[Jerusalem, Israel] Study reveals an important discovery in the realm of nanomachines within living systems. Prof. Sason Shaik from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and Dr. Kshatresh Dutta Dubey from Shiv Nadar University, conducted molecular-dynamics simulations of Cytochromes P450 (CYP450s) enzymes, revealing that these enzymes exhibit unique soft-robotic properties.
Credit: Kshatresh Dutta Dubey
[Jerusalem, Israel] Study reveals an important discovery in the realm of nanomachines within living systems. Prof. Sason Shaik from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and Dr. Kshatresh Dutta Dubey from Shiv Nadar University, conducted molecular-dynamics simulations of Cytochromes P450 (CYP450s) enzymes, revealing that these enzymes exhibit unique soft-robotic properties.
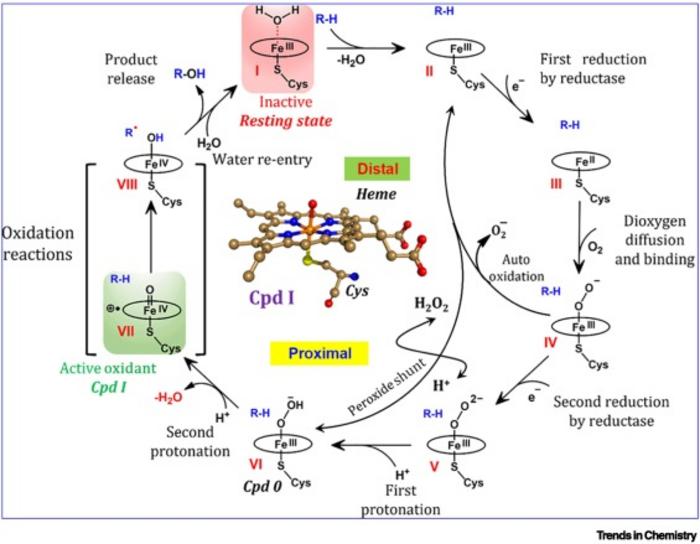
Cytochromes P450 (CYP450s) are enzymes found in living organisms and play a crucial role in various biological processes, particularly in the metabolism of drugs and xenobiotics. The researchers’ simulations demonstrated that CYP450s possess a fourth dimension – the ability to sense and respond to stimuli, making them soft-robot nanomachines in “living matters”.
In the catalytic cycle of these enzymes, a molecule called a substrate binds to the enzyme. This leads to a process called oxidation. The enzyme’s structure has a confined space that allows it to act like as a sensor and a soft robot. It interacts with the substrate using weak interactions, like soft impacts. These interactions transfer energy, causing parts of the enzyme and the molecules inside it to move. This movement generates ultimately a special substance called oxoiron species, which serves the enzyme to oxidize a variety of different substances.
The key takeaway from these molecular-dynamics simulations is that the catalytic cycle of CYP450s is complex but follows a logical sequence. The enzyme’s restricted space, strategic residue placements, and channels allow it to be a sensitive sensor of the substrate, its own heme changes, and conformational shifts in the active site. This sensing-response capability creates a soft-robot with a fourth dimension of sensing, something previously unseen in regular 3D matter.
“We have discovered that CYP450s act as soft-robot machines in ‘living matters,’ displaying a remarkable sensing and response-action capability. This is an exciting revelation, and we believe that similar mechano-transduction mechanisms of soft-impact cues might be at work in other soft-robot machines in nature,” stated Prof. Sason Shaik, one of the lead researchers.
The findings open up new avenues in soft-robotics research, as 4D materials are gaining significance, driven by external triggers. These materials, such as hydrogels produced through 3D printing, resemble enzymes in their ability to sense and induce changes. The implications of this discovery extend beyond the realm of biology and chemistry, potentially revolutionizing fields like artificial intelligence design and self-evolving polymers/gels synthesis.
Dr. Kshatresh Dutta Dubey, co-researcher of the study, added, “We are entering an exciting era for chemistry, where soft-robotics and intelligent design of nanomachines can lead to unprecedented advancements. The future may witness the creation of self-evolving polymers and perpetual nanomachines capable of synthesizing new molecules at will.”
The scientists believe that the integration of the soft-robotic language and machine programming could accelerate progress in the development of 4D materials and unlock the full potential of soft-robotics.
For more information about the study, please refer to the article: “Nanomachines in Living Matters: The Soft-Robot Cytochrome P450” Trends in Chemistry, In press (2023).
Journal
Trends in Chemistry
DOI
10.1016/j.trechm.2023.07.002
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Nanomachines in living matters: the soft-robot cytochrome P450
Article Publication Date
3-Aug-2023




