WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new image reconstruction approach that could contribute to better breast cancer detection. The deep learning algorithm overcomes a major hurdle in multi-modality imaging by allowing images to be recovered in real time.
Credit: Keith Paulsen, Dartmouth College
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new image reconstruction approach that could contribute to better breast cancer detection. The deep learning algorithm overcomes a major hurdle in multi-modality imaging by allowing images to be recovered in real time.
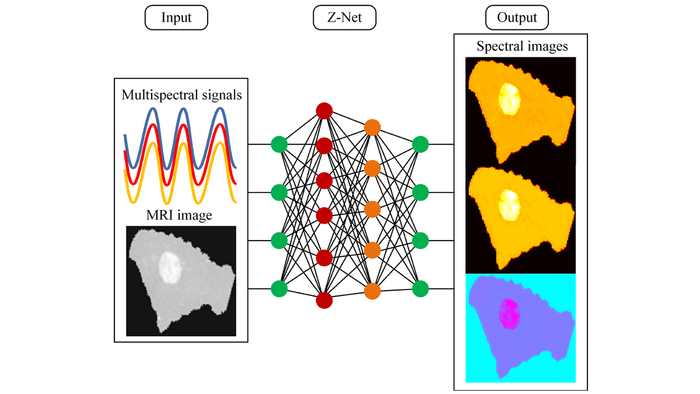
In Optica, Optica Publishing Group’s journal for high-impact research, the researchers described the new algorithm, known as Z-Net, and how it works with an imaging platform that combines optical spectral information with contrast-free magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to improve detection of breast cancer.
“The near infrared spectral tomography (NIRST) and MRI imaging platform we developed has shown promise, but the time and effort involved in image reconstruction has prevented it from being translated into the day-to-day clinical workflow,” said Keith Paulsen, who led the research team from Dartmouth College. “Thus, we designed a deep-learning algorithm that incorporates anatomical image data from MRI to guide NIRST image formation without requiring complex modeling of light propagation in tissue.”
Paulsen and colleagues from the Beijing University of Technology and the University of Birmingham report that their new algorithm can distinguish between malignant and benign tumors using MRI-guided NIRST imaging data from patient breast exams.
“Z-Net could allow NIRST to become an efficient and effective add-on to non-contrast MRI for breast cancer screening and diagnosis because it allows MRI-guided NIRST images to be recovered in nearly real time,” said Paulsen. “It can also be readily adapted for use with other cancers and diseases for which multi-modality imaging data are available.”
Applying deep learning
Today, dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI is recognized as the most sensitive breast cancer detection method. However, DCE MRI requires intravenous injection of a contrast agent and has a substantial false positive rate. Although non-contrast MRI-guided NIRST offers an alternative that doesn’t require contrast injection or ionizing radiation, reconstructing the combined images requires complicated light propagation models as well as time consuming MRI image analysis.
The researchers used deep learning to make the image reconstruction process faster. Deep learning is a machine learning approach that creates connections among pieces of information in a way that is similar to how human brains operate, allowing the researchers to train their algorithm to recognize patterns and complex relationships.
“The Z-Net algorithm reduces the time needed to generate a new image to a few seconds,” said Jinchao Feng, the study’s lead author. “Moreover, the machine learning network we developed can be trained with data generated by computer simulations rather than needing images from actual patient exams, which take a long time to collect and process into training information.”
Clinical tests
After training the algorithm, the researchers used simulated data to confirm that the quality of the reconstructed images was not degraded by eliminating diffuse light propagation modeling or by not segmenting MRI images.
They then applied the new algorithm prospectively to MRI-guided NIRST data collected from two breast imaging exams – one leading to a biopsy-confirmed cancer diagnosis, the other resulting in a benign abnormality. The new algorithm generated images that could tell the difference between the malignant and benign cases.
“In addition to showing the potential of our approach, the results also demonstrate that when in vivo data is insufficient or unavailable for training a deep learning algorithm, a large amount of simulation data may work,” said Shudong Jiang, a study co-author and pioneer in developing simultaneous MRI and optical breast imaging technology.
The researchers are working to adapt the new image reconstruction method to work with 3D data and plan to test it in a larger clinical trial in the near future.
Paper: J. Feng, W. Zhang, Z. Li, K. Jia, S. Jiang, H. Dehghani, B. W. Pogue, K. D. Paulsen, “Deep Learning Based Image Reconstruction for MRI Guided Near Infrared Spectral Tomography,” Optica, 9 (2), (2022).
DOI: 10.1364/OPTICA.446576.
About Optica
Optica is an open-access journal dedicated to the rapid dissemination of high-impact peer-reviewed research across the entire spectrum of optics and photonics. Published monthly by Optica Publishing Group, the Journal provides a forum for pioneering research to be swiftly accessed by the international community, whether that research is theoretical or experimental, fundamental or applied. Optica maintains a distinguished editorial board of more than 60 associate editors from around the world and is overseen by Editor-in-Chief Prem Kumar, Northwestern University, USA. For more information, visit Optica.
About Optica Publishing Group (formerly OSA)
Optica Publishing Group is a division of Optica, the society advancing optics and photonics worldwide. It publishes the largest collection of peer-reviewed content in optics and photonics, including 18 prestigious journals, the society’s flagship member magazine, and papers from more than 835 conferences, including 6,500+ associated videos. With over 400,000 journal articles, conference papers and videos to search, discover and access, Optica Publishing Group represents the full range of research in the field from around the globe.
Journal
Optica
DOI
10.1364/OPTICA.446576
Article Title
Deep Learning based Reconstruction of MRI Guided Near Infrared Spec-tral Tomography Avoids the Limitations of Forward Diffuse Modeling
Article Publication Date
24-Feb-2022




