Block ciphers, a branch of modern cryptography, are playing a more prominent role in protecting information security as 5G technology develops. Although encryption algorithms of the traditional Feistel structure have great advantages in terms of consistent encryption and decryption, they have poor diffusion effects. Besides, they cannot adapt to the high throughput communication environment and resource-constrained devices. The S-box is the crucial nonlinear component in the block cipher and significantly determines the security of an algorithm. Unfortunately, the vast proportion of S-boxes exist in a static manner, which makes it difficult to effectively resist cryptographic attacks based on specific S-boxes.
Credit: Higher Education Press Limited Company
Block ciphers, a branch of modern cryptography, are playing a more prominent role in protecting information security as 5G technology develops. Although encryption algorithms of the traditional Feistel structure have great advantages in terms of consistent encryption and decryption, they have poor diffusion effects. Besides, they cannot adapt to the high throughput communication environment and resource-constrained devices. The S-box is the crucial nonlinear component in the block cipher and significantly determines the security of an algorithm. Unfortunately, the vast proportion of S-boxes exist in a static manner, which makes it difficult to effectively resist cryptographic attacks based on specific S-boxes.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Lang LI published their new research in Frontiers of Computer Science (2023, Vol. 17, Issue 3) co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer·Nature.
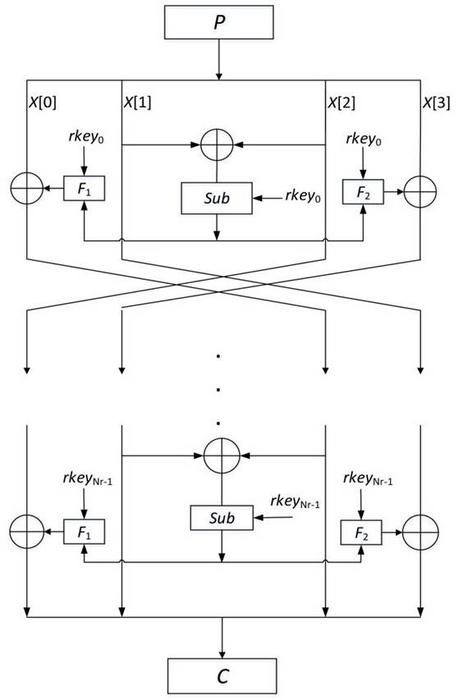
The team proposed a lightweight block cipher based on dynamic s-box named DBST for devices with limited hardware resources and high throughput requirements. The round function of DBST employs a novel generalized Feistel variant structure, which dramatically improves the diffusivity of the traditional Feistel structure. The S-box in the algorithm integrates bit-slice technology with subkeys to create a key-dependent dynamic S-box model that compensates for the shortcomings of static S-boxes.
In the research, they perform security analysis and hardware experiment on DBST. The experimental data demonstrate that the proposed algorithm has high security, high throughput rate and low hardware resources. Furthermore, differential analysis of the S-boxes proves that DBST’s S-boxes have fewer differential properties than RECTANGLE’s S-boxes.
###
Research Article, Published: 15 June 2023
Liuyan YAN, Lang LI, Ying GUO. DBST: a lightweight block cipher based on dynamic S-box. Front. Comput. Sci., 2023, 17(3): 173805, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-022-1677-5
About Frontiers of Computer Science (FCS)
FCS was launched in 2007. It is published bimonthly both online and in print by HEP and Springer. Prof. Zhi-Hua Zhou from Nanjing University serves as the Editor-in-Chief. It aims to provide a forum for the publication of peer-reviewed papers to promote rapid communication and exchange between computer scientists. FCS covers all major branches of computer science, including: architecture, software, artificial intelligence, theoretical computer science, networks and communication, information systems, multimedia and graphics, information security, interdisciplinary, etc. The readers may be interested in the special columns “Perspective” and “Excellent Young Scholars Forum”.
FCS is indexed by SCI(E), EI, DBLP, Scopus, etc. The latest IF is 2.669. FCS solicits the following article types: Review, Research Article, Letter.
Journal
Frontiers of Computer Science
DOI
10.1007/s11704-022-1677-5
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
DBST: a lightweight block cipher based on dynamic S-box
Article Publication Date
15-Jun-2023



