A new U of T Scarborough study finds that climate change is causing a commercially significant marine crab to lose its sense of smell, which could partially explain why their populations are thinning.
Credit: Photo by Cosima Porteus
A new U of T Scarborough study finds that climate change is causing a commercially significant marine crab to lose its sense of smell, which could partially explain why their populations are thinning.
The research was done on Dungeness crabs and found that ocean acidification causes them to physically sniff less, impacts their ability to detect food odours and even decreases activity in the sensory nerves responsible for smell.
“This is the first study to look at the physiological effects of ocean acidification on the sense of smell in crabs,” says Cosima Porteus, an assistant professor in the department of biological sciences at U of T Scarborough and co-author of the study along with postdoc Andrea Durant.
Ocean acidification is the result of the Earth’s oceans becoming more acidic due to absorbing increasing amounts of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. It’s a direct consequence of burning fossil fuels and carbon pollution, and several studies have shown it’s having an impact on the behaviour of marine wildlife.
Dungeness crabs are an economically important species found along the Pacific coast, stretching from California to Alaska. They are one of the most popular crabs to eat and their fishery was valued at more than $250 million in 2019.
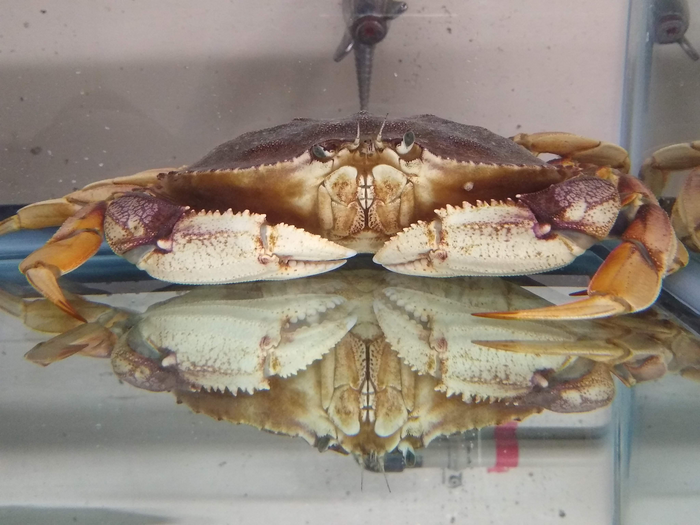
Like most crabs, they have poor vision, so their sense of smell is crucial in finding food, mates, suitable habitats and avoiding predators, explains Porteus. They sniff through a process known as flicking, where they flick their antennules (small antenna) through the water to detect odours. Tiny neurons responsible for smell are located inside these antennules, which send electrical signals to the brain.
The researchers discovered two things when the crabs were exposed to ocean acidification: they were flicking less and their sensory neurons were 50 per cent less responsive to odours.
“Crabs increase their flicking rate when they detect an odour they are interested in, but in crabs that were exposed to ocean acidification, the odour had to be 10 times more concentrated before we saw an increase in flicking,” says Porteus.
There are a few potential reasons why ocean acidification seems to be impacting sense of smell in crabs. Porteus points to other research done at the University of Hull that showed ocean acidification disrupts odour molecules, which can impact how they bind to smell receptors in marine animals such as crabs.
For this study, published in the journal Global Change Biology, Porteus and Durant were able to test the electrical activity in the crabs’ sensory neurons to determine they were less responsive to odours. They also discovered that they had fewer receptors and their sensory neurons were physically shrinking by as much as 25 per cent in volume.
“These are active cells and if they aren’t detecting odours as much, they might be shrinking to conserve energy. It’s like a muscle that will shrink if you don’t use it,” she says.
Porteus says reduced food detection could have implications for other economically important species such as Alaskan king and snow crabs because their sense of smell functions the same way.
“Losing their sense of smell seems to be climate related, so this might partially explain some of the decline in their numbers,” says Porteus.
“If crabs are having trouble finding food, it stands to reason females won’t have as much energy to produce eggs.”
This research was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada. Some of the analysis was performed at U of T’s Centre for the Neurobiology of Stress.
Journal
Global Change Biology
DOI
10.1111/gcb.16738
Article Publication Date
9-May-2023




