronal plasticity, which results in persistence of pain after a subsequent inflammatory stimulus; a perfect model to study what goes wrong during pain resolution. Hanneke and co-workers identified that hyperalgesic priming in mice causes mitochondrial and metabolic disturbances in sensory neurons. The investigators associate these disturbances with an increase in the expression of a mitochondrial protein (ATPSc-KMT) which in a previous study has been linked to chronic pain in patients. By using genetic and pharmacological approaches they showed that inhibit mitochondrial respiration, ATPSCKMT expression and supplementation of one of the affected metabolites restores resolution of inflammatory pain and prevents chronic pain development. The results of this study- which was performed with several collaborators, including the University of Oslo (Norway) – have been published this week in Cell Reports Medicine.
Hanneke Willemen concludes: “In our study we provide evidence that a peripheral inflammation induces persistent mitochondrial and metabolic changes in sensory neurons, which affects the ability of neurons to resolve from hyperalgesia induced by a subsequent inflammatory trigger. Thus, metabolic changes in sensory neurons result in failure of endogenous pain resolution pathways and drive the transition to chronic pain. Importantly, targeting mitochondrial respiration, scavenging reactive oxygen species or supplementation with nicotinamide riboside (vitamin B3) both represent potential therapeutic strategies to restore failing pain resolution pathways, thereby treating chronic inflammatory pain.”
Transition to chronic pain
Chronic pain is a leading cause of years lived in disability and impaired quality of life, yet treatment options are limited and often induce severe side effects. The current dogma is that pain resolution is the consequence of the dissipation of the drivers that induced the pain. However, in 12-30 percent of rheumatic arthritis patients pain persists while they have minimal joint inflammation or even are in remission. Accumulating evidence indicates that pain resolution after tissue damage or inflammation is not passive, but rather an active process that involves endogenous pain resolution mechanisms. Failing pain resolution pathways may lead to the transition from acute to chronic pain. Although the molecular mechanisms that contribute to failure in pain resolution are still poorly understood and need unraveling, this study fills a part of this void and identifies a potential therapeutic approach to promote pain resolution.
Publication
Willemen HLDM, Silva Santos Ribeiro P, Broeks M, Meijer N, Versteeg S, Tiggeler A, de Boer TP, Malecki JM, Falnes PØ, Jans J, Eijkelkamp N. Inflammation-induced mitochondrial and metabolic disturbances in sensory neurons control the switch from acute to chronic pain. Cell Reports Medicine 2023;4:101265.
Journal
Cell Reports Medicine
DOI
10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101265
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Inflammation-Induced Mitochondrial and Metabolic Disturbances in Sensory Neurons Control the Switch from Acute to Chronic Pain
Article Publication Date
8-Nov-2023
COI Statement
The authors declare no competing interests.




