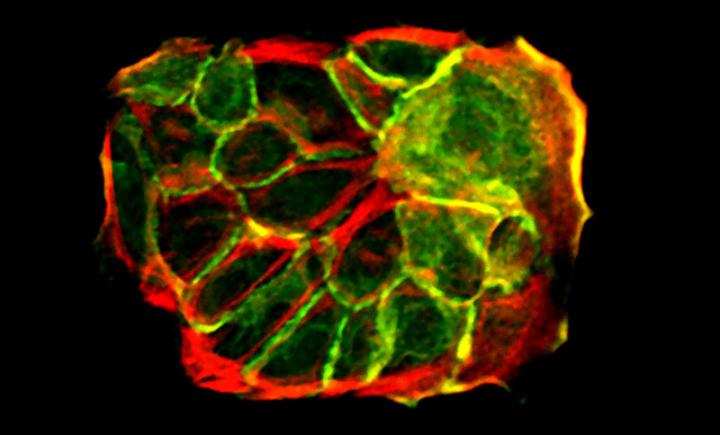
Credit: MPI f. Biology of Ageing
Human skin is a remarkable organ serving as a barrier protecting us from pathogens, toxic substances and others. Our skin needs to constantly renew throughout our lifetime as well as change its size to perfectly fit and cover the body. To fulfill such a complex and dynamic behavior every cell within the skin has a specific task dependent on its position. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing in Cologne have now shown that cell density and crowding play a critical role in instructing single stem cell fate decisions and movement of differentiating cells upwards within the tissue. This ensures that all cell types are correctly positioned within the tissue.
Adult skin epidermis is build of different layers. Stem cells reside in the bottom layer where their task is to produce new cells which then differentiate and move upwards into the more specialized upper layer. This differentiation process involves permanent changes in the cells properties to best suit to serve skin's barrier function. The skin must maintain balanced numbers of stem and differentiated cells as loss of proper balance would result in aberrant tissue structure and therefore function. How this intricate balance is maintained remained largely unknown until recently.
"At the beginning of our study we asked ourselves how the skin cells know where they are and what they are supposed to be doing", explains Yekaterina Miroshnikova, lead author of the study and Postdoctoral Researcher in the lab of Sara Wickström at the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing. The researchers analyzed embryonic mouse tissues and cultured stem cells and found an elegant mechanism based on mechanical guidance.
Local stress induced by crowding leads to differentiation
"We observed that dividing stem cells induced a local crowding effect to the stem cell layer which deformed the cells in the vicinity of this event. Intriguingly, this compression and deformation triggered the differentiation of the neighboring cell", explains Miroshnikova. The crowded and squeezed cells change their properties, leading to their 'escape' from the local stress in the bottom layer and upward movement. "The fact that cells sense what their neighbors are doing and do the exact opposite provides a very efficient and simple way to maintain tissue size, architecture and function", says Miroshnikova.
These results for the first time demonstrate how a complex tissue such as the human skin can generate and maintain its structure through very simple principles of self-organization. In the future, the group will continue using a combination of computational modeling and cell biology to uncover how genetic mutations that occur during cancer target stem cell proliferation and mechanics to impair this process.
###
Original publication
Yekaterina A. Miroshnikova, Huy Q. Le, David Schneider, Torsten Thalheim, Matthias Rübsam, Nadine Bremicker, Julien Polleux, Nadine Kamprad, Marco Tarantola, Irène Wang, Martial Balland, Carien M. Niessen, Joerg Galle, Sara A.Wickström
Adhesion forces and cortical tension couple cell proliferation and differentiation to drive epidermal stratification.
Nature Cell Biology; 11 December, 2017
Media Contact
Dr. Sara Wickström
[email protected]
49-221-379-70770
@maxplanckpress
http://www.mpg.de
Original Source
https://www.mpg.de/11847272/skin-stem-cells-jostling http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41556-017-0005-z