Credit: © Lunghammer – TU Graz
Whether networked vehicles that warn of traffic jams in real time, household appliances that can be operated remotely, “wearables” that monitor physical activity, or industrial plants that detect possible production errors in time and notify technical support, the number of intelligent products that communicate wirelessly with other devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) age has increased rapidly in recent years. However, not all of these devices are compatible with each other because they use different wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth (low energy) or ZigBee, depending on the requirements and application. More than that, many devices often have the same radio frequencies and interfere with each other. This delays data transmission, data can be lost, energy consumption increases and battery life decreases.
New component for direct communication between IoT devices
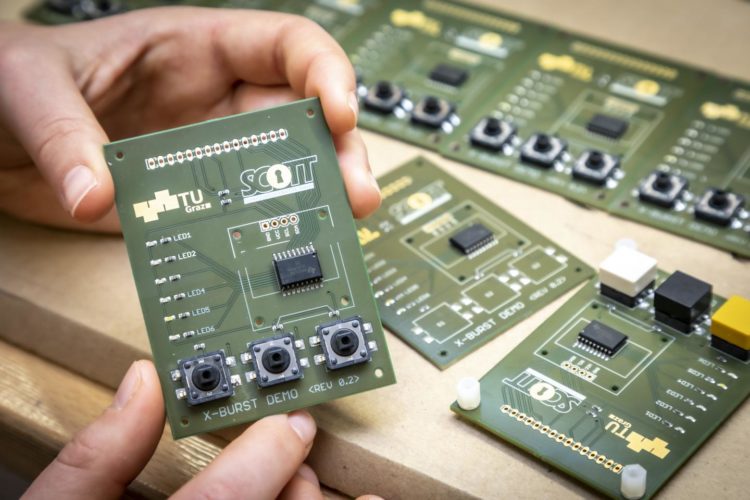
Researchers at TU Graz’s Institute of Technical Informatics have now developed a system that enables direct information exchange between commercially available devices that use different radio technologies but the same radio frequencies. This is a generic framework called X-Burst, which companies will be able to integrate into the operating systems of their IoT products in the future. The researchers make use of time-controlled energy pulses (“energy bursts”) in the radio channel, which can be generated by any smart device and detected by most of them: “We send standard-compliant data packets of varying lengths. These packets are encoded in their length, i.e. the information is stored in the duration of the packets. The receivers monitor the energy level in the radio channel and can thus detect the packets, determine their duration and finally extract the information contained in them,” explain Rainer Hofmann and Hannah Brunner, who were in charge of the project together with colleague Carlo Alberto Boano.
System supports the most common technologies
In their work, the researchers concentrated primarily on data exchange in the license-free 2.4 GHz band. This frequency range is used by many radio standards – including the most common technologies Wi-Fi, Bluetooth (low energy) and ZigBee, which were the focus of the investigations. Using a prototype, the team was able to demonstrate that X-Burst enables successful communication between different wireless technologies without the need for expensive and inflexible gateways, as are currently required for devices with different wireless technologies.
Promising benefits
The invention also enables the system clocks of the various devices to be synchronized, which enables them, for example, to perform certain actions simultaneously. X-Burst also lays the foundation for the intelligent use of radio frequencies by allowing all devices to communicate with each other and adjust their frequencies accordingly. This minimizes cross-technology interference and improves the reliability and energy consumption of the devices. The group is currently working on a new prototype that will demonstrate and illustrate the advantages of X-Burst in an actual smart home scenario.
Great success at international conferences
The Paper X-Burst: Enabling Multi-Platform Cross-Technology Communication between Constrained IoT Devices was awarded the Best Paper Award at the International Conference on Sensing, Communication and Networking 2019 (SECON’19). The Live Demo of X-Burst was awarded the Best Demo Award at the International Conference on Embedded Wireless Systems and Networks (EWSN’20).
This research was carried out in cooperation with TU Darmstadt and was partly funded by the COMET Center Pro2Future and within the framework of the EU project SCOTT (Secure Connected Trustable Things), which is funded by the Austrian Research Promotion Agency (FFG) and the European Commission. This research was also supported by the Austria Wirtschaftsservice Gesellschaft mbH (aws), with funds from Nationalstiftung für Forschung, Technologie und Entwicklung. (national foundation for research, technology and development). This research topic is anchored in the Field of Expertise Information, Communication & Computing, one of the five strategic research foci at TU Graz.
###
Media Contact
Carlo Alberto BOANO
[email protected]
43-316-873-6413
Original Source
https:/