New study is first to show how two types of sand can behave like liquids, shedding light on geological processes from mudslides to volcanoes and potentially enabling new technologies from pharmaceutical production to carbon capture
Credit: Alex Penn/ETH Zurich
New study is first to show how two types of sand can behave like light and heavy liquids, shedding light on geological processes from mudslides to volcanos and potentially enabling new technologies from pharmaceutical production to carbon capture
New York, NY–April 22, 2019–The flow of granular materials, such as sand and catalytic particles used in chemical reactors, and enables a wide range of natural phenomena, from mudslides to volcanos, as well as a broad array of industrial processes, from pharmaceutical production to carbon capture. While the motion and mixing of granular matter often display striking similarities to liquids, as in moving sand dunes, avalanches, and quicksand, the physics underlying granular flows is not as well-understood as liquid flows.
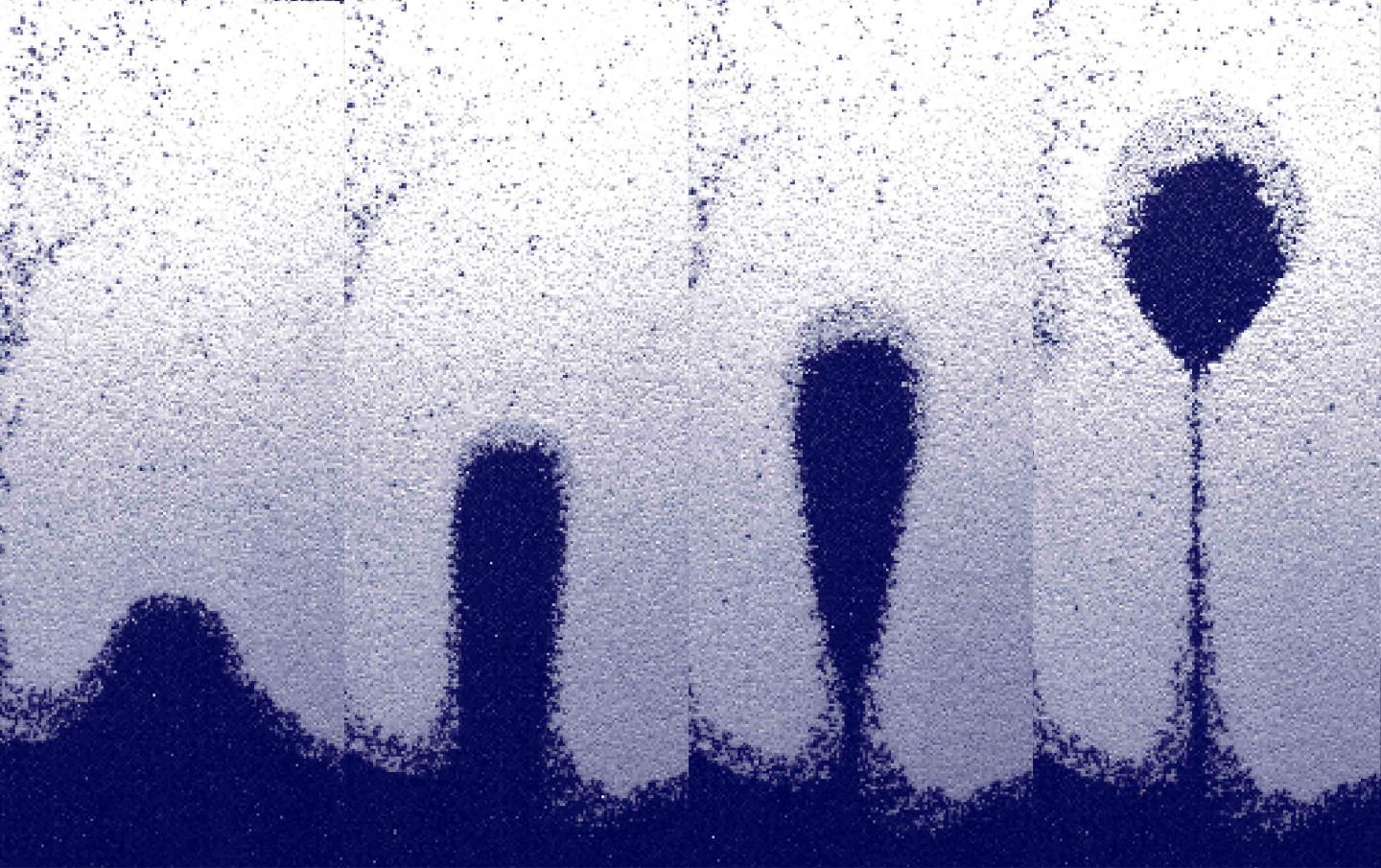
Now, a recent discovery by Chris Boyce, assistant professor of chemical engineering at Columbia Engineering, explains a new family of gravitational instabilities in granular particles of different densities that are driven by a gas-channeling mechanism not seen in fluids. In collaboration with Energy and Engineering Science Professor Christoph Müller’s group at ETH Zurich, Boyce’s team observed an unexpected Rayleigh-Taylor (R-T)-like instability in which lighter grains rise through heavier grains in the form of “fingers” and “granular bubbles.” R-T instabilities, which are produced by the interactions of two fluids of different densities that do not mix–oil and water, for example–because the lighter fluid pushes aside the heavier one, have not been seen between two dry granular materials.
The study, published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is the first to demonstrate that “bubbles” of lighter sand form and rise through heavier sand when the two types of sand are subject to vertical vibration and upward gas flow, similar to the bubbles that form and rise in lava lamps. The team found that, just as air and oil bubbles rise in water because they are lighter than water and do not want to mix with it, bubbles of light sand rise through heavier sand even though two types of sand like to mix.
“We think our discovery is transformational,” says Boyce “We have found a granular analog of one of the last major fluid mechanical instabilities. While analogs of the other major instabilities have been discovered in granular flows in recent decades, the R-T instability has eluded direct comparison. Our findings could not only explain geological formations and processes that underlie mineral deposits, but could also be used in powder-processing technologies in the energy, construction, and pharmaceuticals industries.”
Boyce’s group used experimental and computational modeling to show that gas channeling through lighter particles triggers the formation of finger and bubble patterns. The gas channeling occurs because the clusters of lighter, larger particles have a higher permeability to gas flow than do the heavier, smaller grains. The R-T-like instability in granular materials arises from a competition between upward drag force increased locally by gas channeling and downward contact forces, a physical mechanism entirely different from that found in liquids.
They found that this gas-channeling mechanism also generates other gravitational instabilities, including the cascading branching of a descending granular droplet. They also demonstrated that the R-T-like instability can occur under a wide variety of gas flow and vibration conditions, forming different structures under different excitation conditions.
“These instabilities, which can be applied to a variety of systems, shed new light on granular dynamics and suggest new opportunities for patterning within granular mixtures to form new products in the pharmaceutical industry, for example,” Boyce adds. “We are especially excited about the potential impact of our findings on the geological sciences–these instabilities can help us understand how structures have formed over the long history of the Earth and predict how others may form in the future.”
Boyce is now investigating other liquid-like and structured phenomena in sand particles and quantifying their behavior. He is also in conversations with geologists and volcanologists to explore more about how this process and similar ones occur in the natural world.
###
About the Study
The study is titled “Gravitational Instabilities in Binary Granular Materials.”
Authors are: C. McLaren1, T. M. Kovar2, A. Penn1, C. R. Müller1*, C. M. Boyce1,2*
1 Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, ETH Zürich
2 Chemical Engineering, Columbia Engineering
The study was supported by Swiss National Science Foundation 200021_153290.
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest.
LINKS:
Paper: https:/
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1820820116
https:/
http://engineering.
https:/
https:/
Columbia Engineering
Columbia Engineering, based in New York City, is one of the top engineering schools in the U.S. and one of the oldest in the nation. Also known as The Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science, the School expands knowledge and advances technology through the pioneering research of its more than 220 faculty, while educating undergraduate and graduate students in a collaborative environment to become leaders informed by a firm foundation in engineering. The School’s faculty are at the center of the University’s cross-disciplinary research, contributing to the Data Science Institute, Earth Institute, Zuckerman Mind Brain Behavior Institute, Precision Medicine Initiative, and the Columbia Nano Initiative. Guided by its strategic vision, “Columbia Engineering for Humanity,” the School aims to translate ideas into innovations that foster a sustainable, healthy, secure, connected, and creative humanity.
Media Contact
Holly Evarts
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




