Credit: Cornell Lab of Ornithology
ITHACA, N.Y. – Human activities could change the pace of evolution, similar to what occurred 66 million years ago when a giant asteroid wiped out the dinosaurs, leaving modern birds as their only descendants. That's one conclusion drawn by the authors of a new study published in Systematic Biology.
Cornell University Ph.D. candidate Jacob Berv and University of Bath Prize Fellow Daniel Field suggest that the meteor-induced mass extinction (a.k.a. the K-Pg event) led to an acceleration in the rate of genetic evolution among its avian survivors. These survivors may have been much smaller than their pre-extinction relatives.
"There is good evidence that size reductions after mass extinctions may have occurred in many groups of organisms," says Berv. "All of the new evidence we have reviewed is also consistent with a Lilliput Effect affecting birds across the K-Pg mass extinction." Paleontologists have dubbed this phenomenon the "Lilliput Effect" — a nod to the classic tale Gulliver's Travels.
"Smaller birds tend to have faster metabolic rates and shorter generation times," Field explains. "Our hypothesis is that these important biological characters, which affect the rate of DNA evolution, may have been influenced by the K-Pg event."
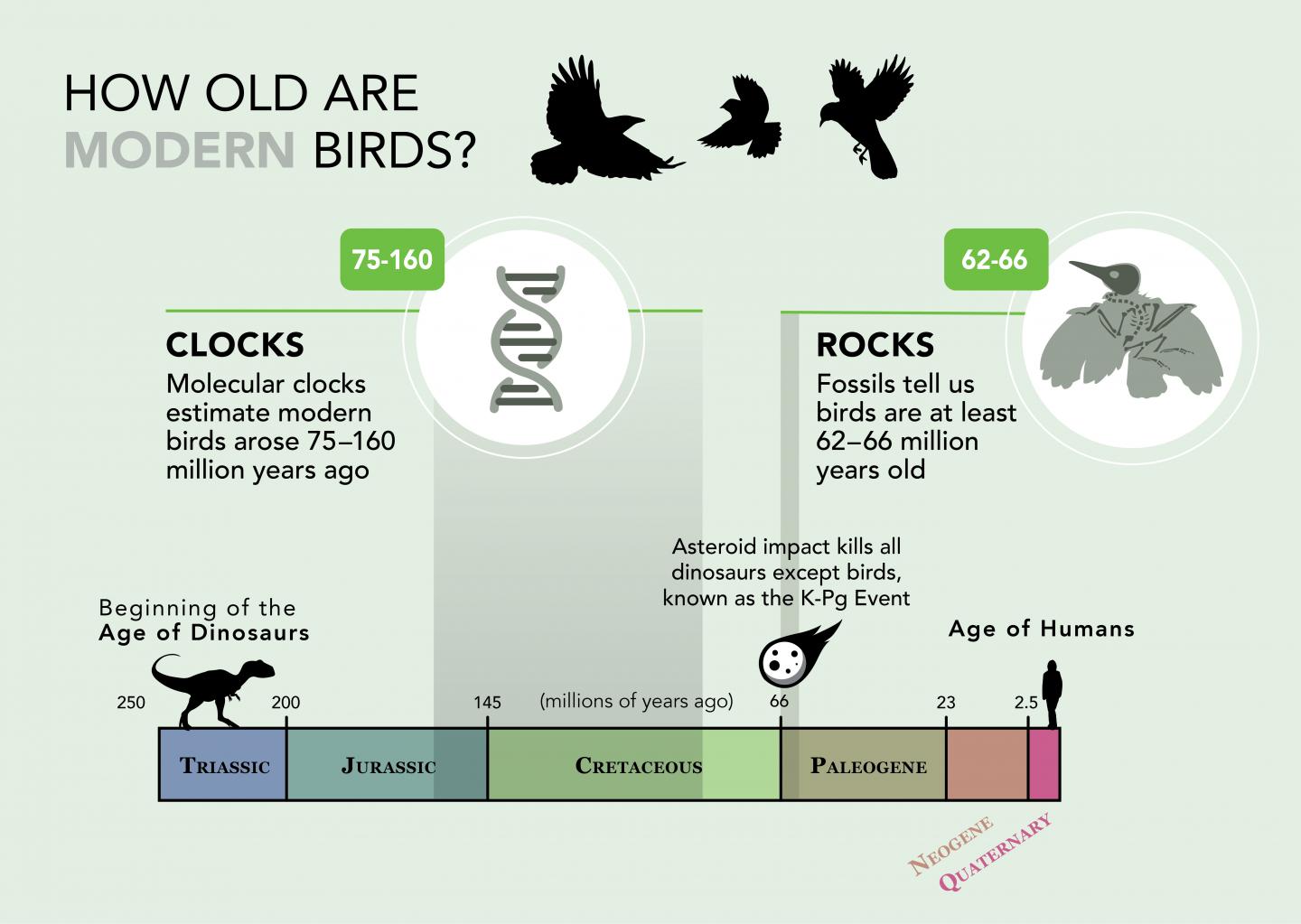
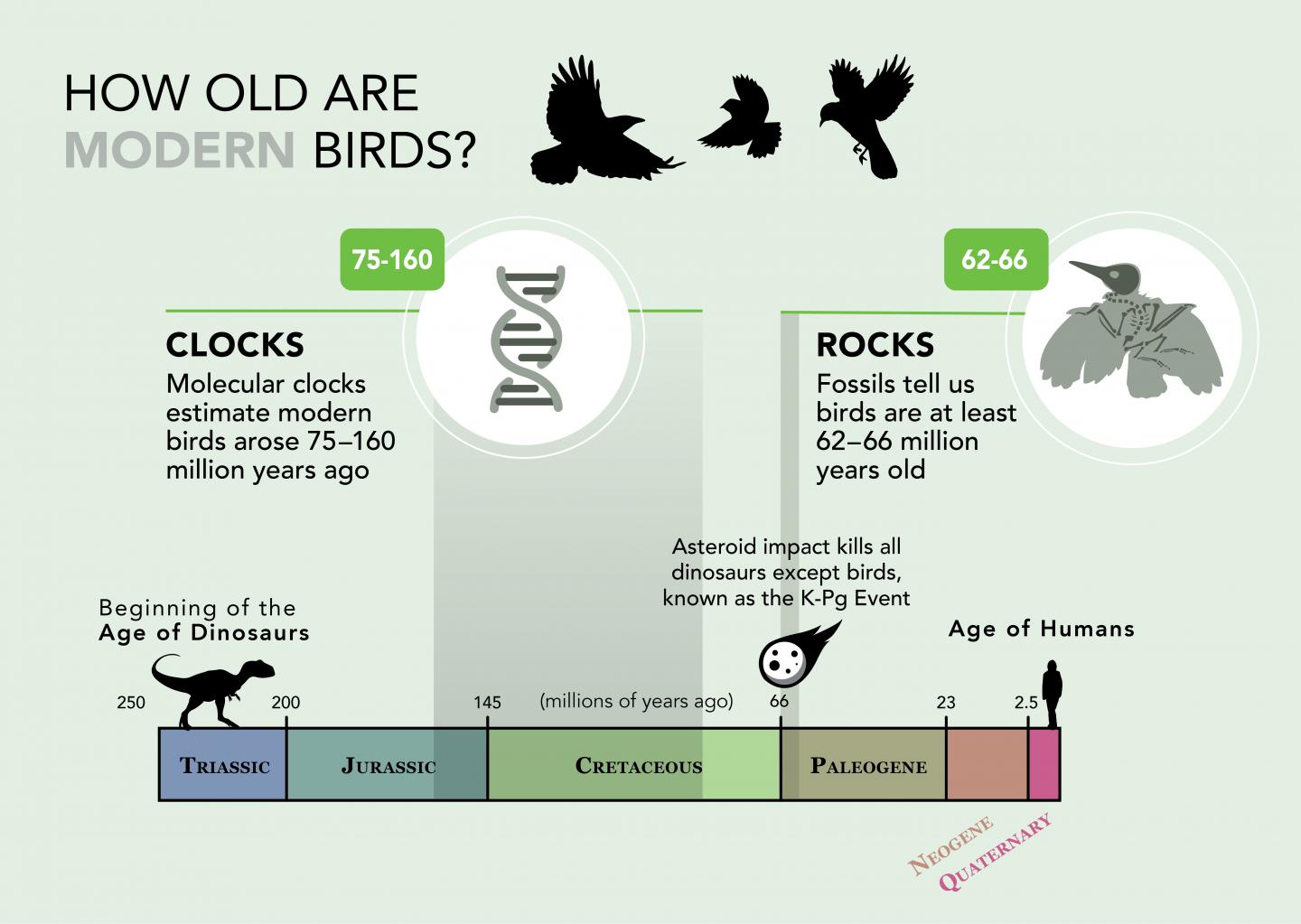
The researchers jumped into this line of inquiry because of the long-running "rocks and clocks" debate. Different studies often report substantial discrepancies between age estimates for groups of organisms implied by the fossil record and estimates generated by molecular clocks. Molecular clocks use the rate at which DNA sequences change to estimate how long ago new species arose, assuming a relatively steady rate of genetic evolution. But if the K-Pg extinction caused avian molecular clocks to temporarily speed up, Berv and Field say this could explain at least some of the mismatch. "Size reductions across the K-Pg extinction would be predicted to do exactly that," says Berv.
"The bottom line is that, by speeding up avian genetic evolution, the K-Pg mass extinction may have temporarily altered the rate of the avian molecular clock," says Field. "Similar processes may have influenced the evolution of many groups across this extinction event, like plants, mammals, and other forms of life."
The authors suggest that human activity may even be driving a similar Lilliput-like pattern in the modern world, as more and more large animals go extinct because of hunting, habitat destruction, and climate change.
"Right now, the planet's large animals are being decimated–the big cats, elephants, rhinos, and whales," notes Berv. "We need to start thinking about conservation not just in terms of functional biodiversity loss, but about how our actions will affect the future of evolution itself."
###
This research was supported by a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship and Doctoral Dissertation Improvement Grant to Berv, and a National Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada Graduate Scholarship to Field. Berv was also supported by a Cornell Lab of Ornithology Athena Grant. Field is supported by a 50th Anniversary Prize Fellowship at the University of Bath.
Cornell University has television, ISDN and dedicated Skype/Google+ Hangout studios available for media interviews.
Media Contact
Lindsey Hadlock
[email protected]
607-255-6121
@cornell
http://pressoffice.cornell.edu
Original Source
http://blogs.cornell.edu/mediarelations/2017/09/21/dino-killing-asteroids-impact-on-bird-evolution/ http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syx064