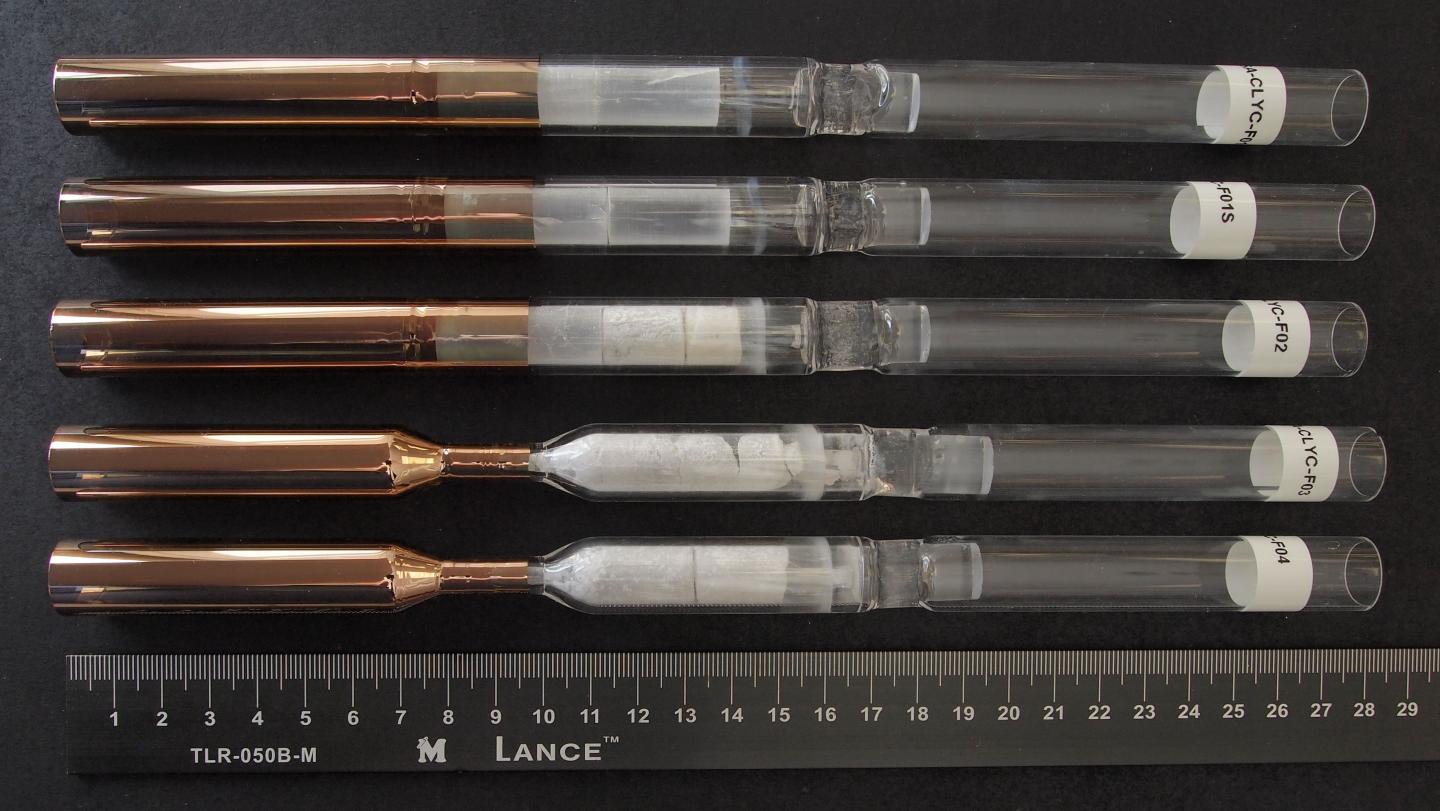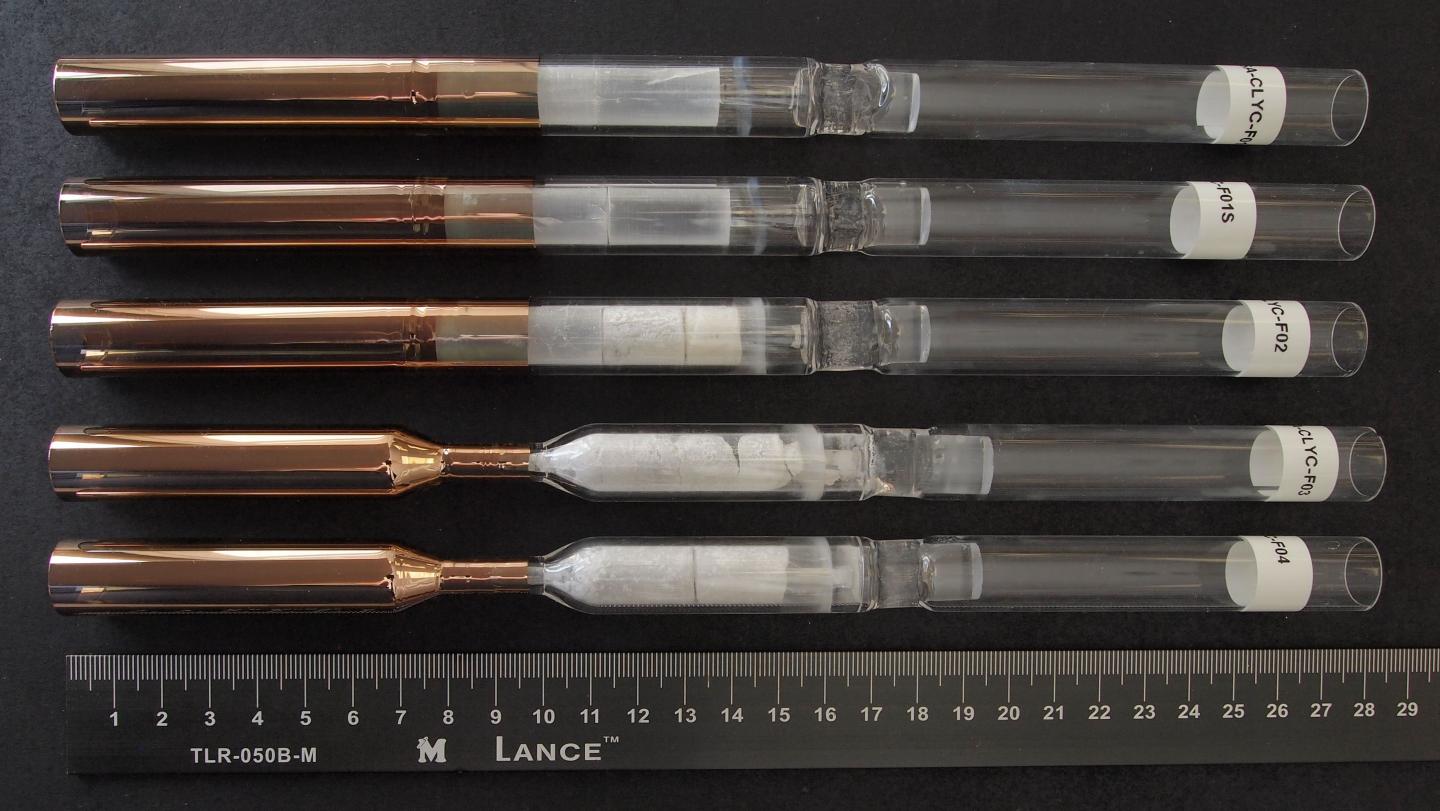
Credit: Alexei Churilov
Research into crystal growth in microgravity was one of the earliest investigations conducted aboard the International Space Station and is continued to this day. The unique microgravity environment of space provides an ideal setting for producing crystals that are more perfect than their terrestrial-grown counterparts. The Crystal Growth of Cs2LiYCl6:Ce Scintillators in Microgravity (CLYC-Crystal Growth), a Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS)-sponsored investigation, will study the potential benefits of growing the CYLC crystal in microgravity.
The CLYC crystal is a special kind of multicomponent crystal system used to make scintillator radiation detectors, a device that is sensitive to both gamma rays and neutrons.
"It's a spectroscopic crystal, which means, using this crystal, we can detect the presence and intensity of radiation, as well as identify which isotopes emit radiation by measuring the energy," said Dr. Alexei Churilov, primary investigator and senior scientist at Radiation Monitoring Devices Inc. (RMD).
The CLYC crystal is produced as a commercial product by RMD and is largely used to detect and differentiate both harmful and harmless levels of radiation. The crystal's main application is homeland security as a method of detected smuggled nuclear materials, but may also be used for oil and gas exploration, medical imaging, particle and space physics and scientific instruments.
However, the Earth-grown crystals have shown defects such as cracks, grain boundaries and inclusions, incidents which scientists like Churilov hope to eliminate by using the space station's microgravity environment as a growth habitat.
Research has shown that many, though not all, crystals benefit from growth in microgravity. Although the reasoning behind this phenomena is still being investigated, research points to the lack of buoyancy-induced convection, which affects transport of molecules in the crystal.
"Our ultimate goal is to study the growth of CLYC in microgravity without the interference of convection and to improve the production of the crystal on Earth," said Churilov.
The research for the CLYC Crystal Growth investigation will be conducted within the Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules Furnaces and Inserts (SUBSA Furnaces and Inserts). SUBSA helps researchers advance the understanding of processes involved in semiconductor crystal growth. It offers a gradient freeze furnace for materials science investigations. SUBSA was originally operated aboard the space station in 2002, the SUBSA hardware has been modernized and updated with data acquisition, high resolution video and communication interfaces.
During the investigation, four crystal growth runs will be conducted aboard the space station and then in the ground-based SUBSA furnaces, giving researchers a view into the gravitational effect on their growth. Once the investigation is complete, the space-grown crystals will be compared against their counterparts on Earth and tested for imperfections and effectiveness as radiation detectors.
Although microgravity can't be mimicked or reproduced on the ground, results from the investigation will provide information about which crystal methods to use on Earth, how to improve ampoule and furnace design and which crystal growth parameters to change in pursuit of a more perfect crystallization process.
Though the total weight of the CLYC Crystal Growth investigation is small, only a few kilograms together with packaging, the benefits can be immense as the data gathered during the investigation will be put to immediate use in the production of CLYC crystals.
###
Follow @ISS_Research for more information about the science happening on the space station.
Media Contact
Rachel Barry
[email protected]
@NASA_Johnson
http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/home
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag