“The proposed NOD/SCID model, with its accelerated ovarian aging, holds particular value as it will enable the observation of ovarian changes within a shorter timeframe.”
Credit: 2023 Marchante et al.
“The proposed NOD/SCID model, with its accelerated ovarian aging, holds particular value as it will enable the observation of ovarian changes within a shorter timeframe.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 7, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 20, entitled, “Deciphering reproductive aging in women using a NOD/SCID mouse model for distinct physiological ovarian phenotypes.”
Female fertility is negatively correlated with age, with noticeable declines in oocyte quantity and quality until menopause. To understand this physiological process and evaluate human approaches for treating age-related infertility, preclinical studies in appropriate animal models are needed. In this new study, researchers María Marchante, Noelia Ramirez-Martin, Anna Buigues, Jessica Martinez, Nuria Pellicer, Antonio Pellicer, and Sonia Herraiz from IVIRMA, University of Valencia and Instituto Investigación Sanitaria La Fe aimed to characterize an immunodeficient physiological aging mouse model displaying ovarian characteristics of different stages during women’s reproductive life.
“The main purpose of our study was to establish a physiological ovarian aging mouse model that could be employed to evaluate potential therapeutic interventions derived from human origin.”
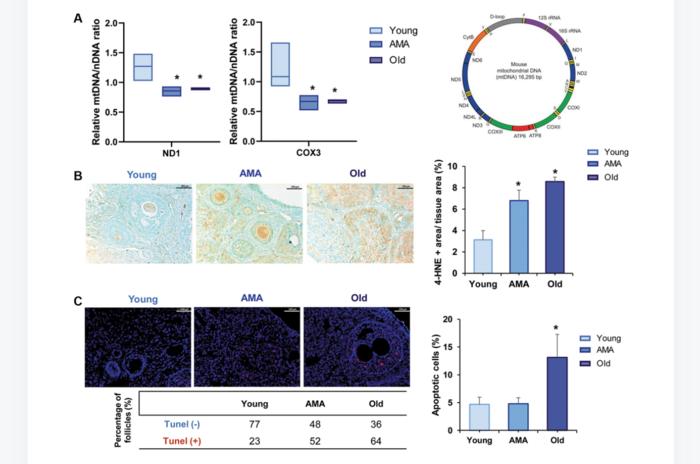
NOD/SCID mice of different ages (8-, 28-, and 36–40-week-old) were employed to mimic ovarian phenotypes of young, Advanced Maternal Age (AMA), and old women (~18–20-, ~36–38-, and >45-years-old, respectively). Mice were stimulated, mated, and sacrificed to recover oocytes and embryos. Then, ovarian reserve, follicular growth, ovarian stroma, mitochondrial dysfunction, and proteomic profiles were assessed. Age-matched C57BL/6 mice were employed to cross-validate the reproductive outcomes.
The quantity and quality of oocytes were decreased in AMA and Old mice. These age-related effects associated spindle and chromosome abnormalities, along with decreased developmental competence to blastocyst stage. Old mice had less follicles, impaired follicle activation and growth, an ovarian stroma inconducive to growth, and increased mitochondrial dysfunctions. Proteomic analysis corroborated these histological findings. Based on that, NOD/SCID mice can be used to model different ovarian aging phenotypes and potentially test human anti-aging treatments.
“In summary, in this study we characterized the quality of the ovarian microenvironment and reproductive outcomes of an immunodeficient murine model of physiological ovarian aging by evaluating fertility outcomes, ovarian reserve and stroma, mitochondrial dysfunctions, and the ovarian proteome at different stages. This model adequately mimicked the characteristics of the reproductive stages in women, without external agents compromising folliculogenesis, or disrupting molecular mechanisms and ovarian function, which could mask the processes of physiological aging.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205086
Corresponding Author: Sonia Herraiz
Corresponding Email: [email protected]
Keywords: age-related infertility, ovarian aging, mouse model, oocyte quality, embryo development, mitochondrial function
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205086
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- SoundCloud
- X, formerly known as Twitter
- YouTube
- LabTube
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.205086
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Deciphering reproductive aging in women using a NOD/SCID mouse model for distinct physiological ovarian phenotypes
Article Publication Date
16-Oct-2023




