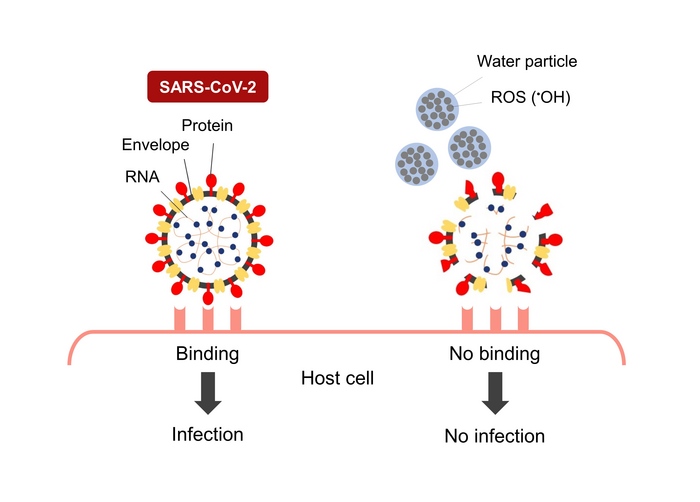
Current disinfection strategies have major drawbacks, which is why the World Health Organization does not advise routine spraying or fogging of biocidal agents, or UV light sterilization, in occupied areas. One possible alternative is nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles generated by an electrospray device developed by Panasonic Corporation. The water particles contain reactive oxygen species (ROS) that damage lipid, protein, and DNA and are reported to disinfect several bacterial and viral species.
Credit: Osaka Metropolitan University
Current disinfection strategies have major drawbacks, which is why the World Health Organization does not advise routine spraying or fogging of biocidal agents, or UV light sterilization, in occupied areas. One possible alternative is nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles generated by an electrospray device developed by Panasonic Corporation. The water particles contain reactive oxygen species (ROS) that damage lipid, protein, and DNA and are reported to disinfect several bacterial and viral species.
In their previous research, Associate Professor Yasugi’s team showed that nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles disinfect SARS-CoV-2, but the mechanism remained a mystery. Their new paper published in the Journal of Nanoparticle Research describes the damage they observed when SARS-CoV-2 was exposed to the nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles.
The researchers showed the atomized water particles decreased the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 to cells while observing the damage to the virus. “We observed that the nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles damaged the viral envelope, protein, and RNA, making them unable to bind to host cells,” Associate Professor Yasugi explained. “The phenomena we observed are considered the main mechanism by which the nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles disinfect SARS-CoV-2.We found that the target of the water particles is not the specific viral specific structure or specific proteins. Because the water particles impact viral envelope, protein, and RNA, they may disinfect other enveloped viral species as well.”
While this proof of concept demonstrates how the nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles destroy SARS-CoV-2, the full extent of their application remains to be seen. “We don’t know the precise factor destroying SARS-CoV-2; ROS in the particles may be that factor because ROS damage lipid, protein, and DNA/RNA through their oxidation. Furthermore, our studies showed the water particles disinfect SARS-CoV-2 on surfaces under closed experimental conditions. But the efficacy of the nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles can change depending on the humidity, temperature, and other environmental factors; for this method to be practical, it would have to work in numerous environments,” Associate Professor Yasugi concluded. “Our future studies will focus on the ROS mechanism of action and test if the nano-sized electrostatic atomized water particles are effective against airborne SARS-CoV-2.”
###
About Osaka Metropolitan University
Osaka Metropolitan University is a new public university established in April 2022, formed by merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University. For more research news visit https://www.upc-osaka.ac.jp/new-univ/en-research/research/ or follow @OsakaMetUniv_en and #OMUScience.
Journal
Journal of Nanoparticle Research
DOI
10.1007/s11051-022-05485-5
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Mechanisms underlying inactivation of SARS‑CoV‑2 by nano‑sized electrostatic atomized water particles
Article Publication Date
11-May-2022
COI Statement
This study was performed in collaboration with Panasonic Corporation Living Appliances and Solutions Company, and was financially supported by the company.




