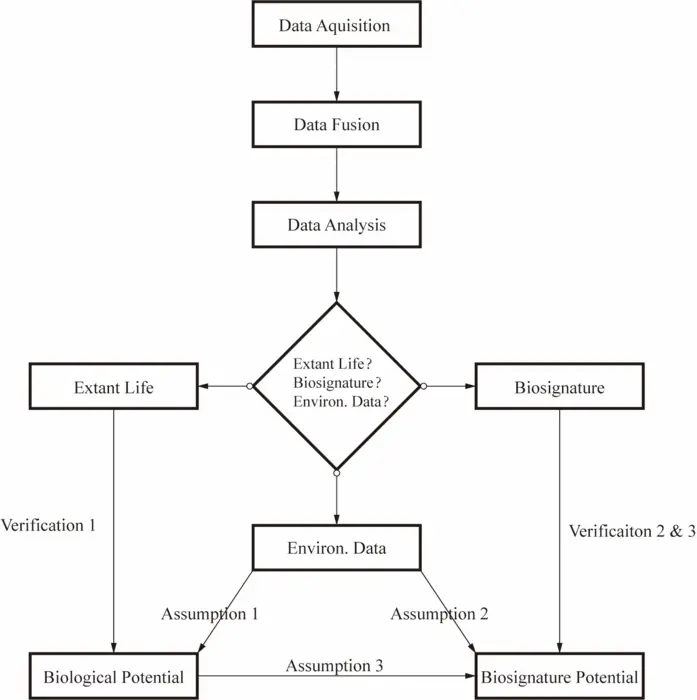
In the quest to discover extraterrestrial life beyond our planet, icy celestial bodies such as Europa and Enceladus have emerged as promising candidates. These moons harbor subsurface oceans beneath thick ice shells, creating potentially habitable environments where microbial life could thrive. To effectively explore these worlds, scientists propose a groundbreaking strategy centered on the use of Extraterrestrial Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (Exo-AUVs), which are designed to autonomously navigate and gather data from the frigid depths of these aquatic realms. This innovative approach aims to uncover vital biosignatures and elusive signs of life by targeting regions with high biological potential, a strategy that could redefine our understanding of life across the cosmos.
Icy worlds like Europa, with its potential for vast oceanic expanses beneath a shell of ice, present a unique opportunity for astrobiological exploration. The proposed mission framework emphasizes the need to identify and investigate specific locations that may harbor life, such as the icy shell, the interface where ice meets water, and the seafloor. These areas are of particular interest because they are believed to have the necessary chemical and physical conditions for life to exist and evolve. By focusing on biological potential rather than strictly hunting for life, researchers can avoid the pitfalls of binary thinking that artificially constrains our understanding of extraterrestrial biology.
Central to this life detection strategy is the deployment of Exo-AUVs, which combine advanced technological capabilities with the ecological niche theory. These autonomous vehicles are equipped to perform a series of actions categorized as assuming, sampling, analyzing, and verifying. Equipped with diverse scientific instruments, Exo-AUVs will be able to collect detailed data from multiple dimensions, enabling scientists to paint a clearer picture of the conditions present in these icy environments. By leveraging ecological principles from Earth, the mission plans to autonomously identify micro-zones that exhibit signs of biological activity and collect a variety of biosignatures, potentially leading to the discovery of extant life.
The operational context for the Exo-AUV missions is multi-faceted and involves several key elements. Each expedition will navigate unique environmental conditions while employing a carrier craft designed to penetrate thick ice layers. With innovations in energy generation and navigation, the mission architecture will utilize small modular reactors (SMRs) or radioisotope thermal generators (RTGs) to power both the carrier and the AUVs. These energy sources provide the longevity needed for operations in the extreme conditions a few kilometers below the icy crust of moons like Europa, while advanced sonar and radar assist in navigation and obstacle avoidance.
Crucially, the planned Exo-AUV missions tackle one of the main challenges of space exploration—the autonomy of operations. With communication delays of up to 30 minutes, Exo-AUVs must independently localize and adapt to ever-changing conditions without waiting for directives from Earth. This operational independence is vital for effective exploration, especially in regions where life signatures could be sparse and heterogeneous. The vehicles will autonomously plan their exploration paths, employ onboard tests for data acquisition, and analyze their findings directly in real-time before transmitting vital data back to Earth.
With the vast expanses of icy water and ice-covered landscapes, Exo-AUVs carry the challenge of detecting life across scales from several kilometers down to microscopic levels. Utilizing microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technology, the scientific payloads will be miniaturized to fit within the size and weight constraints of launch vehicles. This means the mission can include a wide array of instruments capable of capturing detailed information on water characteristics, microbial life, and other biologically relevant features. By analyzing morphology, movement, and distribution, researchers hope to gain insights into the ecological niches that could harbor life, akin to those found on Earth in environments like deep-sea hydrothermal vents or polar ice.
The adaptability of the Exo-AUV is also essential for overcoming the harsh environmental conditions expected on Europa. The icy surface is subject to extreme radiation from Jupiter, which poses significant risks to electronic equipment. By employing rugged, pressure-resistant materials and protective shielding, the AUVs can withstand the challenges of this unique environment. This resilience enhances the likelihood of successful missions, allowing these vehicles to explore various depths and locations to uncover hidden biosignatures and prebiotic chemical systems autonomously.
A modular approach is also proposed for the Exo-AUV fleet, with the potential for multiple vehicles to operate synergistically. Each team will function as part of a comprehensive system; for instance, the ice-penetrating carrier can deploy various AUV configurations for specialized tasks. These can include a survey module designed to detect larger features or an observation module for investigating localized microenvironments. By dispersing operational capabilities across multiple vehicles, the mission can efficiently cover vast areas and maximize the potential for discovering biosignatures by addressing diverse contextual elements unique to each location on Europa.
Evidently, the approach to exploring icy worlds is multifaceted and requires a delicate balance between technological capabilities, mission objectives, and environmental considerations. The roadmap for the development of Exo-AUVs emphasizes innovation to solve the challenges faced in the search for life. It is clear that the success of these missions relies not only on the vehicles themselves but also on their ability to work in tandem to provide a comprehensive understanding of the icy subsurface and its potential to host life.
In summary, the future of astrobiological exploration is increasingly tied to the capabilities of autonomous vehicles, particularly in the harsh conditions of icy bodies like Europa. Through meticulous planning, innovative engineering, and a focus on biological potential, researchers aim to unlock the secrets of these alien worlds. The proactive search for biosignatures and the potential detection of extraterrestrial life symbolize a new chapter in the quest for understanding our place in the cosmos. As we stand on the brink of this frontier, the promise of discovery beckons us to delve deeper into the icy worlds beyond.
Subject of Research: Life Detection Strategies on Icy Worlds
Article Title: Exploring the Depths: A New Approach to Life Detection on Icy Worlds
News Publication Date: October 2023
Web References: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-023-1390-6
References: Science China Earth Sciences
Image Credits: ©Science China Press
Keywords: Europa, Exo-AUV, astrobiology, extraterrestrial life, icy worlds, life detection, biosignatures, autonomous exploration.